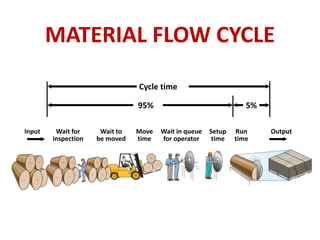
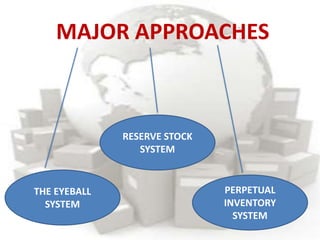
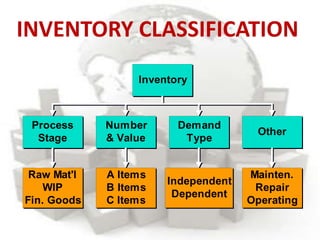
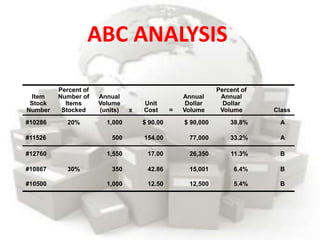
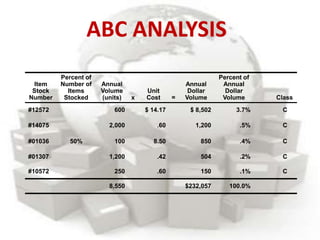
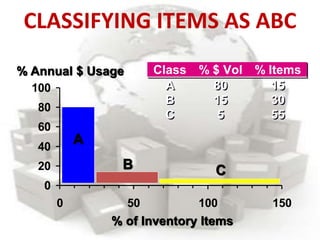
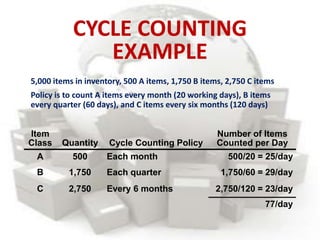
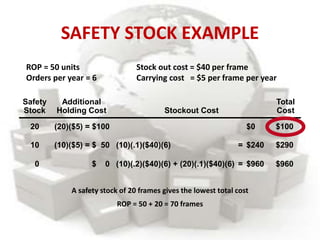
This document defines inventory and discusses different types, functions, and classifications of inventory. It also covers inventory management approaches like the eyeball system, perpetual inventory system, and reserve stock system. Additional topics covered include ABC analysis, economic order quantity models, reorder points, safety stock, and probabilistic inventory models. The key aspects of inventory discussed are raw materials, work-in-process, finished goods, dependent and independent demand, and inventory costs.