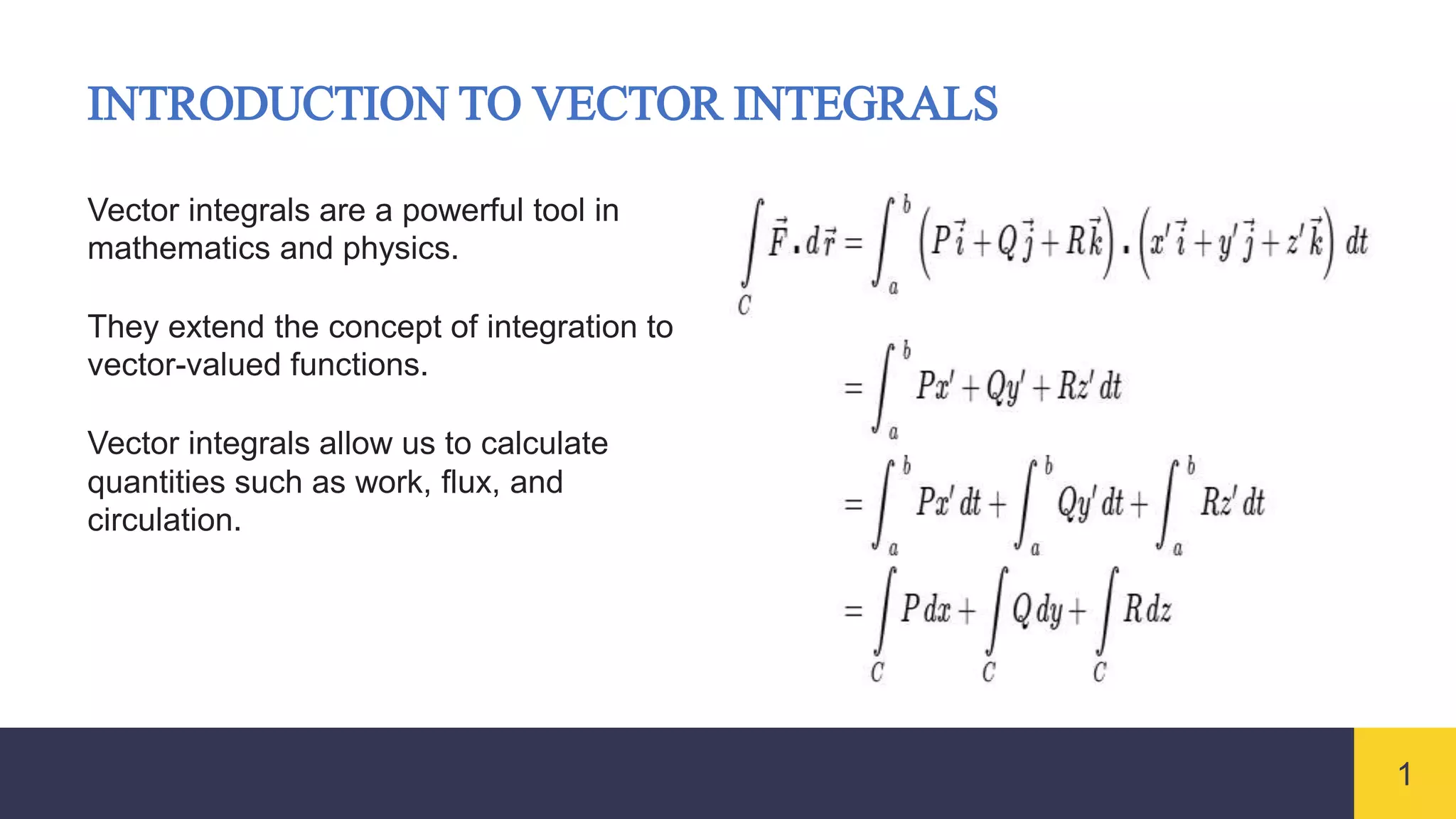
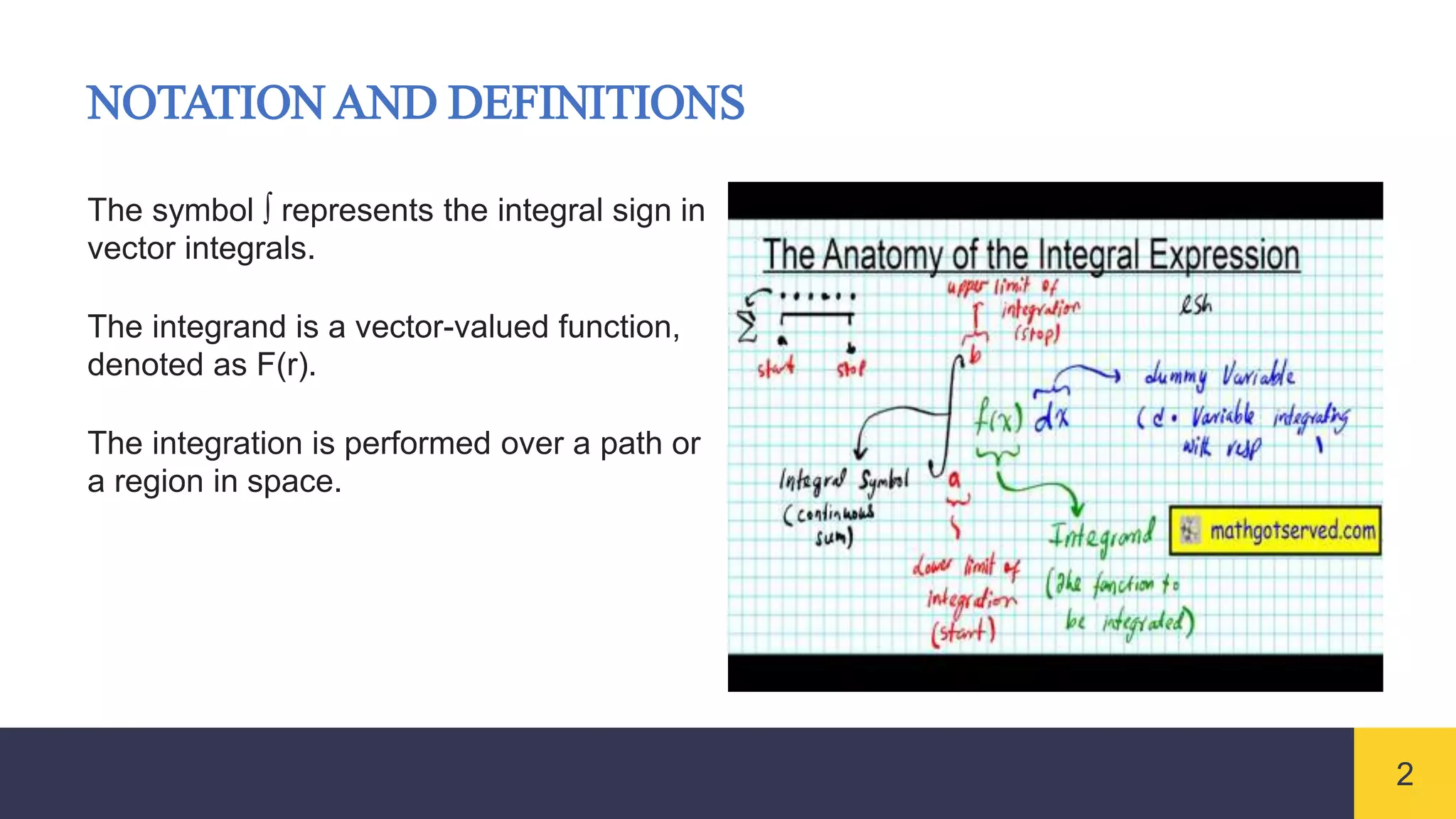
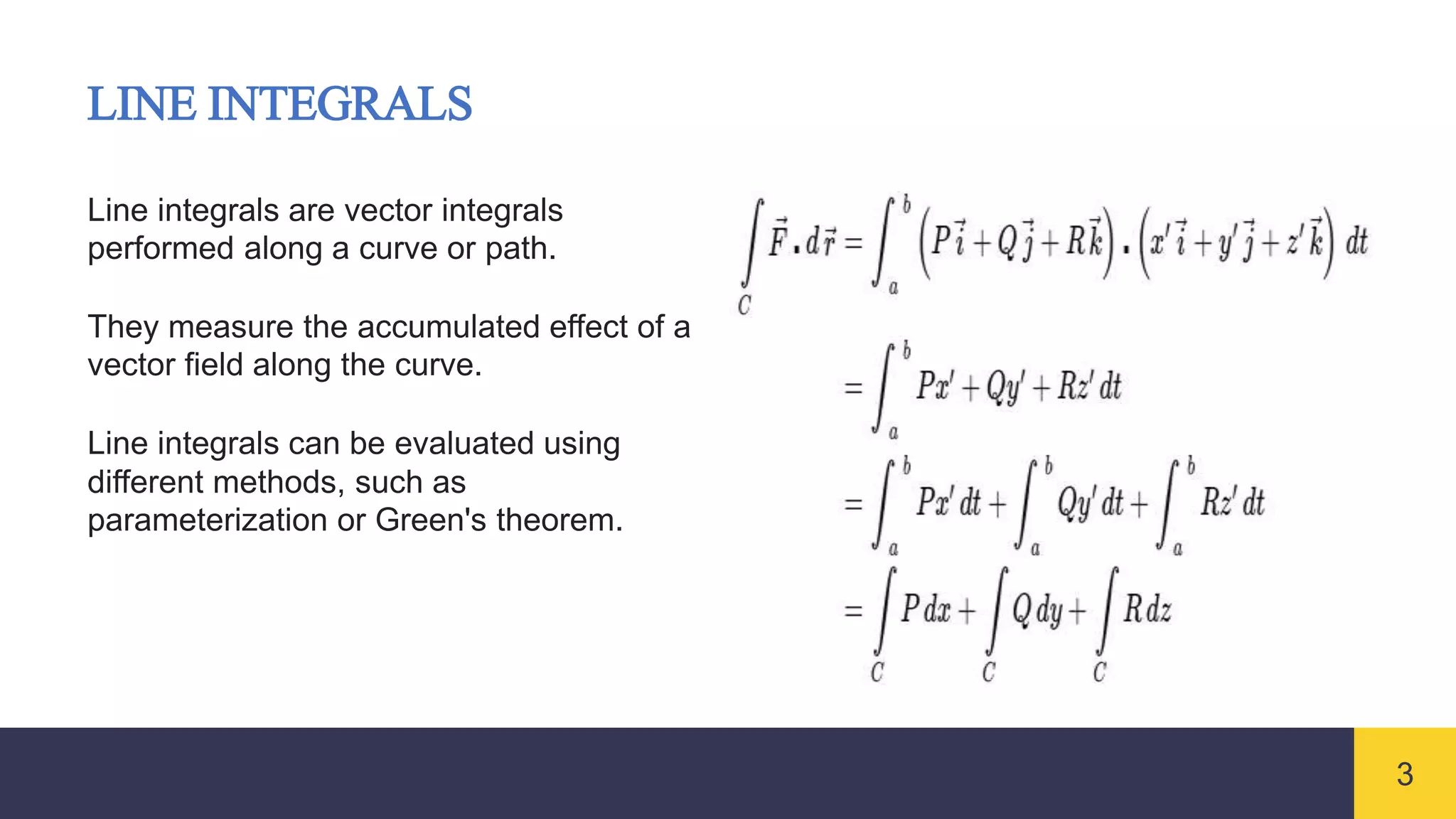
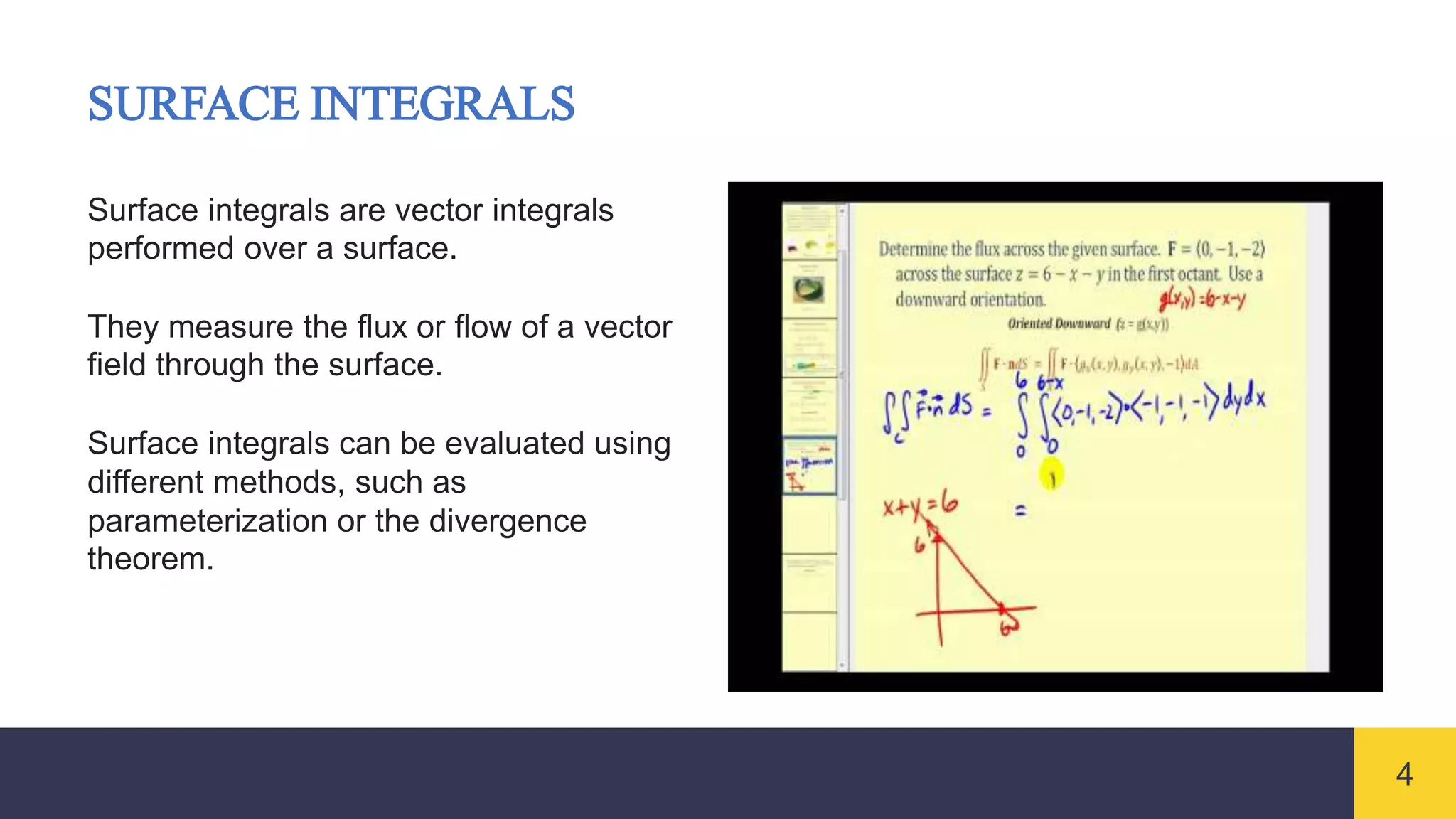
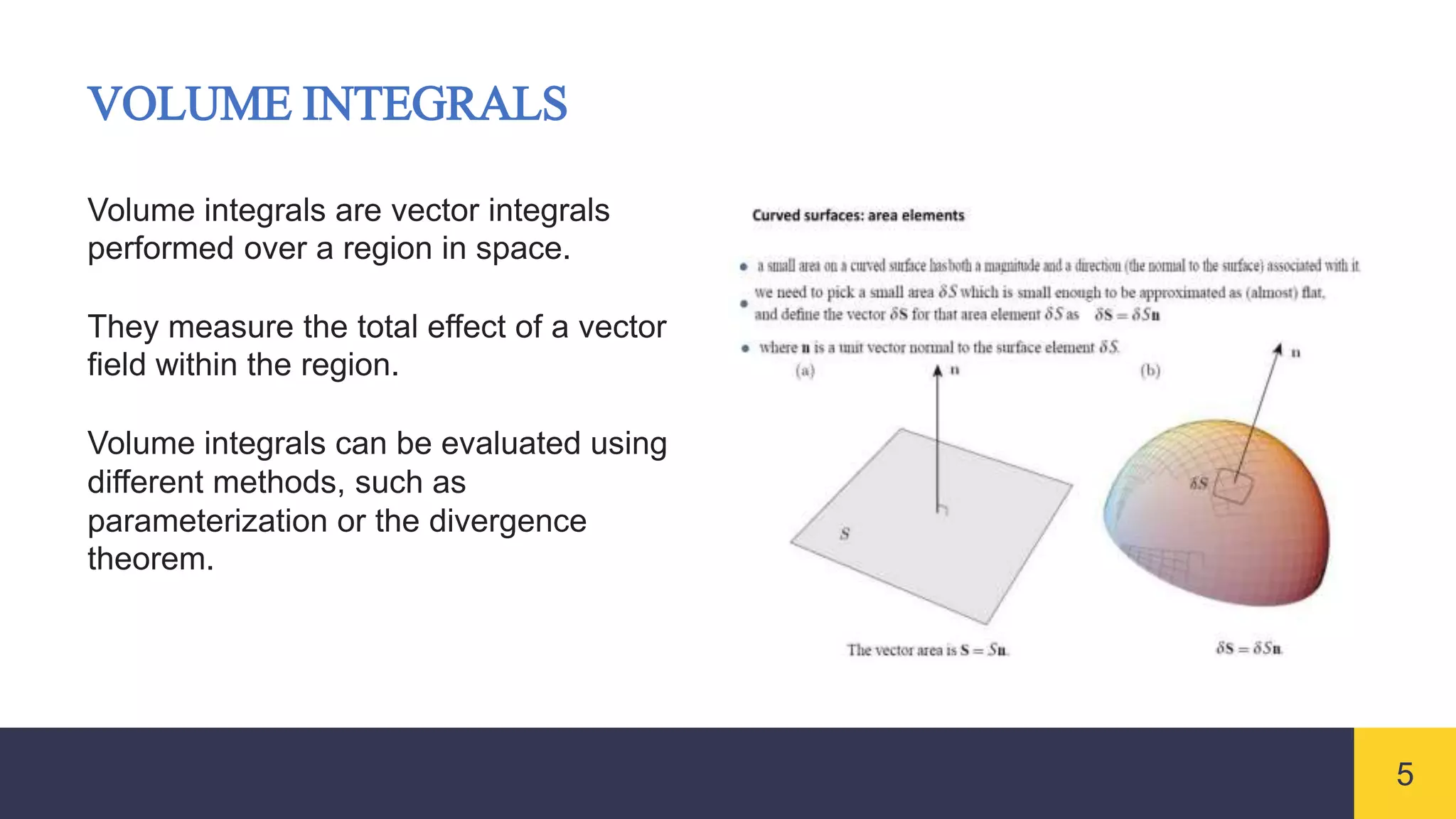
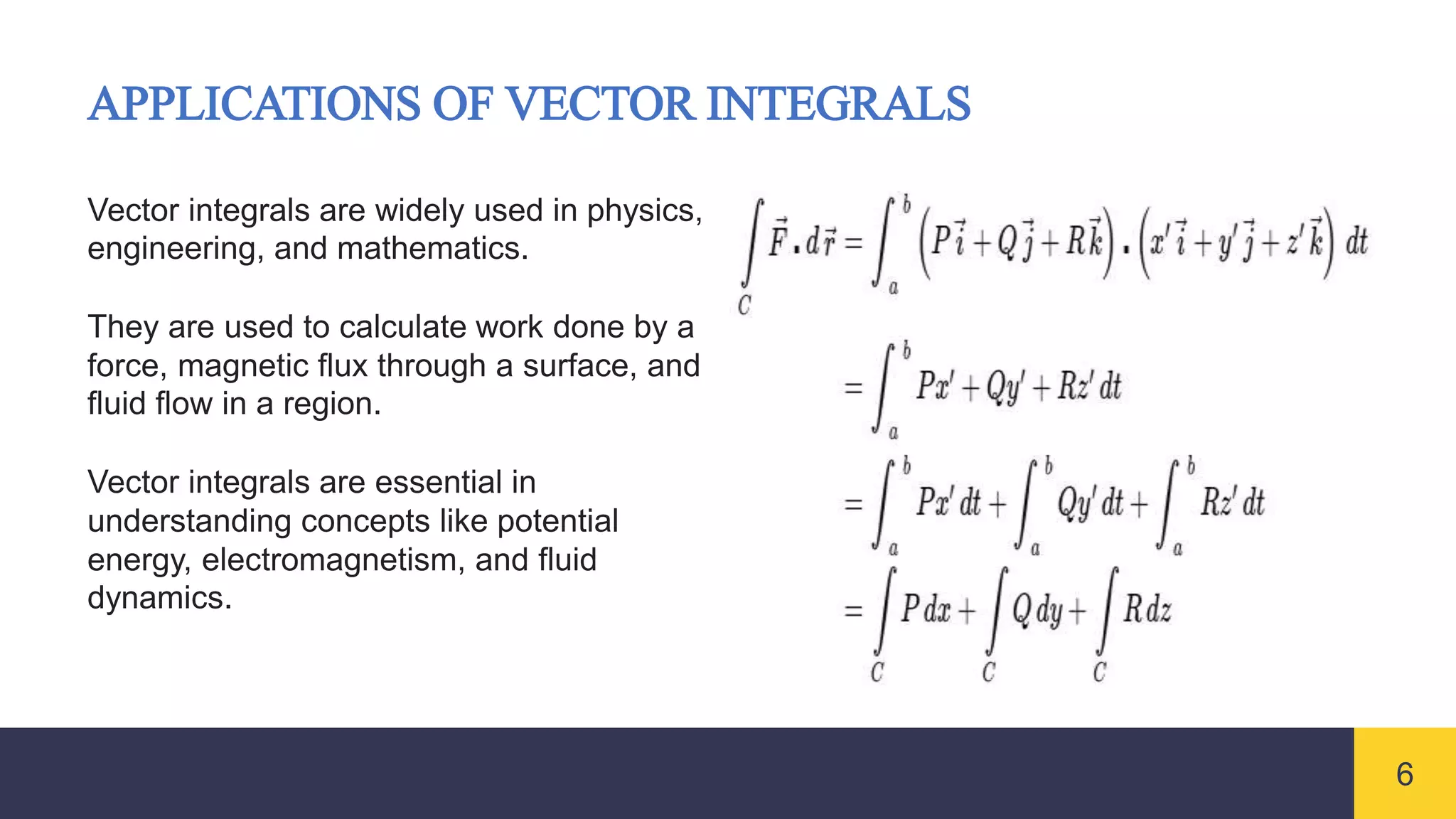
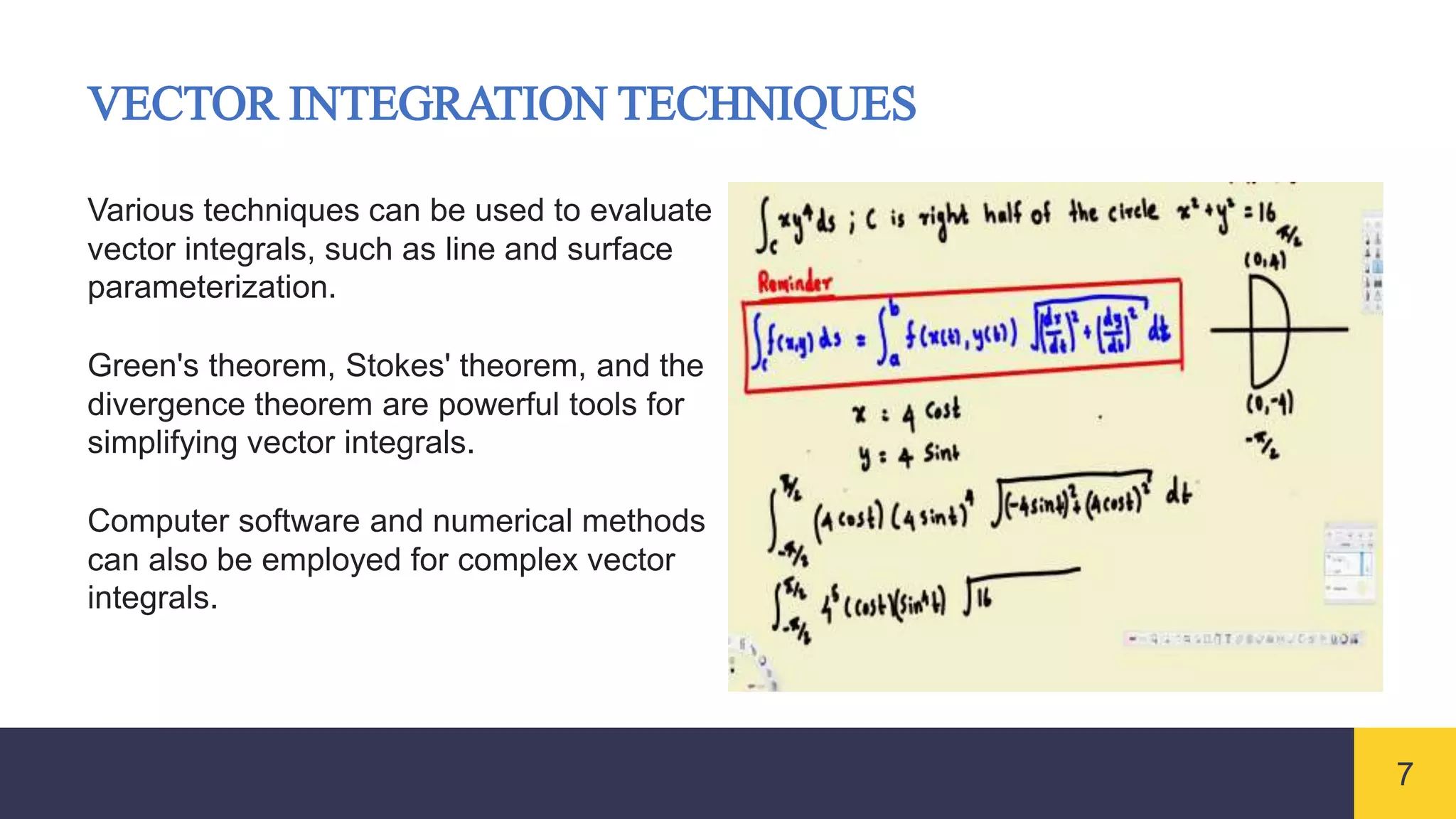
Vector integrals generalize integration to vector-valued functions. Line integrals measure the accumulated effect of a vector field along a curve, surface integrals measure flux through a surface, and volume integrals measure the total effect within a region. Vector integrals are used widely in physics and engineering to calculate quantities such as work, magnetic flux, and fluid flow.