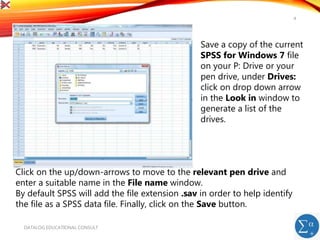
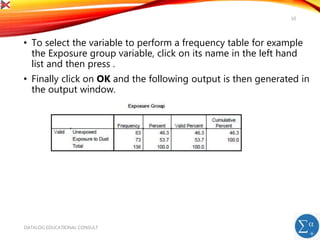
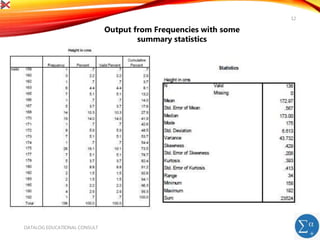
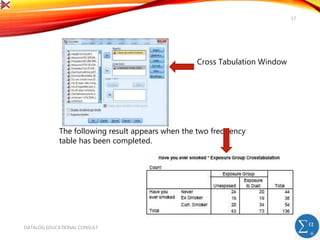
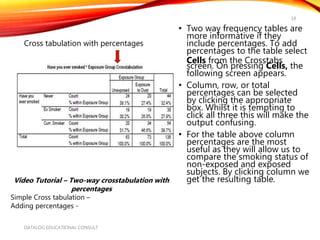
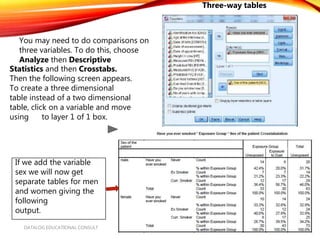
The document introduces SPSS for data management and descriptive statistics, covering file saving, backup, and retrieval processes. It details various techniques for generating descriptive statistics such as frequency analyses and cross-tabulations to identify data inconsistencies. Additionally, it provides step-by-step guidance for performing these analyses within the SPSS environment.