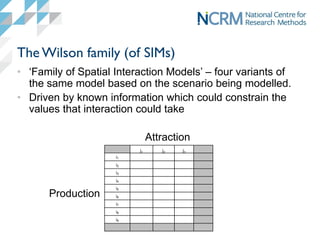
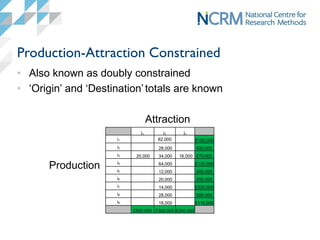
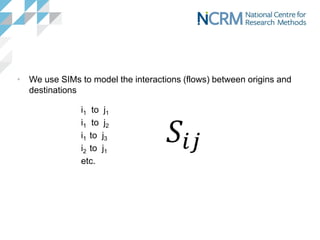
Spatial interaction models (SIMs) are used to model flows between origins and destinations based on demand, accessibility, attractiveness, and competition. SIMs capture the mathematical relationship between these factors and observed flows. There are four main variants - production-attraction constrained, unconstrained, attraction constrained, and production constrained - depending on whether origin and destination totals are known. SIMs have wide-ranging applications in geography, planning, transportation and other fields to estimate missing data and model flows under different scenarios.

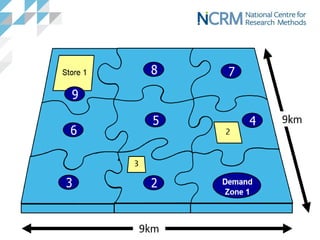



![The flow between i1 and j1 is proportional to
• The demand available in origin zone i1
• The attractiveness of destination j1
• The accessibility of destination j1 to [consumers] in origin zone i1
• Intervening opportunities – the relative accessibility and
attractiveness of destination j1 to [consumers] in origin zone i1
versus all other destinations (j2, j3, etc.) [Competition]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontospatialinteractionmodelling-180917133428/85/Introduction-to-spatial-interaction-modelling-8-320.jpg)