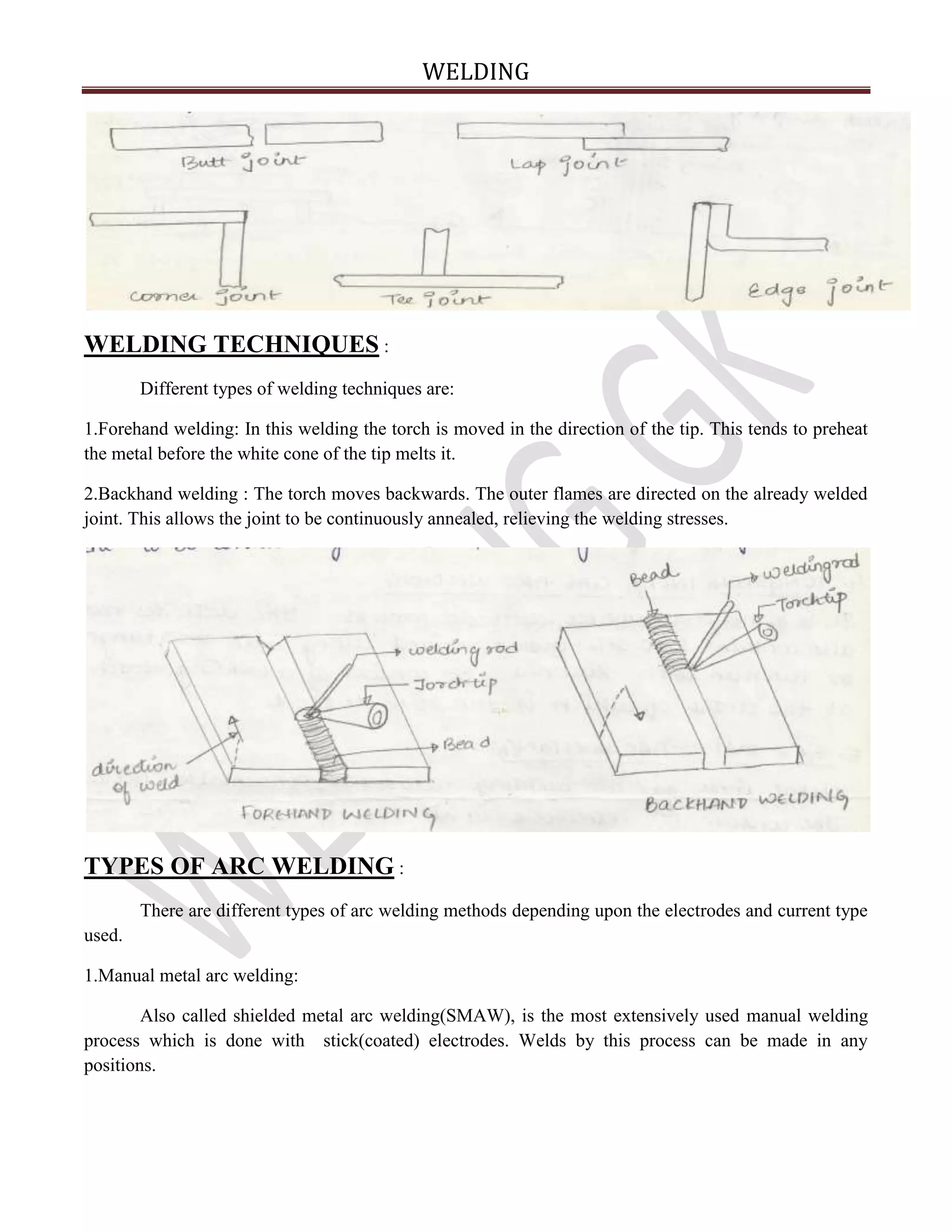
Welding is a process that joins two metal pieces by heating them to melting point and allowing them to fuse together. Various welding processes include electric arc, gas, thermit, resistance, and friction welding. Fluxes are used to prevent oxidation during welding. Gas welding uses the heat from combustion of a fuel gas like acetylene with oxygen. Resistance welding uses high current to heat and fuse the joint. Electric arc welding generates an arc between an electrode and the workpiece to produce welding heat. There are many types of arc welding including manual, TIG, MIG, and submerged arc welding. Proper preparation of the workpiece, parameters like current and speed, and welding positions are important for quality welds.