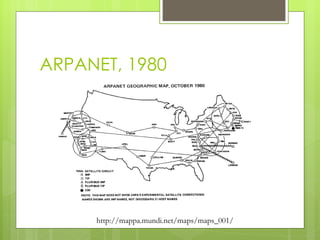
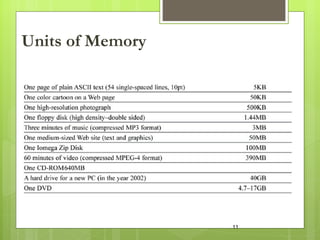
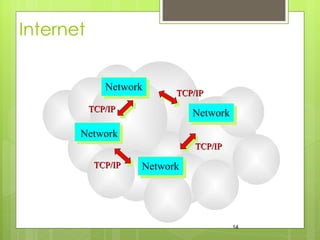
The document provides an introduction and history of the Internet. It discusses how the Internet originated from ARPANET in the late 1950s and 1960s and key developments like the first email in 1976 and creation of the World Wide Web in 1990. The document also covers basics of how data is transmitted over the Internet using protocols like TCP/IP and defines common terms like URLs, domain names, and IP addresses.