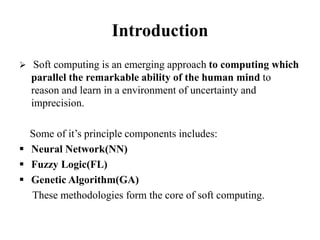
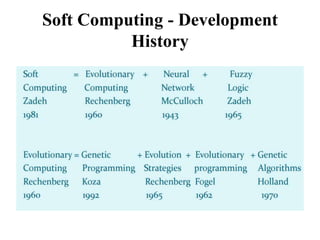
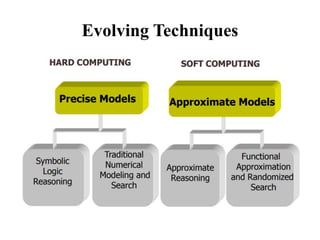
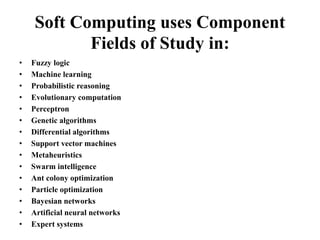
This document provides an introduction to soft computing. Soft computing is an emerging approach to computing that aims to mimic the human mind's ability to reason and learn with uncertainty and imprecision. The key components of soft computing include neural networks, fuzzy logic, and genetic algorithms. The goals of soft computing are to develop intelligent machines to solve real-world problems that may not have ideal or mathematically modeled solutions, while achieving practicality, robustness, and low cost. Soft computing uses techniques like machine learning, evolutionary computation, and artificial neural networks to approach problems that traditional computing cannot always solve.