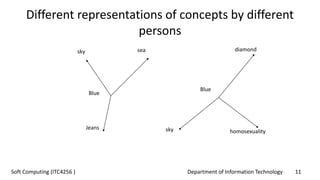
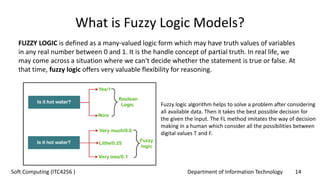
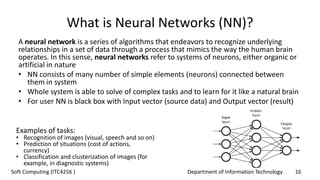
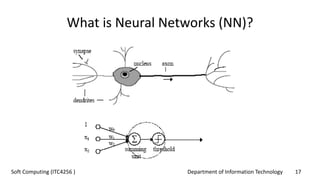
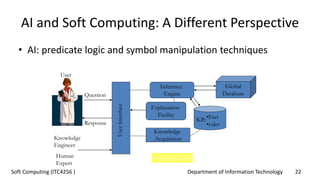
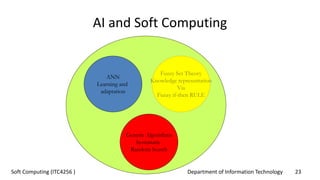
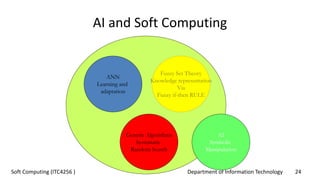
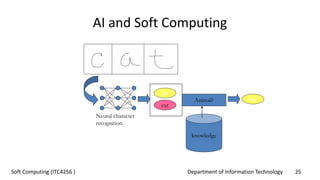
The document outlines the concept of soft computing, which differs from hard computing by being tolerant of imprecision and uncertainty, emulating the flexible reasoning of the human mind. It includes various methodologies like fuzzy logic, neural networks, genetic algorithms, and probabilistic reasoning, highlighting their applications in real-world problems. The future of soft computing is portrayed as significant in both science and engineering, indicating a shift in how information is processed compared to traditional computing.