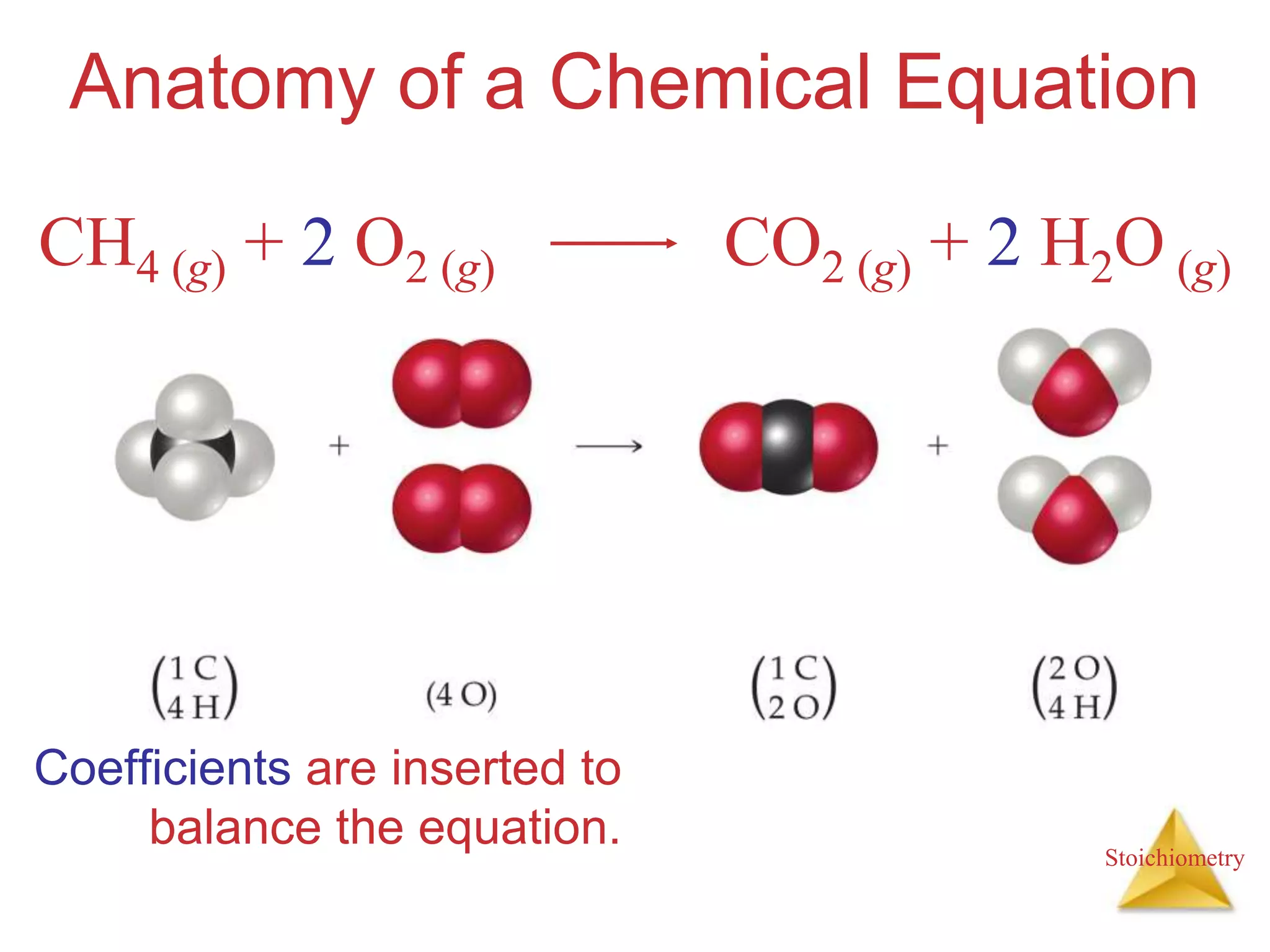
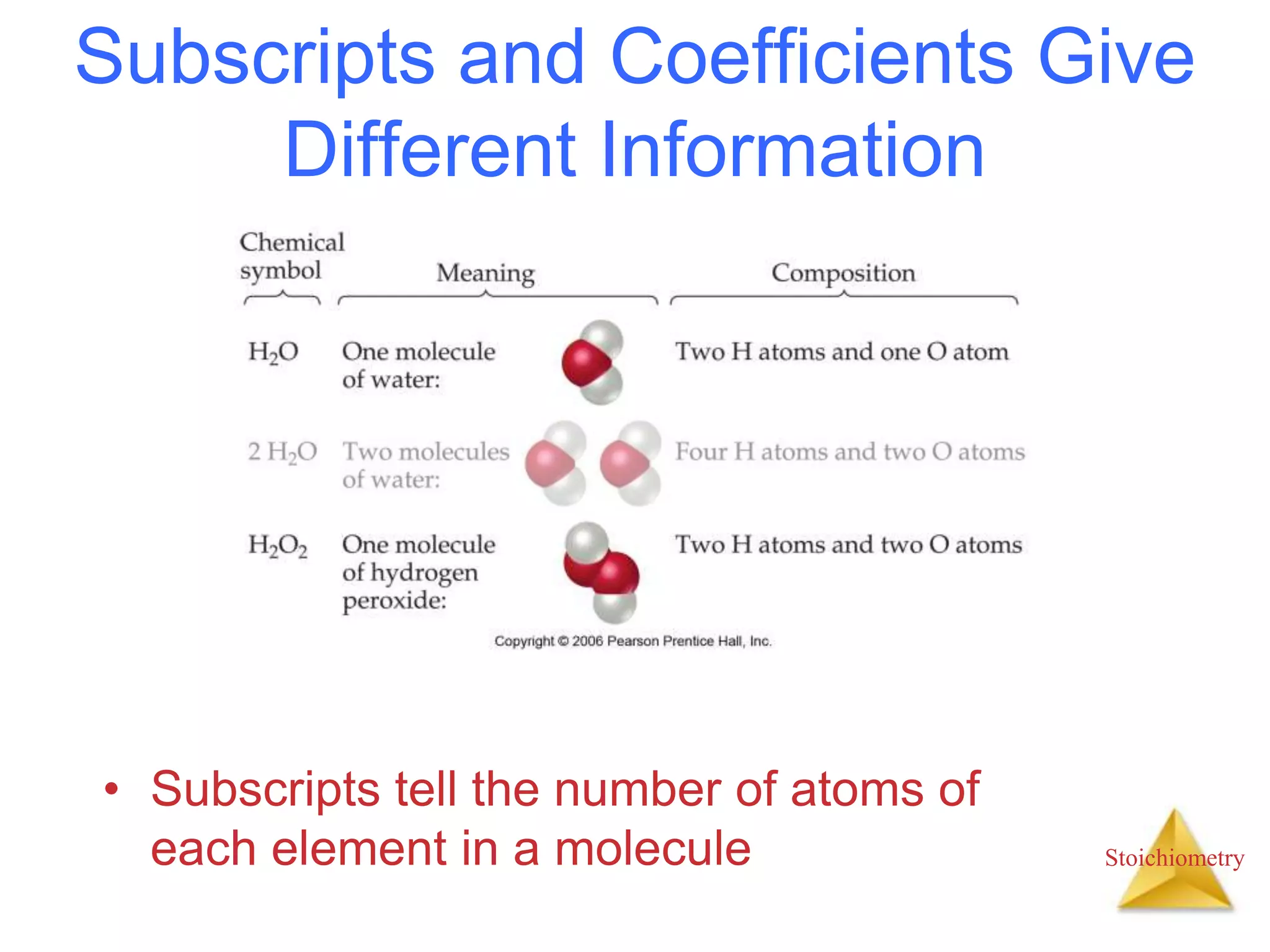
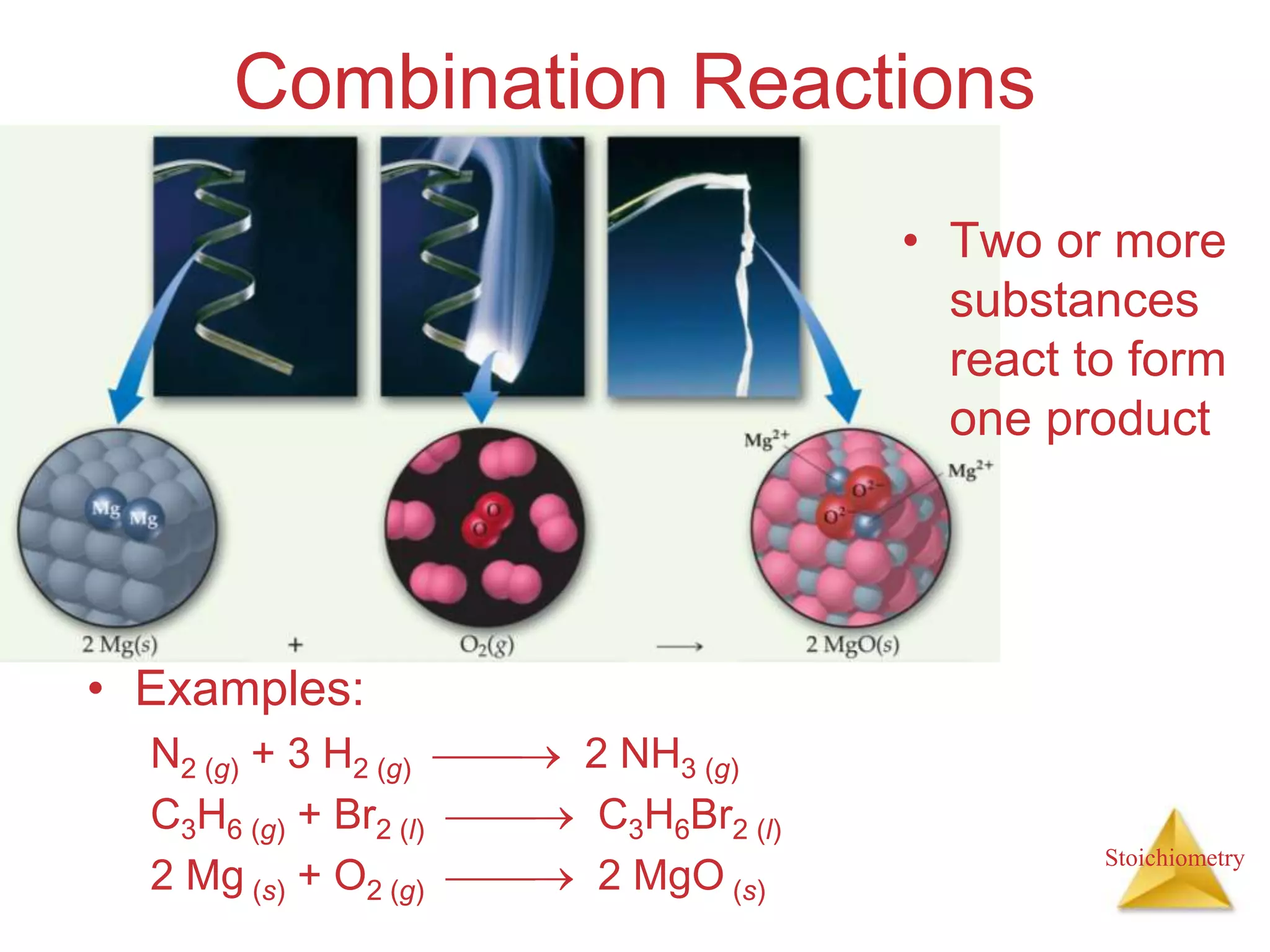
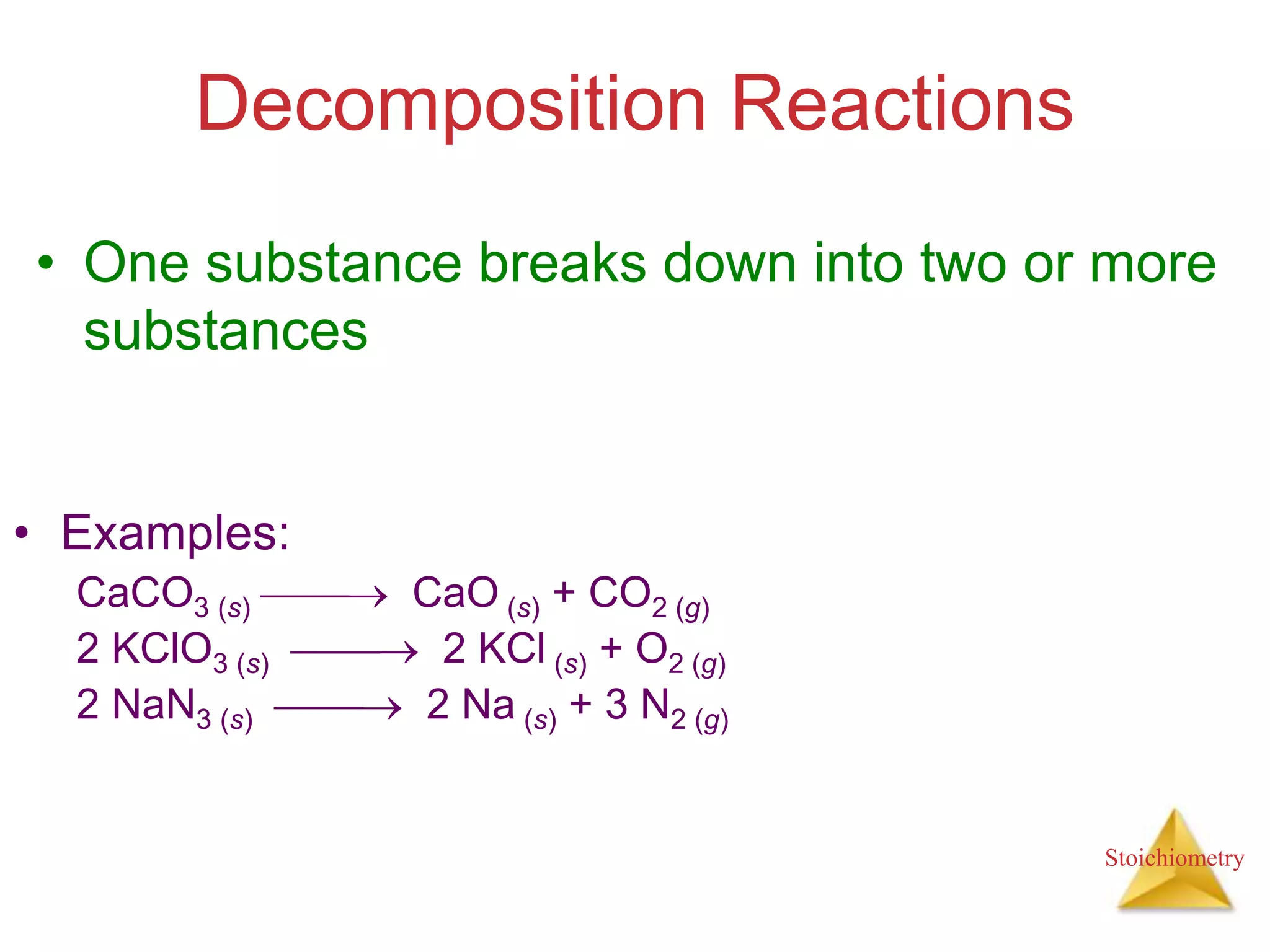
This document provides an overview of stoichiometry concepts including:
- The anatomy of chemical equations including reactants, products, states, and coefficients.
- Types of chemical reactions such as combination, decomposition, combustion.
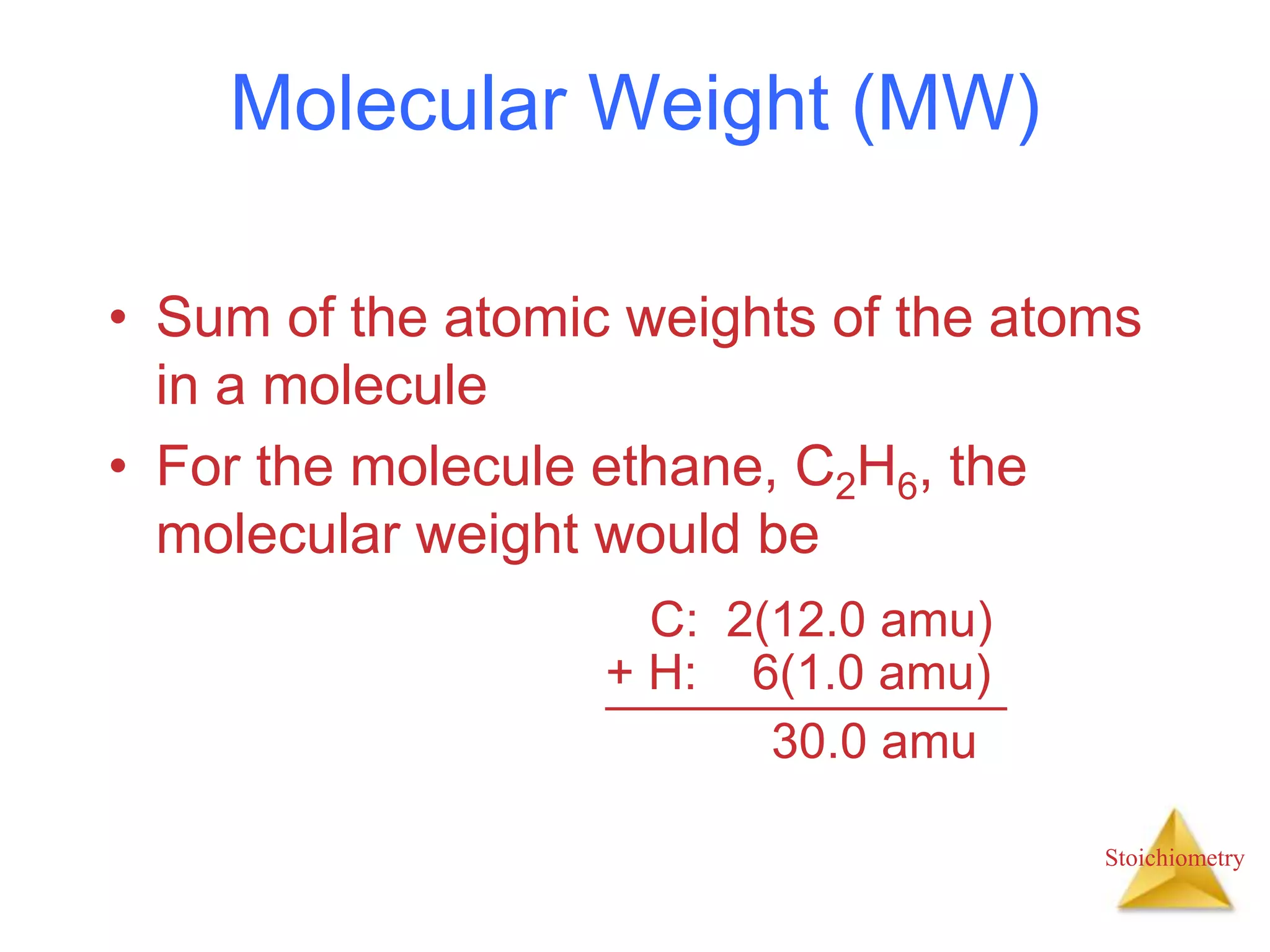
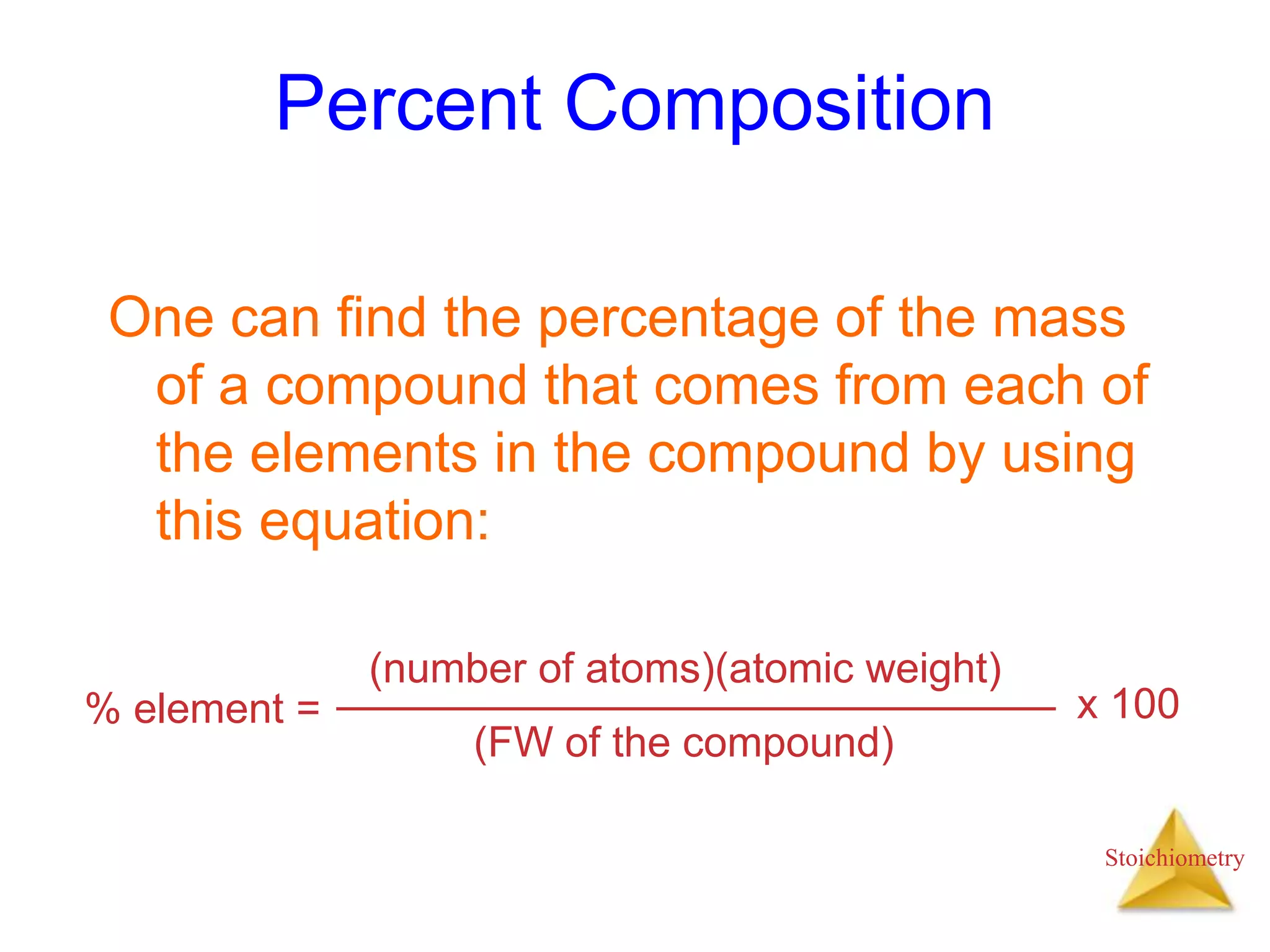
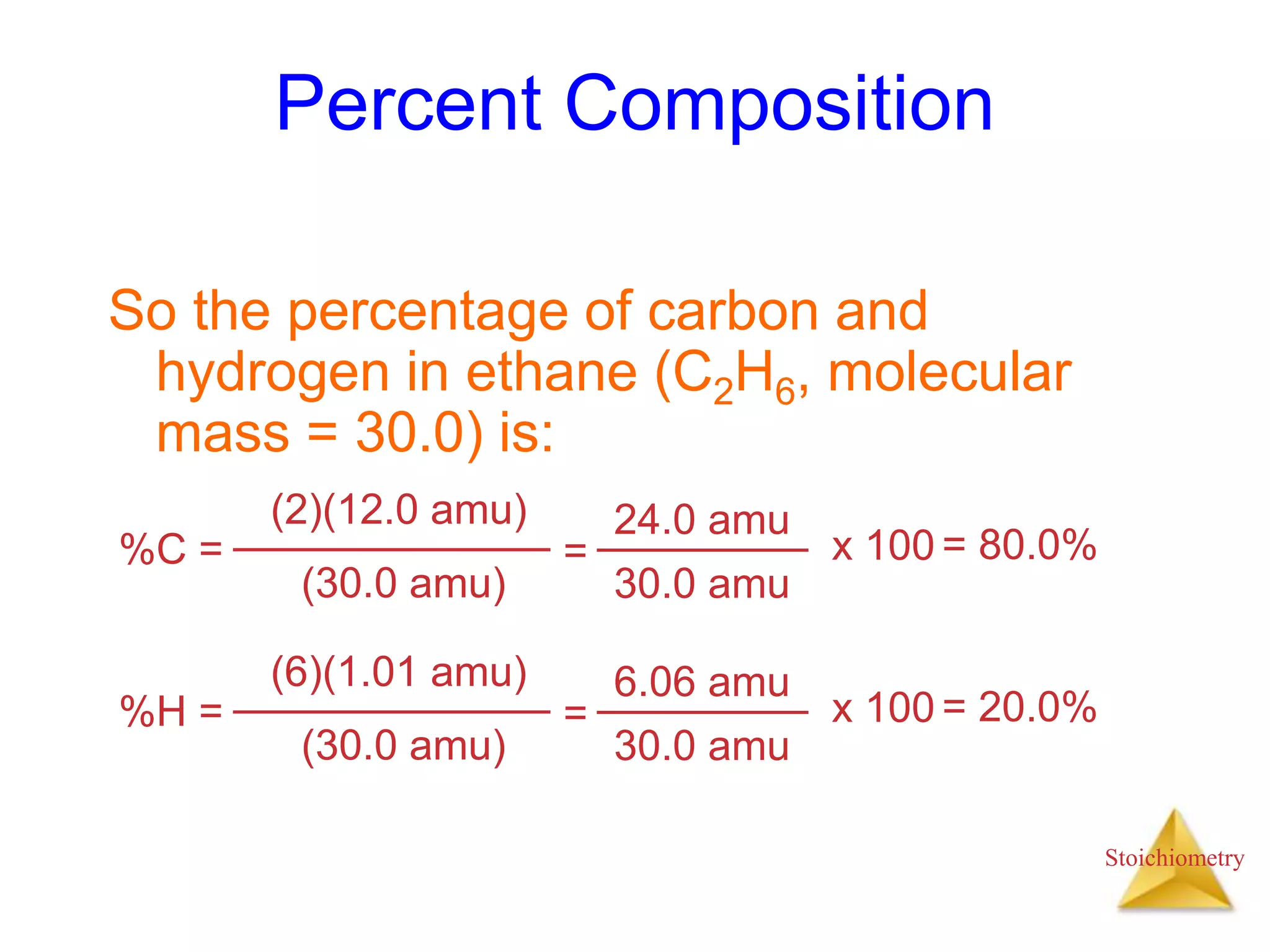
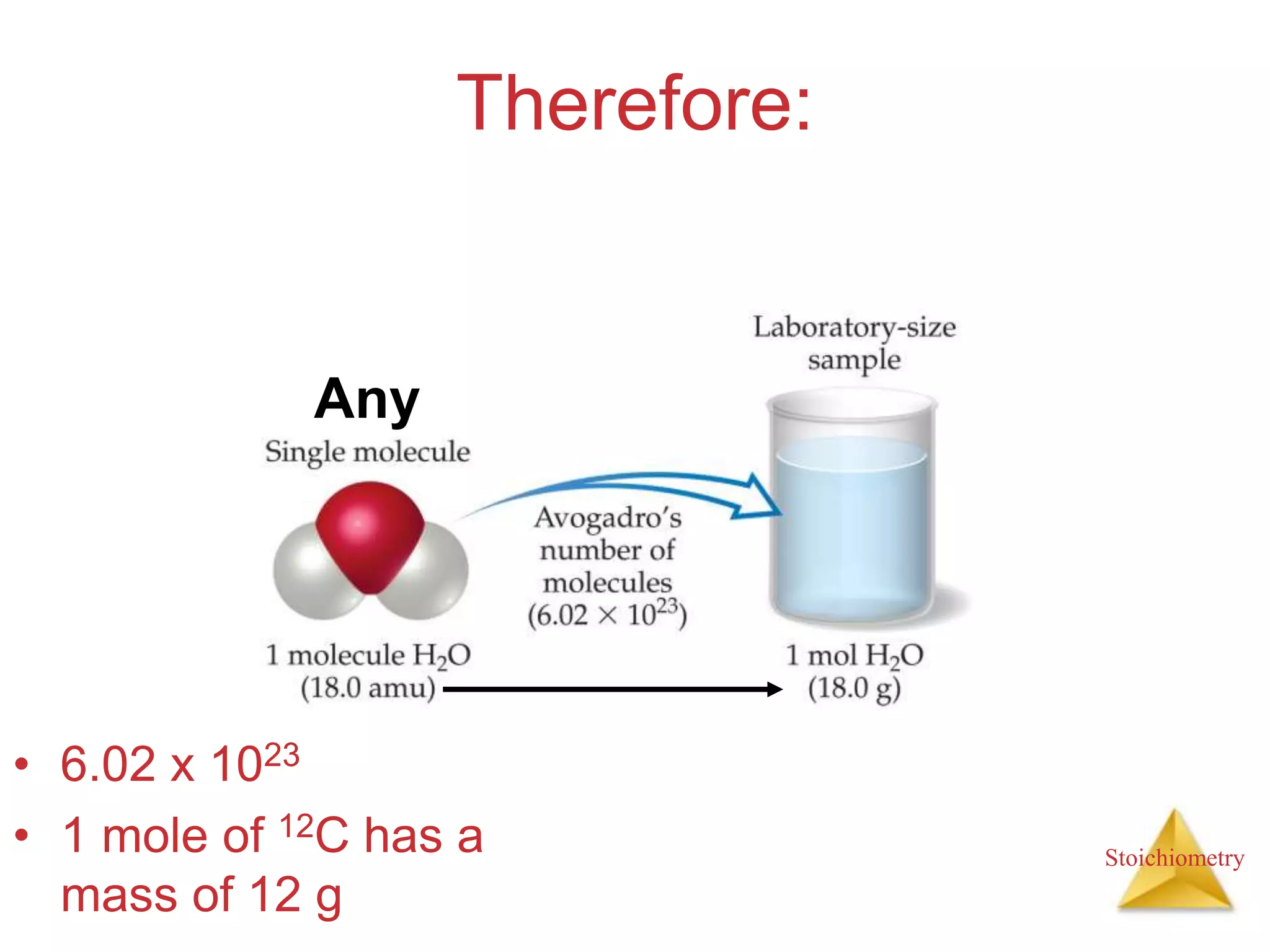
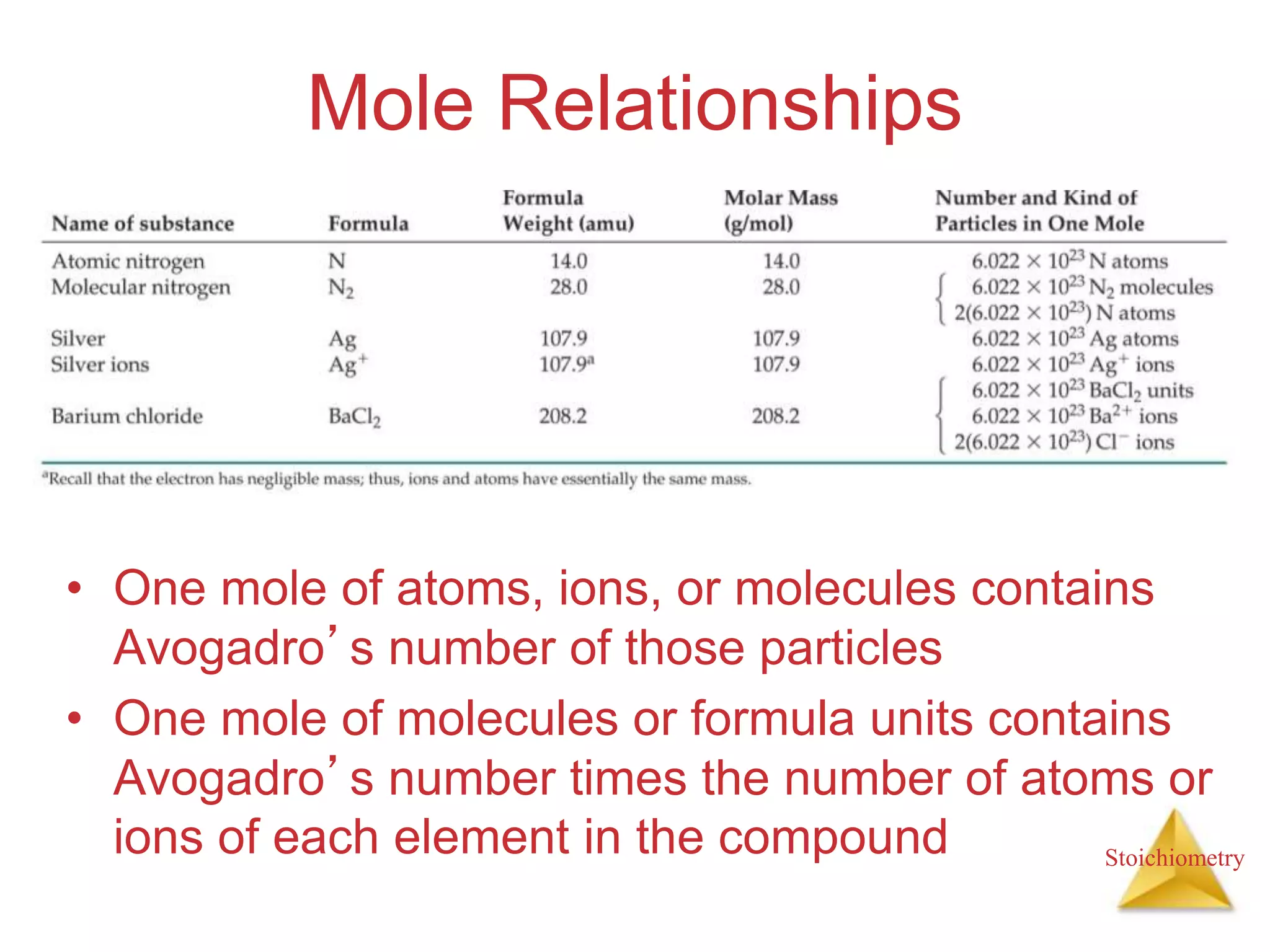
- Formula weights, molecular weights, and molar masses which allow conversion between moles and mass.
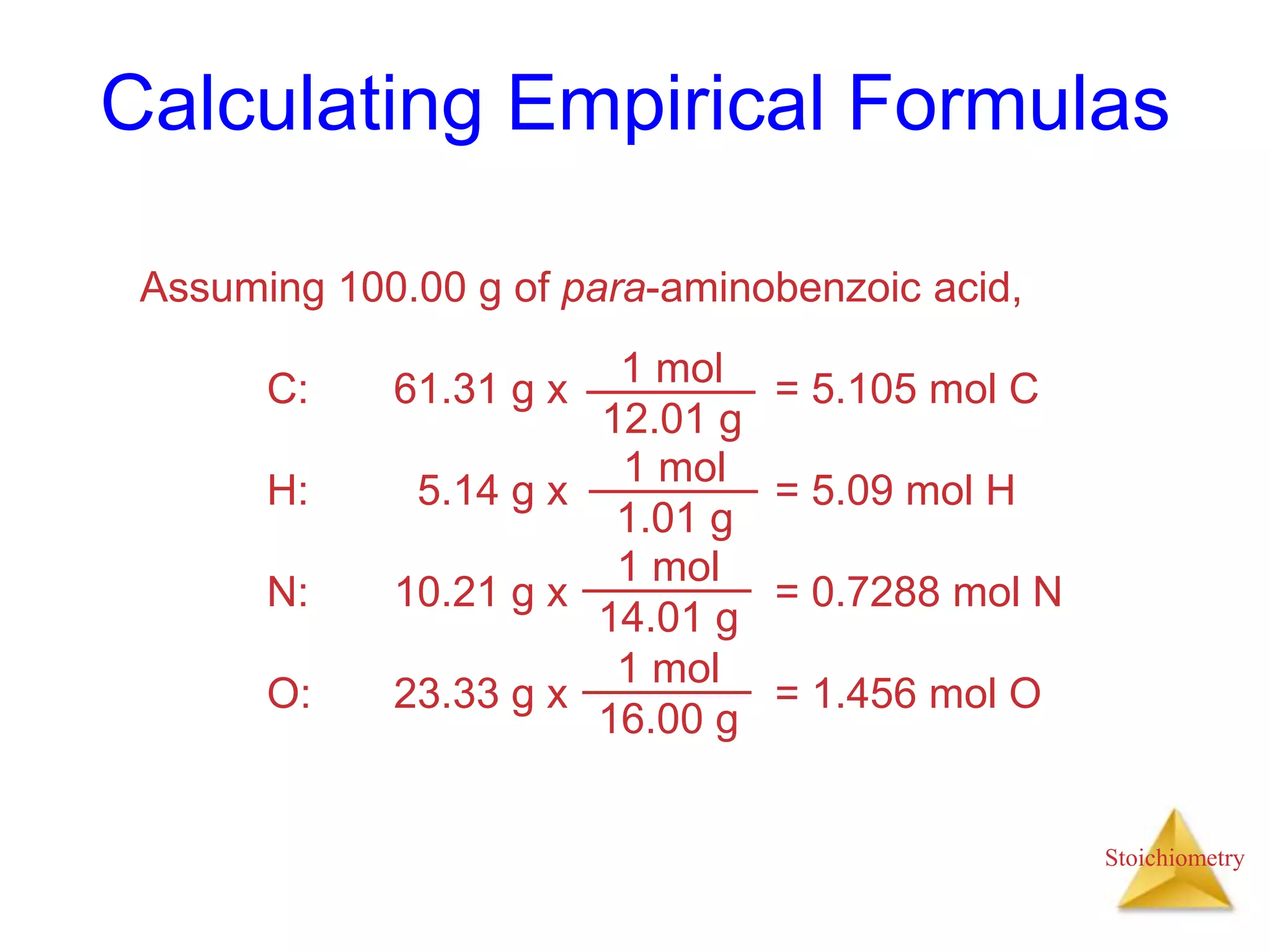
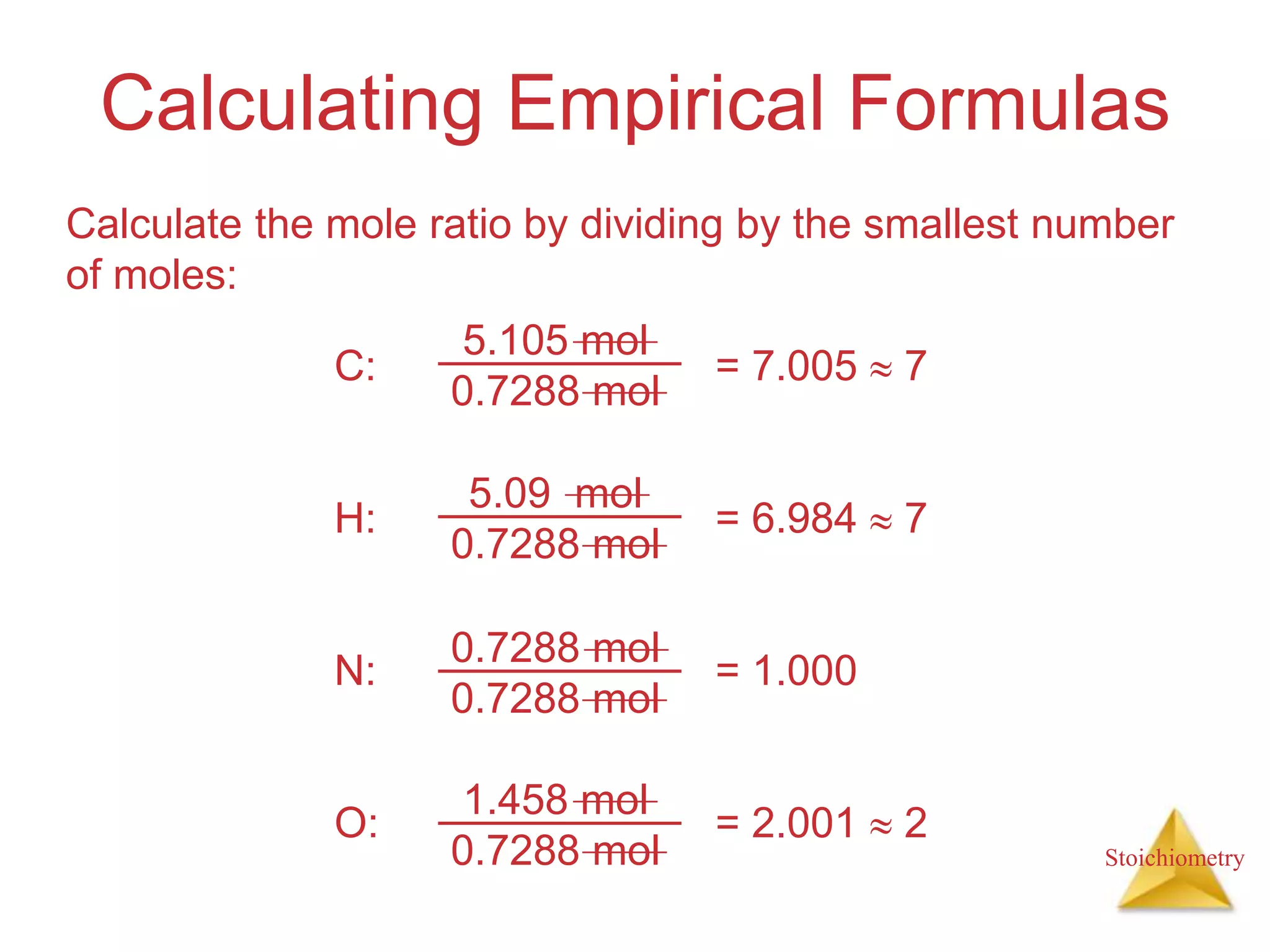
- Empirical formulas which can be calculated from elemental analysis data.
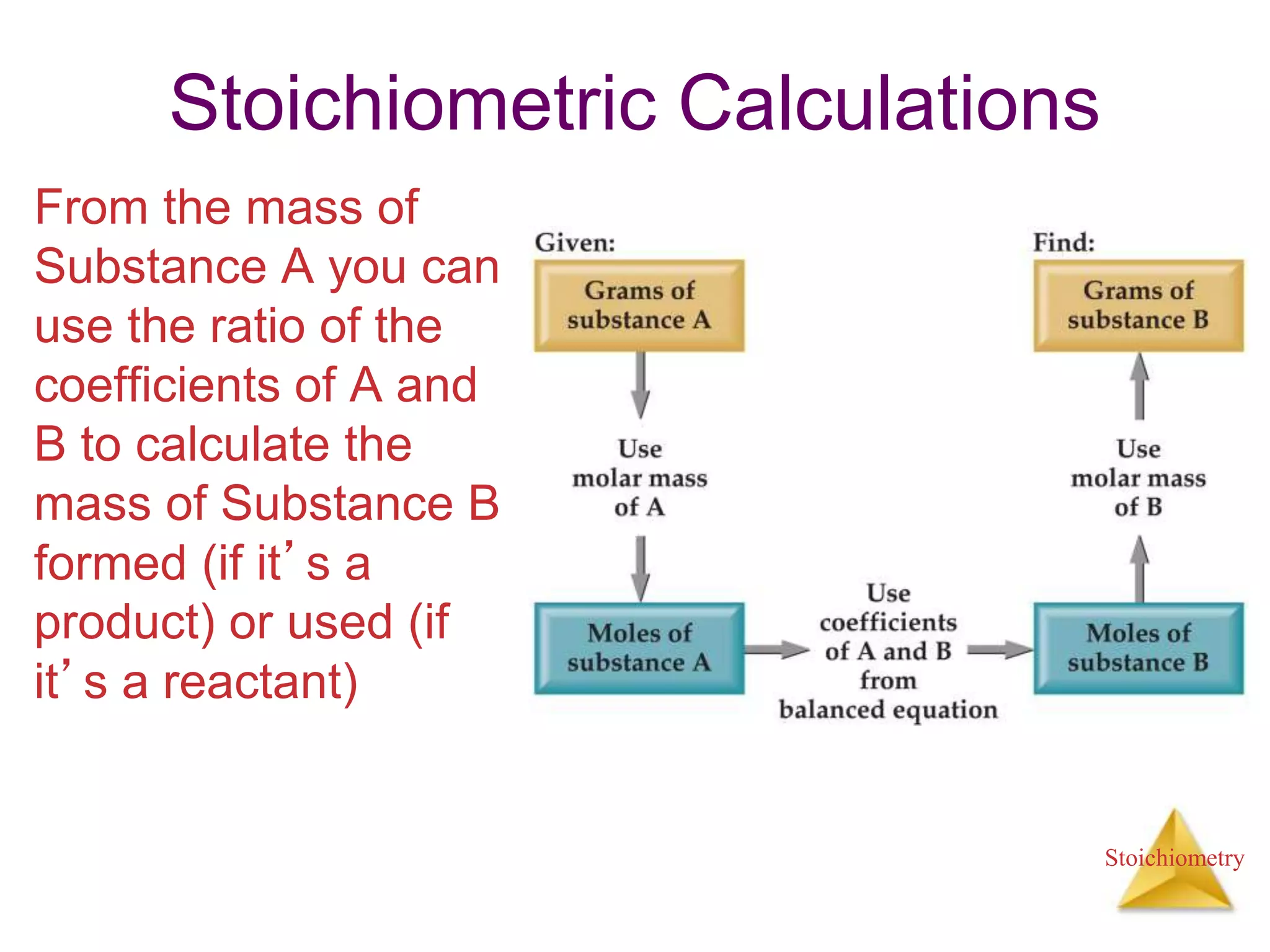
- Stoichiometric calculations to determine amounts of reactants and products from balanced chemical equations.
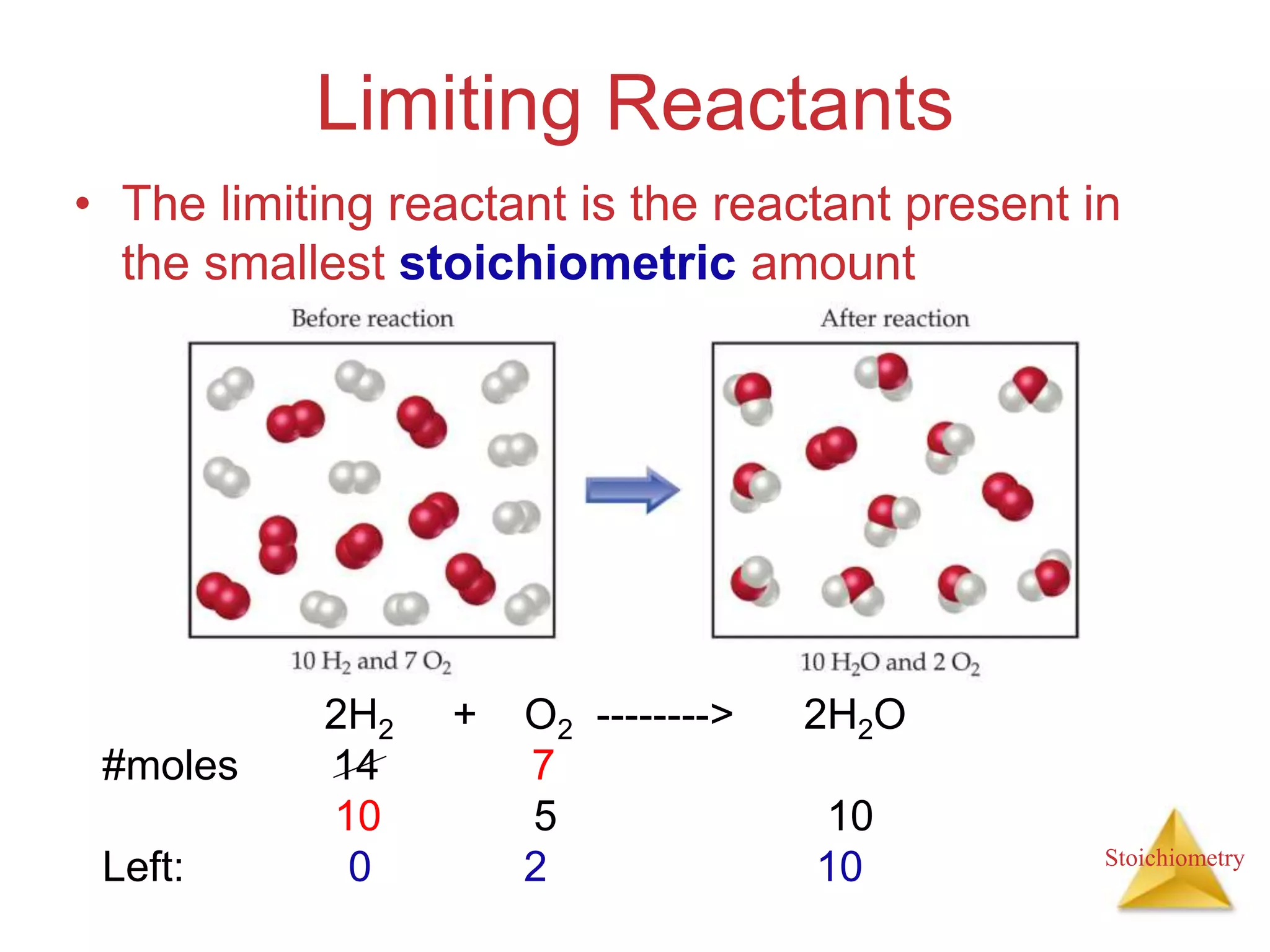
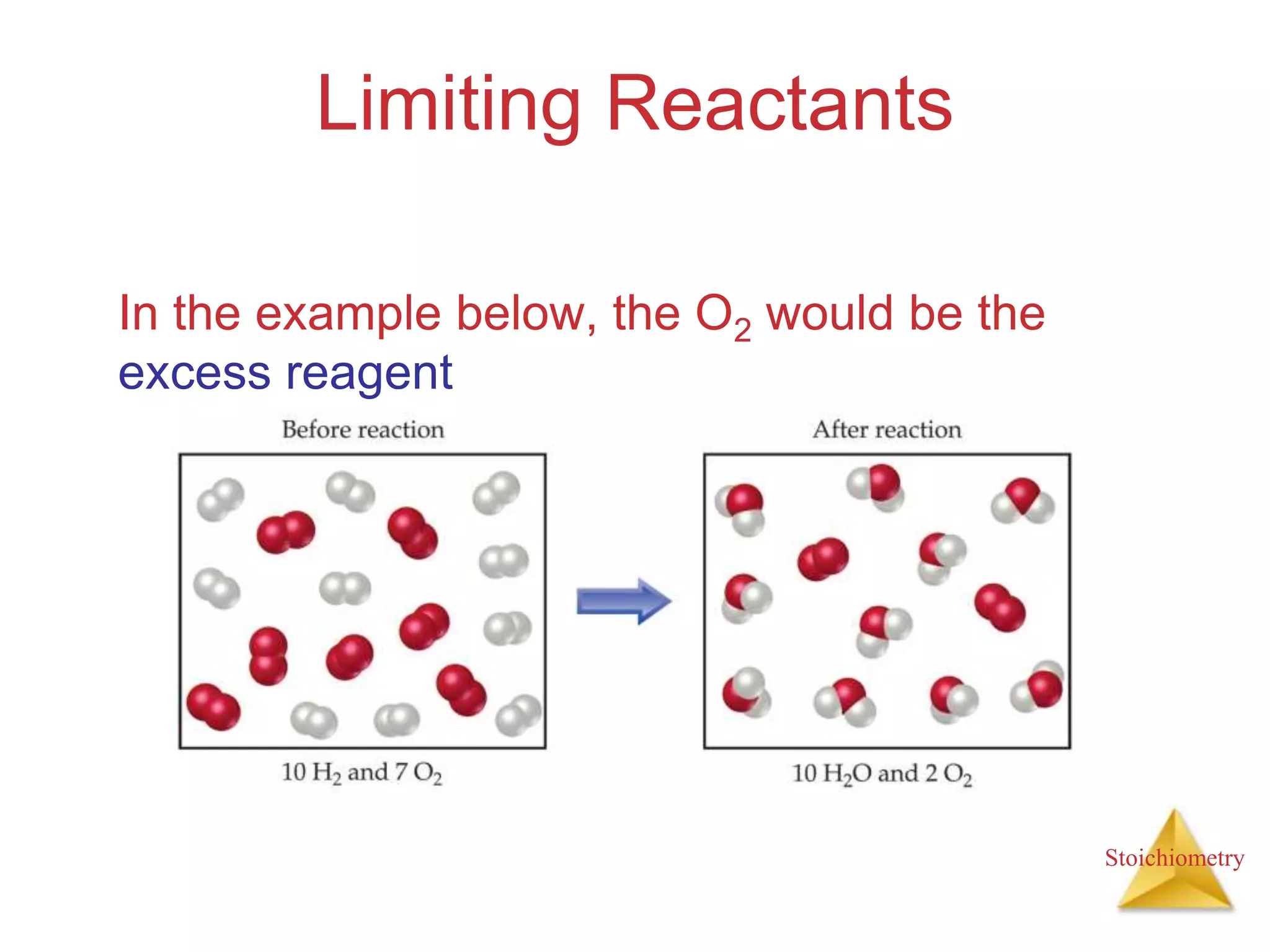
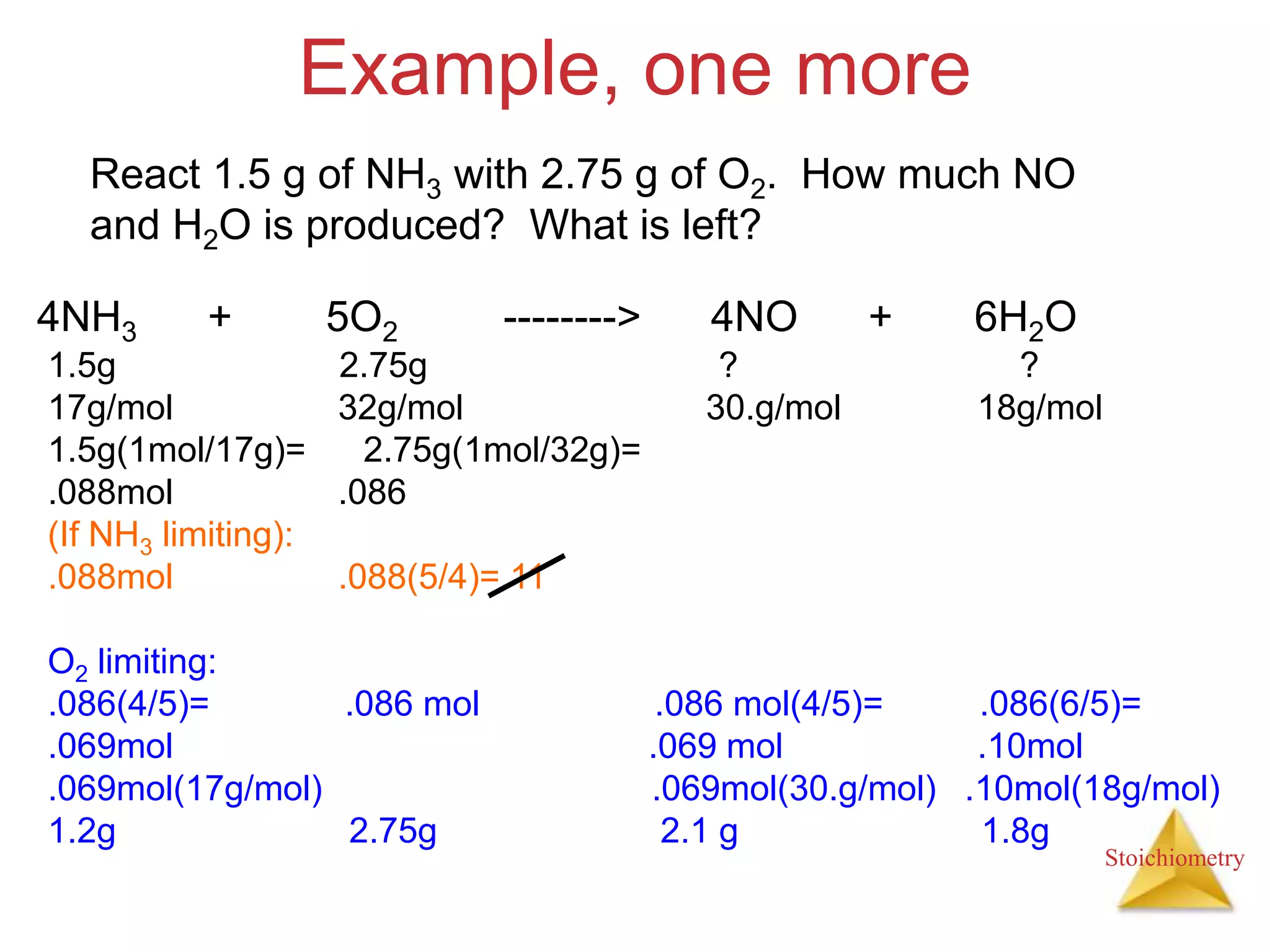
- The concept of limiting reactants and how to determine theoretical and percent yields.