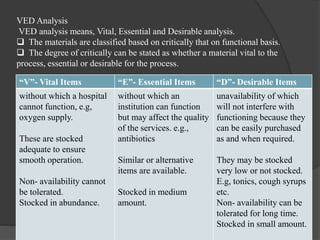
Inventory control involves planning and coordinating all activities related to materials and inventory from acquisition to use in manufacturing or services. It aims to ensure adequate supply of necessary items while minimizing costs through various classification and analysis methods. Nurses play a key role in inventory control by indenting, receiving, storing, and replenishing supplies and equipment and maintaining accurate records to facilitate smooth hospital operations.