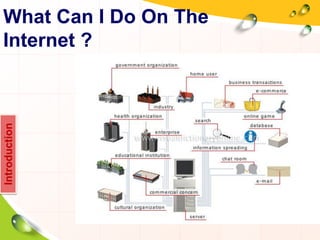
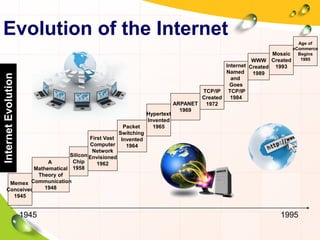
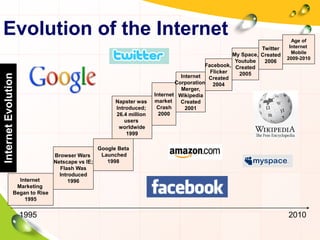
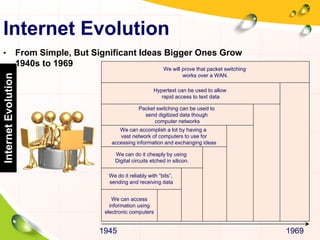
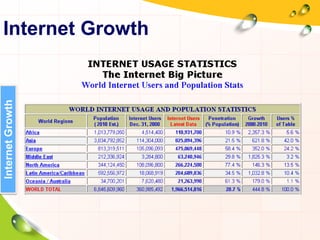
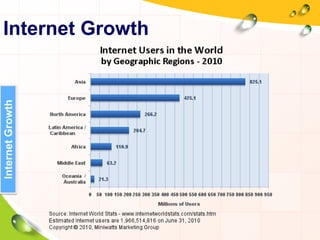
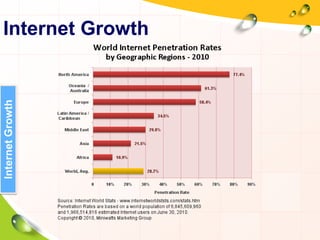
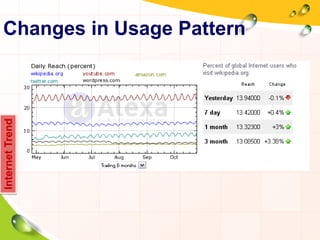
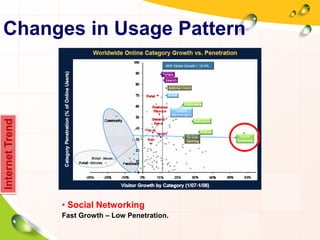
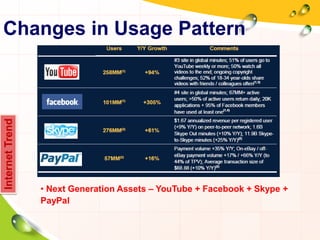
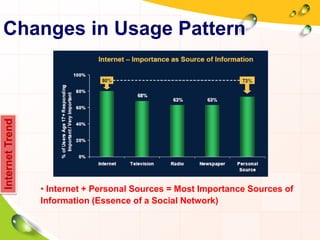
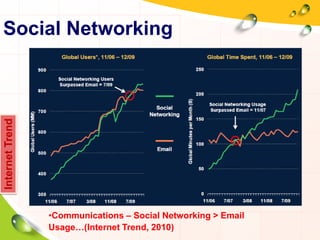
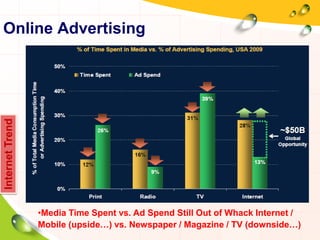
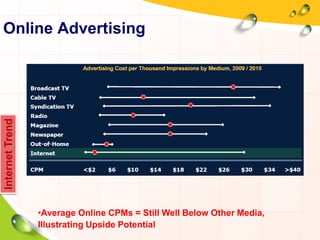
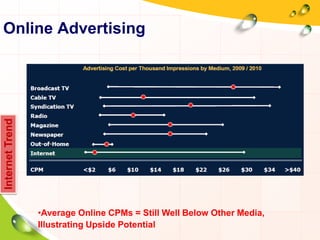
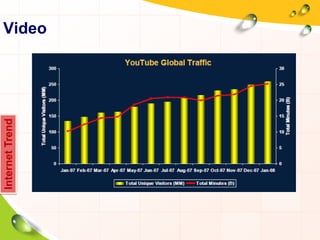
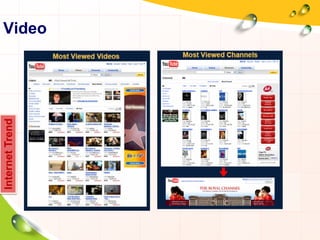
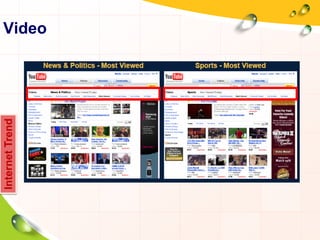
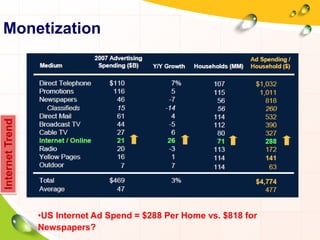
This document provides an overview of the history and evolution of the Internet. It discusses how the Internet originated from early computer networks developed by ARPA and DARPA in the 1960s-1970s to connect government and university research computers. It then covers the creation of TCP/IP in the 1970s which established the fundamental communication protocols of the Internet. The document also summarizes the commercial opening of the Internet in the 1990s and the creation of the World Wide Web in 1989-1991 by Tim Berners-Lee, which allowed for easy access to hyperlinked documents and multimedia over the Internet.