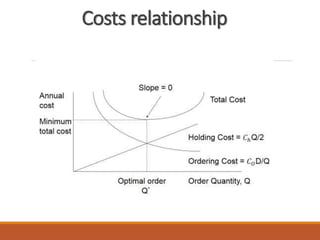
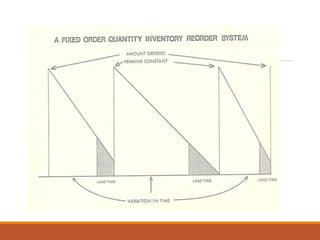
1) The document discusses various aspects of inventory control including types of inventory, reasons for carrying inventory, benefits and costs of inventory control, inventory models, parameters that influence inventory levels, safety stock, and replenishment systems.
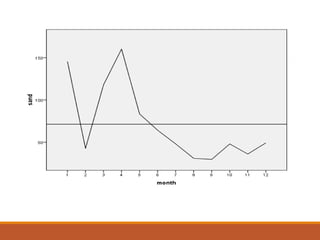
2) It then summarizes a case study on inventory management that analyzed the inventory levels and economic order quantities of different products for a company to determine optimal inventory levels and control costs.
3) The study's findings recommended the company pay closer attention to fast-moving items and sales growth when determining inventory levels, and suggested measures to control raw material wastage and maintain optimal inventory levels.