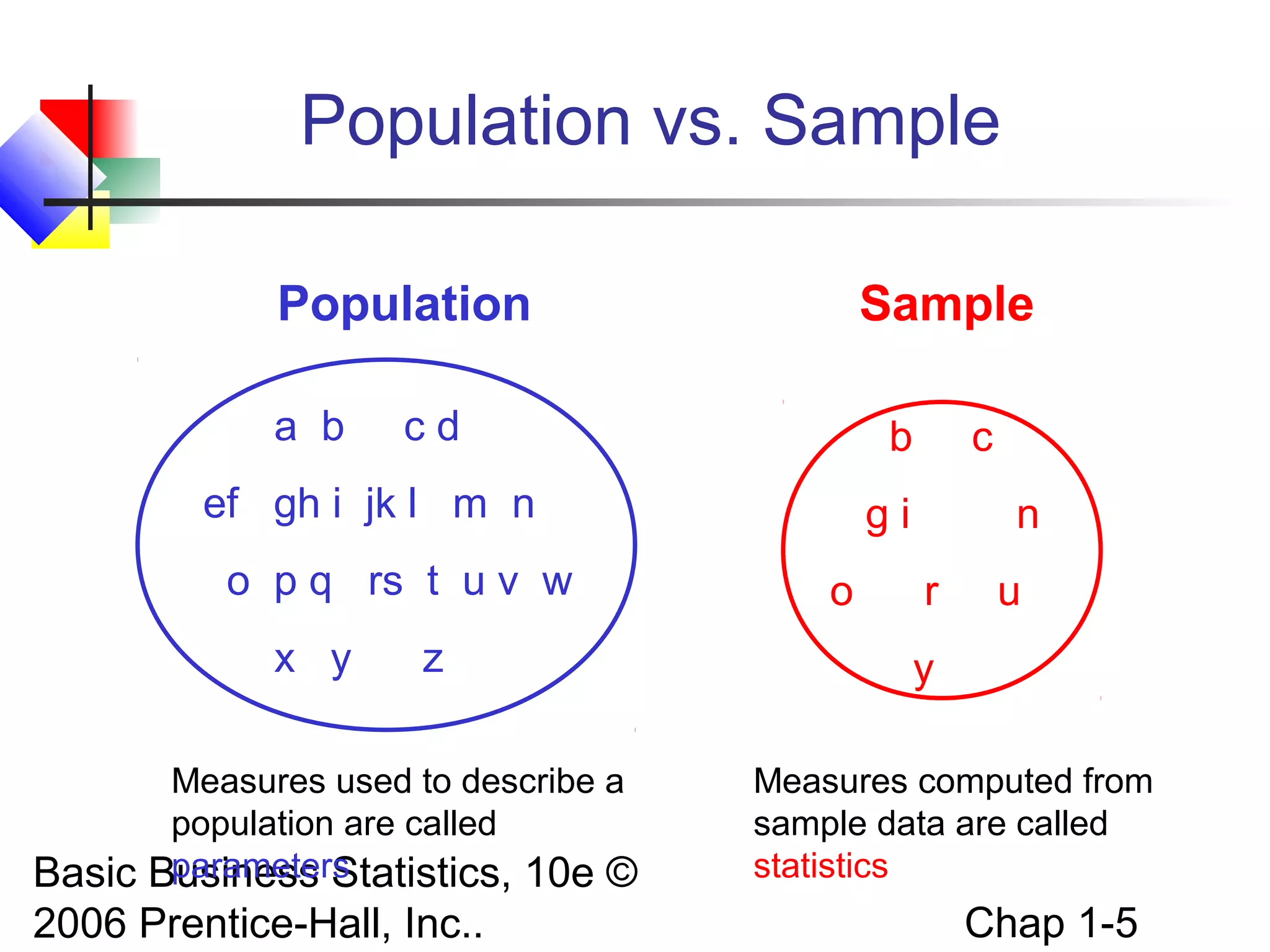
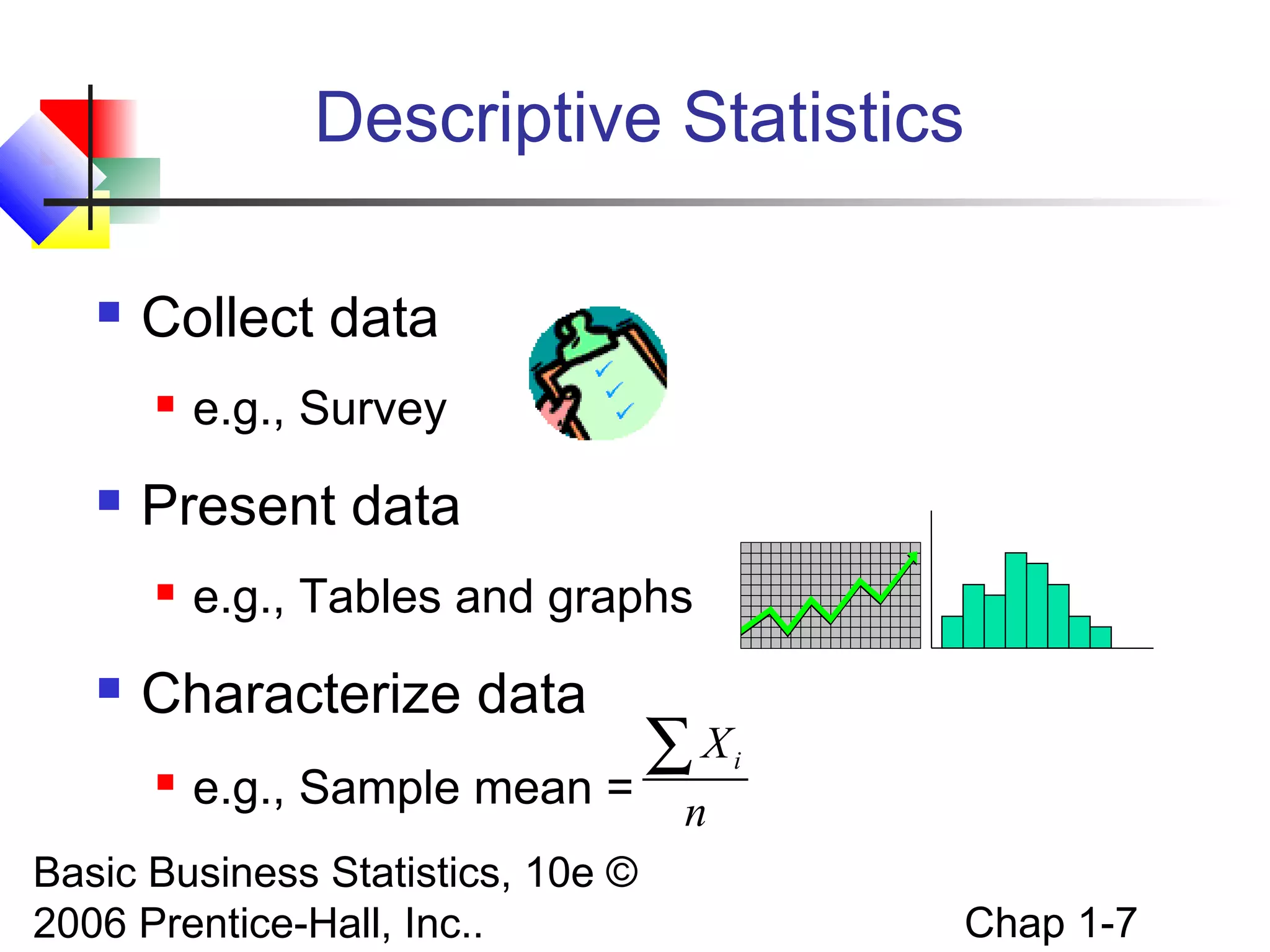
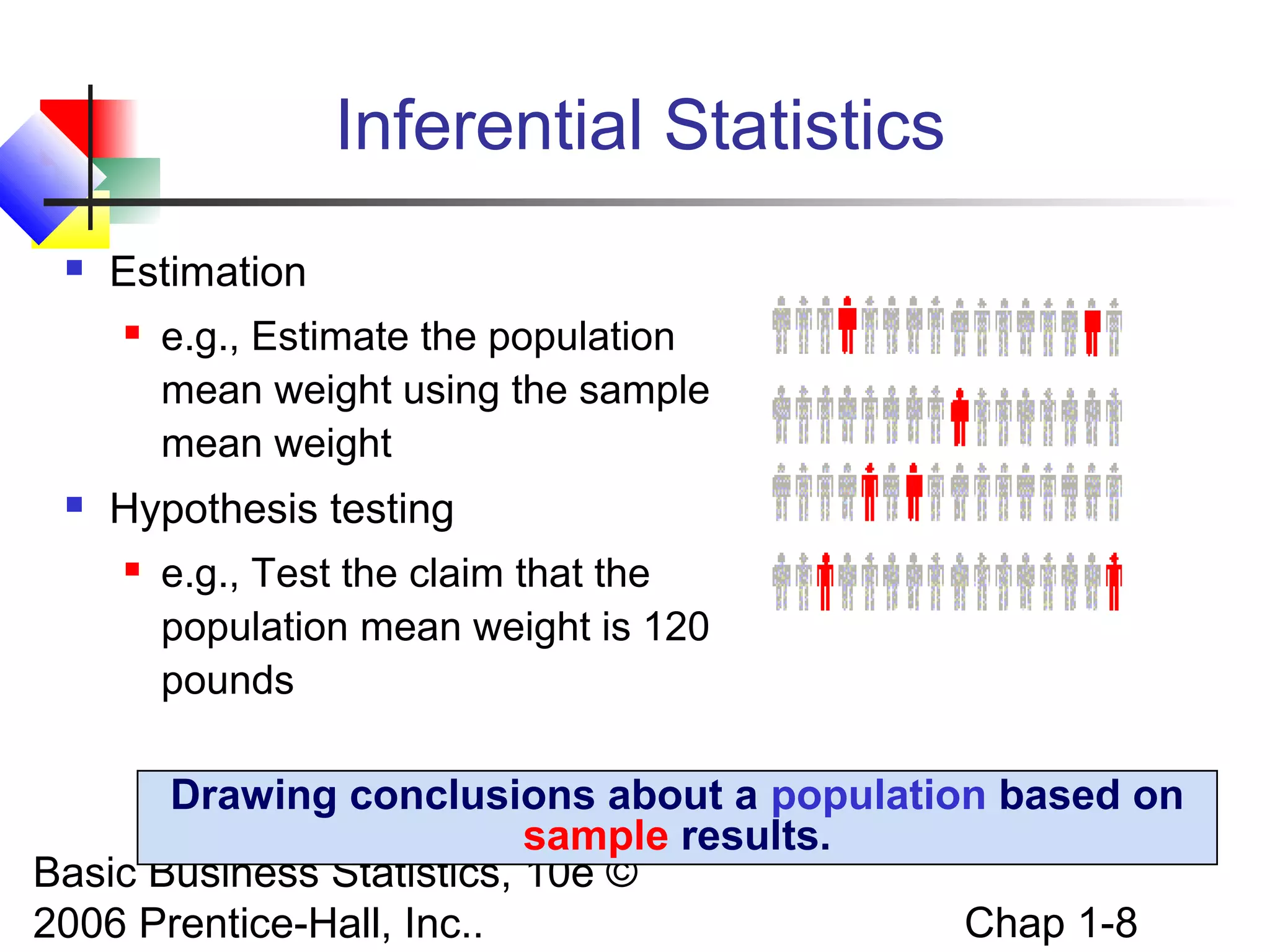
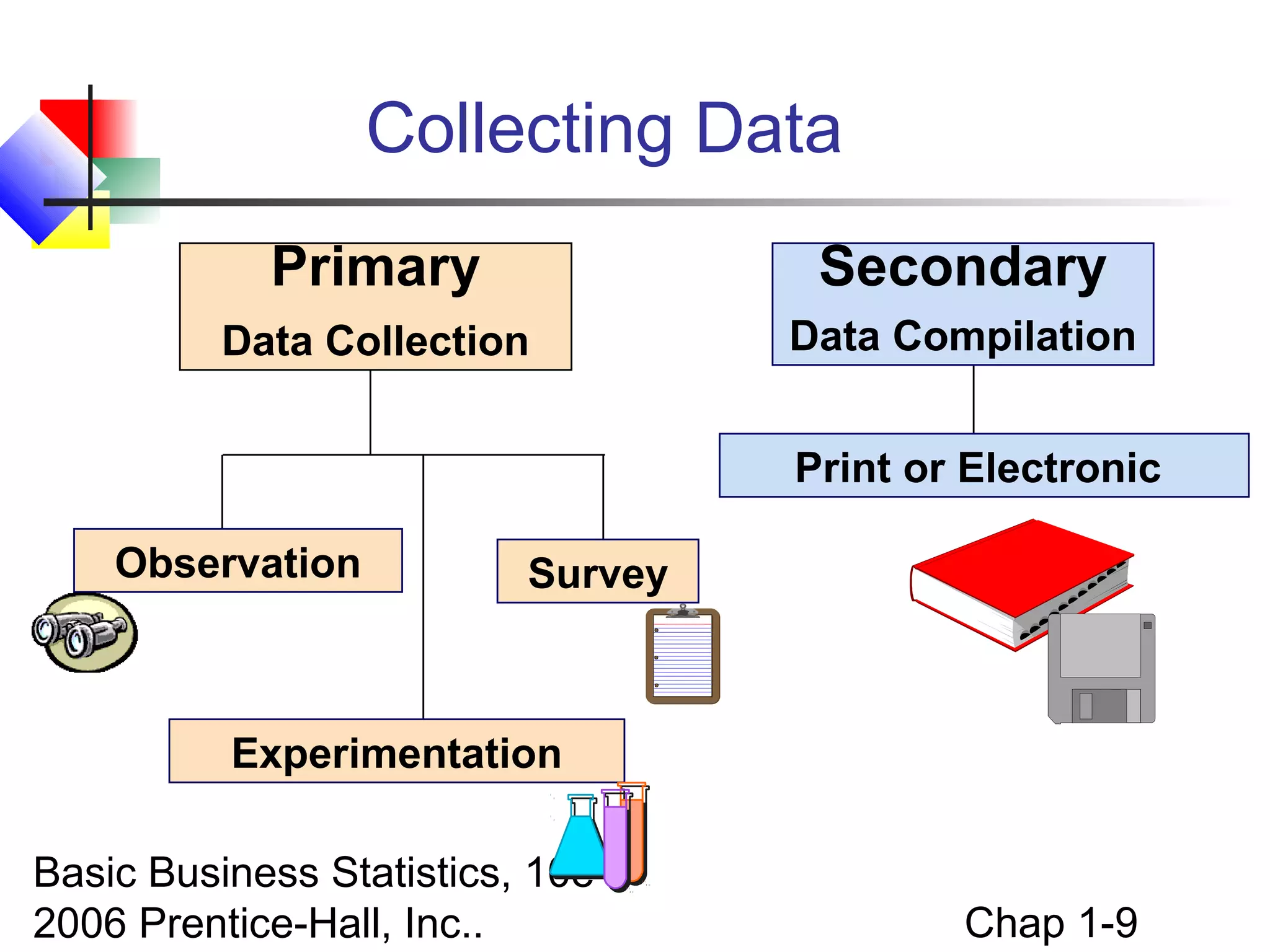
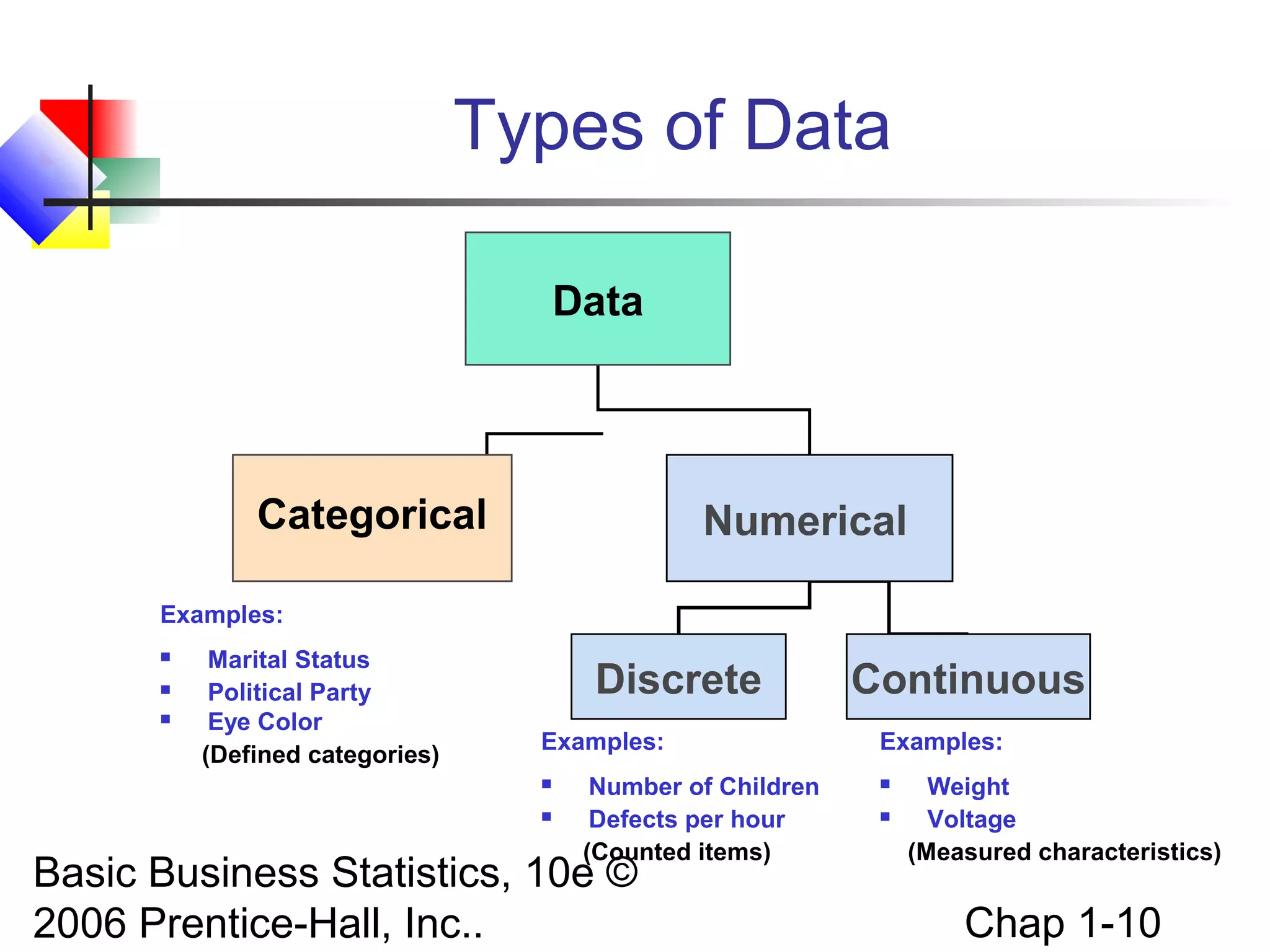
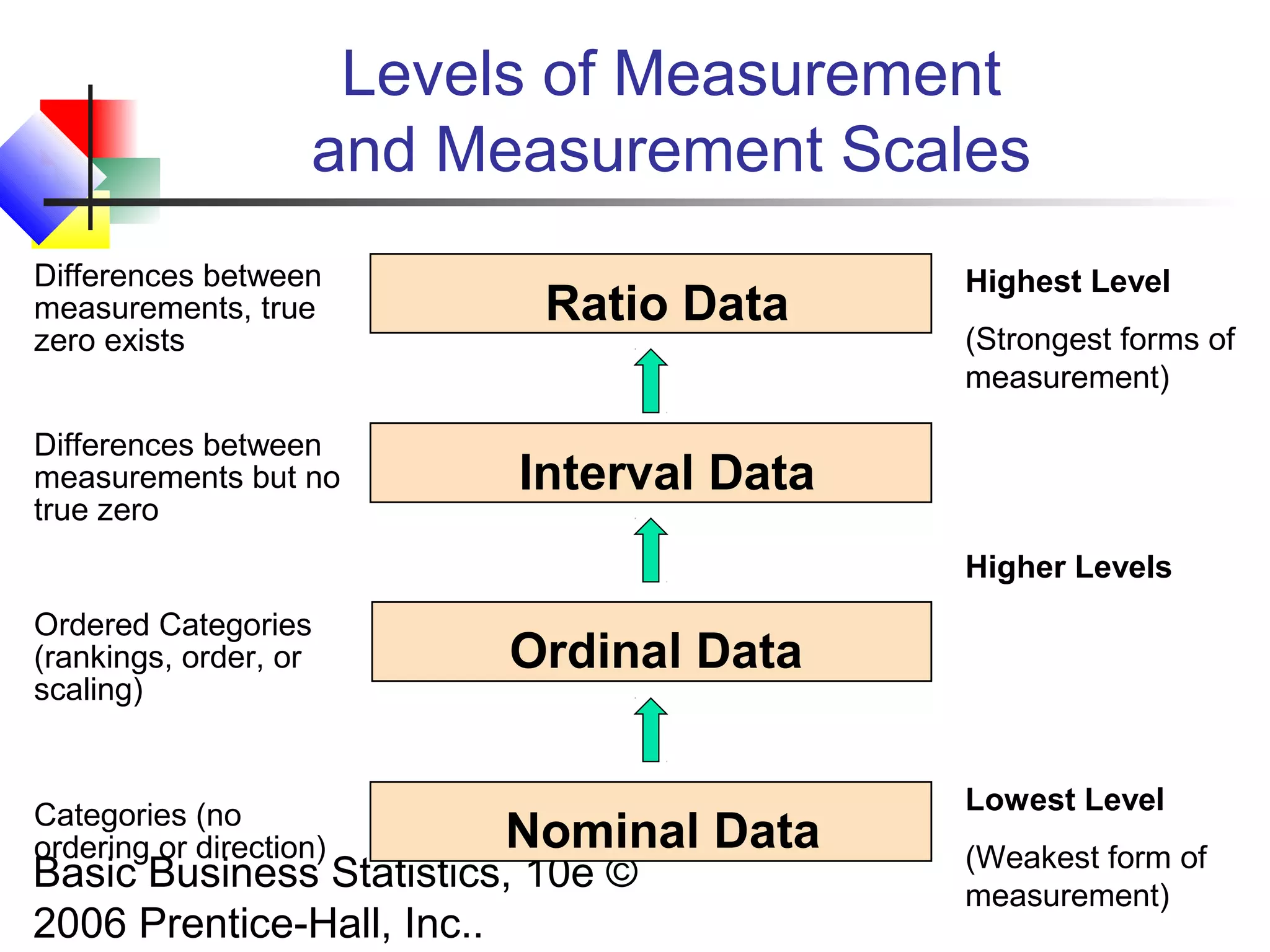
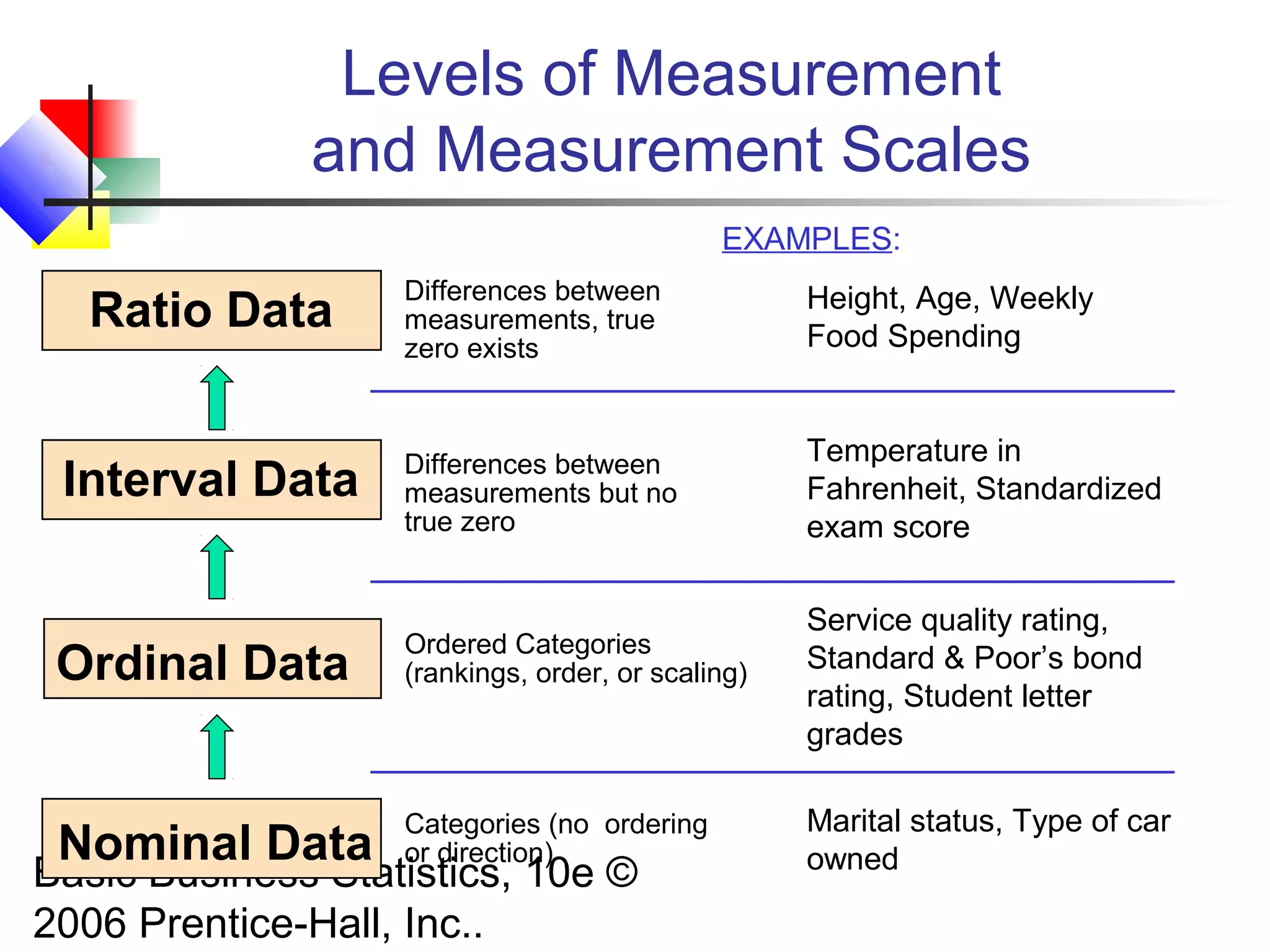
This chapter introduces basic concepts in statistics including the difference between populations and samples, parameters and statistics. It discusses the two main branches of statistics - descriptive statistics which involves collecting, summarizing and presenting data, and inferential statistics which involves drawing conclusions about populations from samples. The chapter also covers different types of data that can be collected including categorical vs. numerical, discrete vs. continuous, and different measurement scales for levels of data.