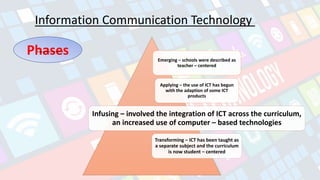
The document discusses the evolution of technology for instruction from early tools like quill pens and slates to modern digital technologies. It outlines four phases of integrating information communication technology (ICT) in schools: Emerging (teacher-centered), Applying (beginning use of some ICT products), Infusing (integrating ICT across the curriculum), and Transforming (ICT as a separate subject and student-centered curriculum). Finally, it lists ways technology can support learning, such as gaining students' attention, illustrating real-world relevance, engaging students through production work, and allowing collaboration.