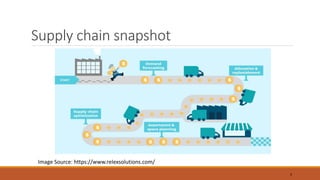
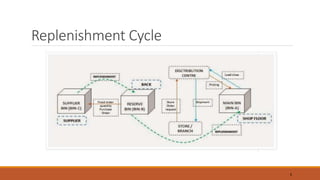
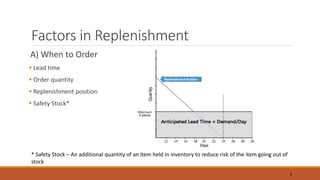
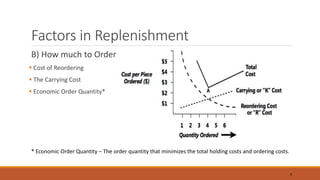
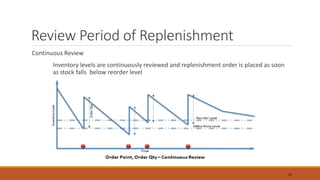
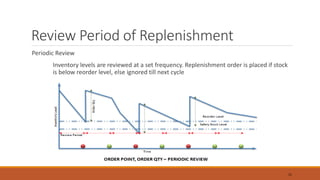
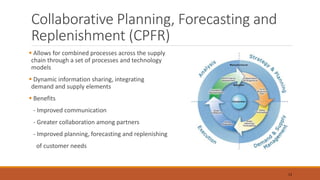
The document discusses the replenishment process in modern trade, particularly within the context of supermarkets and hypermarkets in India. It outlines the importance of effective supply chain management to maintain inventory flow and minimize costs while introducing methods like automated stock replenishment and collaborative planning. Additionally, it highlights technology's role in optimizing supply chain processes and improving overall efficiency and customer experience.