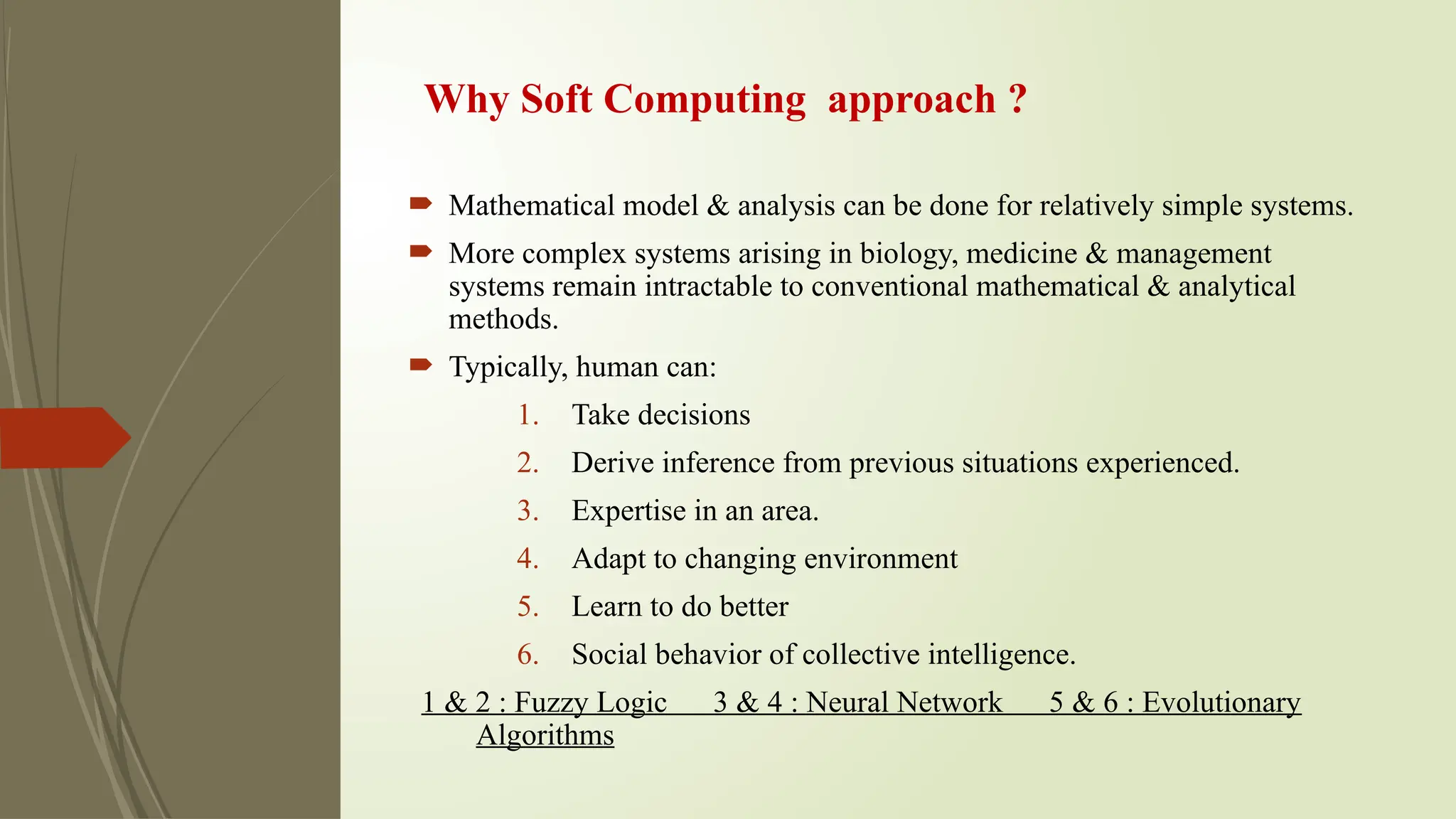
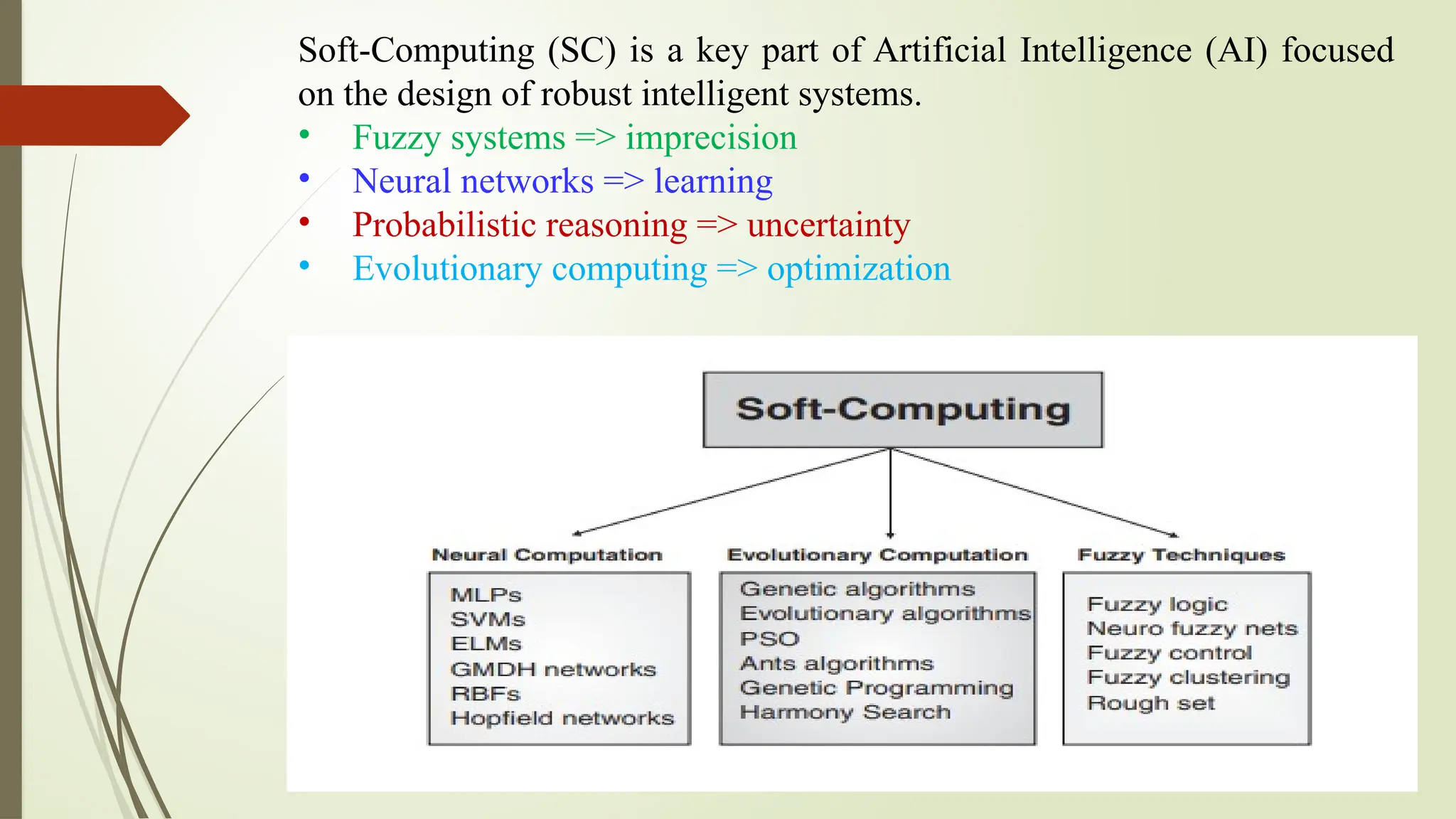
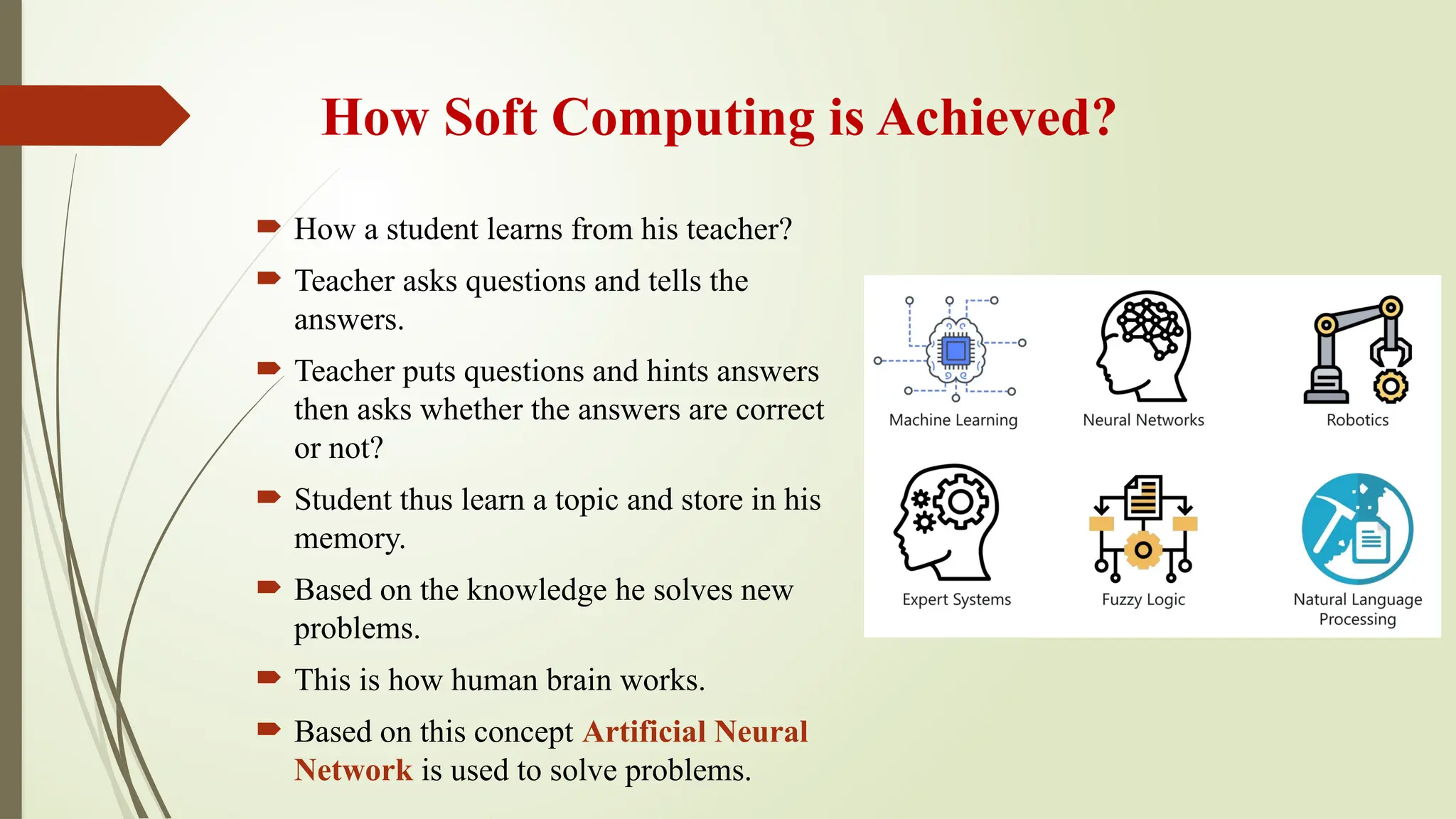
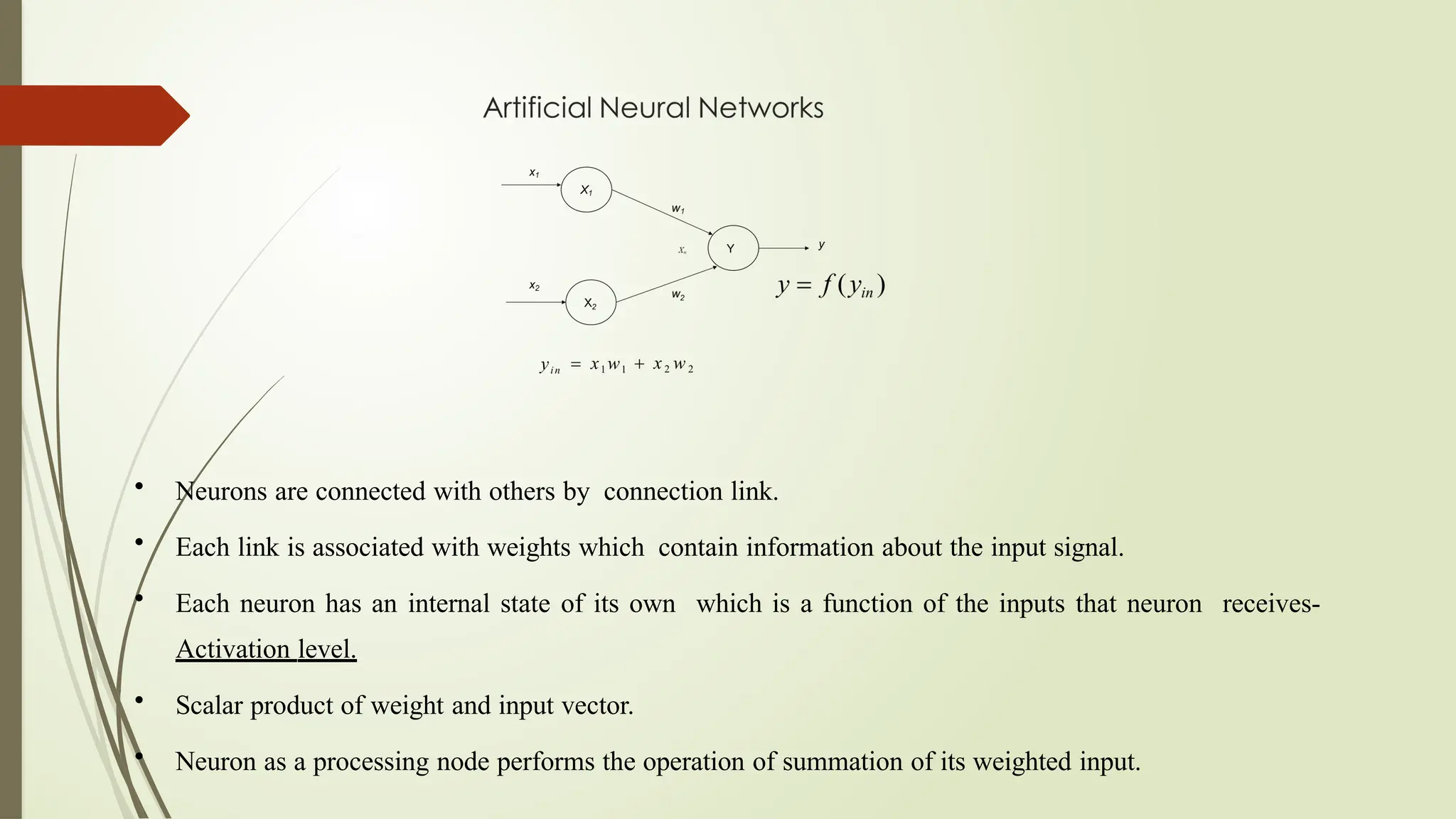
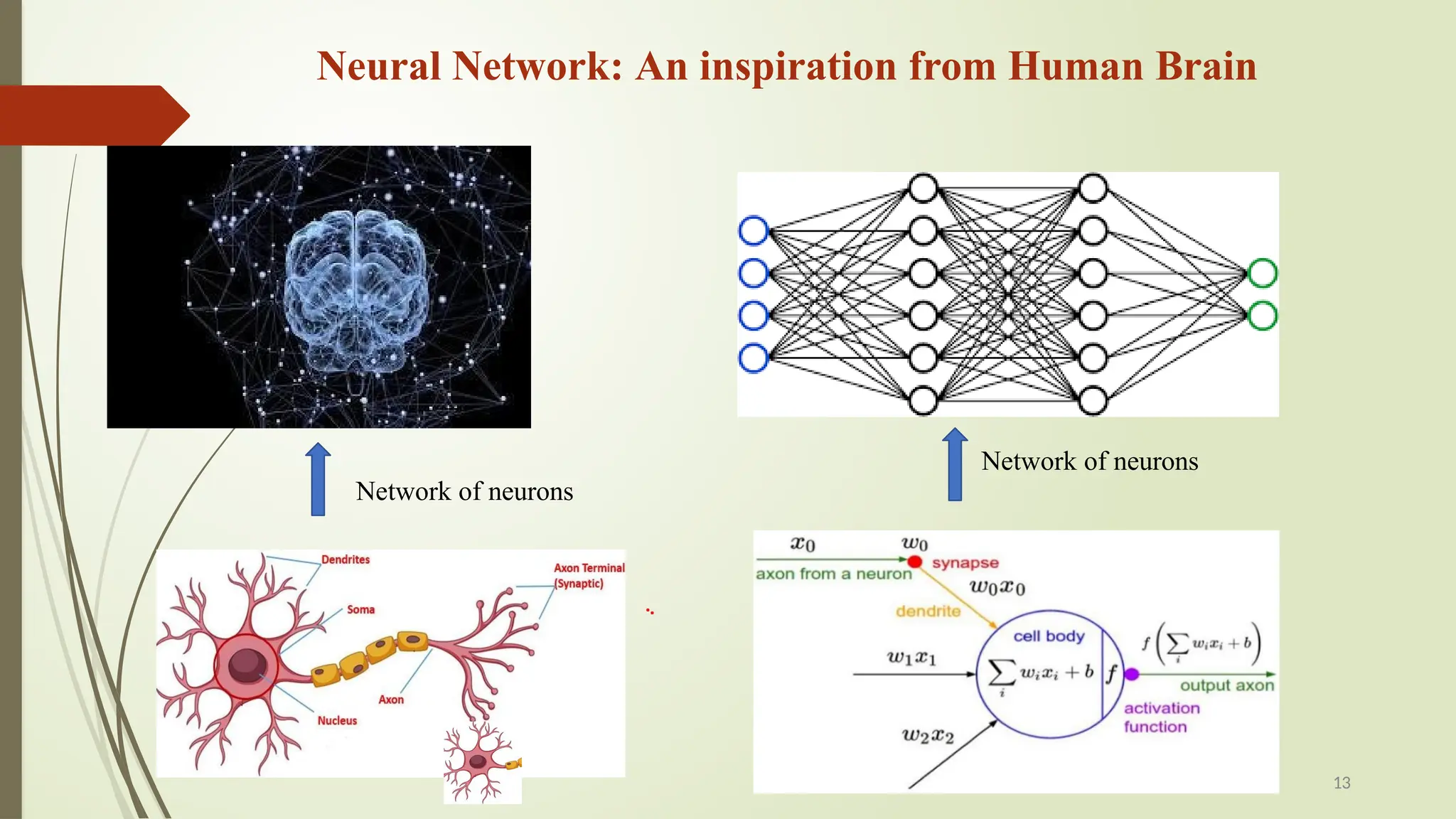
The document discusses the advancements in soft computing and its transformative role in technology and society, covering topics such as intelligent systems, artificial neural networks, fuzzy logic, and evolutionary algorithms. It highlights the importance of soft computing in modeling real-world problems where traditional methods fail, and outlines its applications across various industries including healthcare, finance, and education. The future impact of AI is explored, along with the challenges, risks, and ethical considerations associated with its integration into daily life.





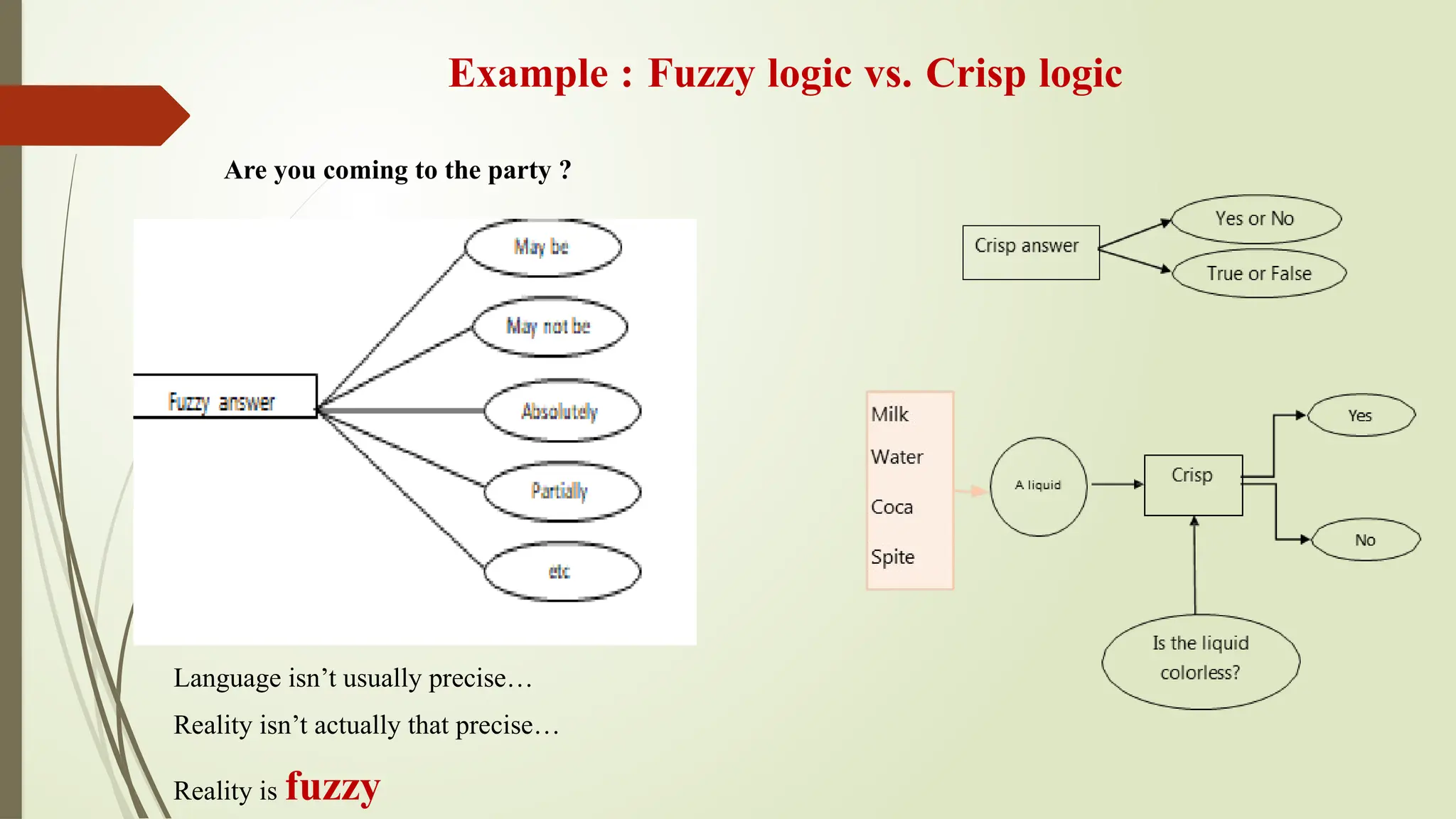
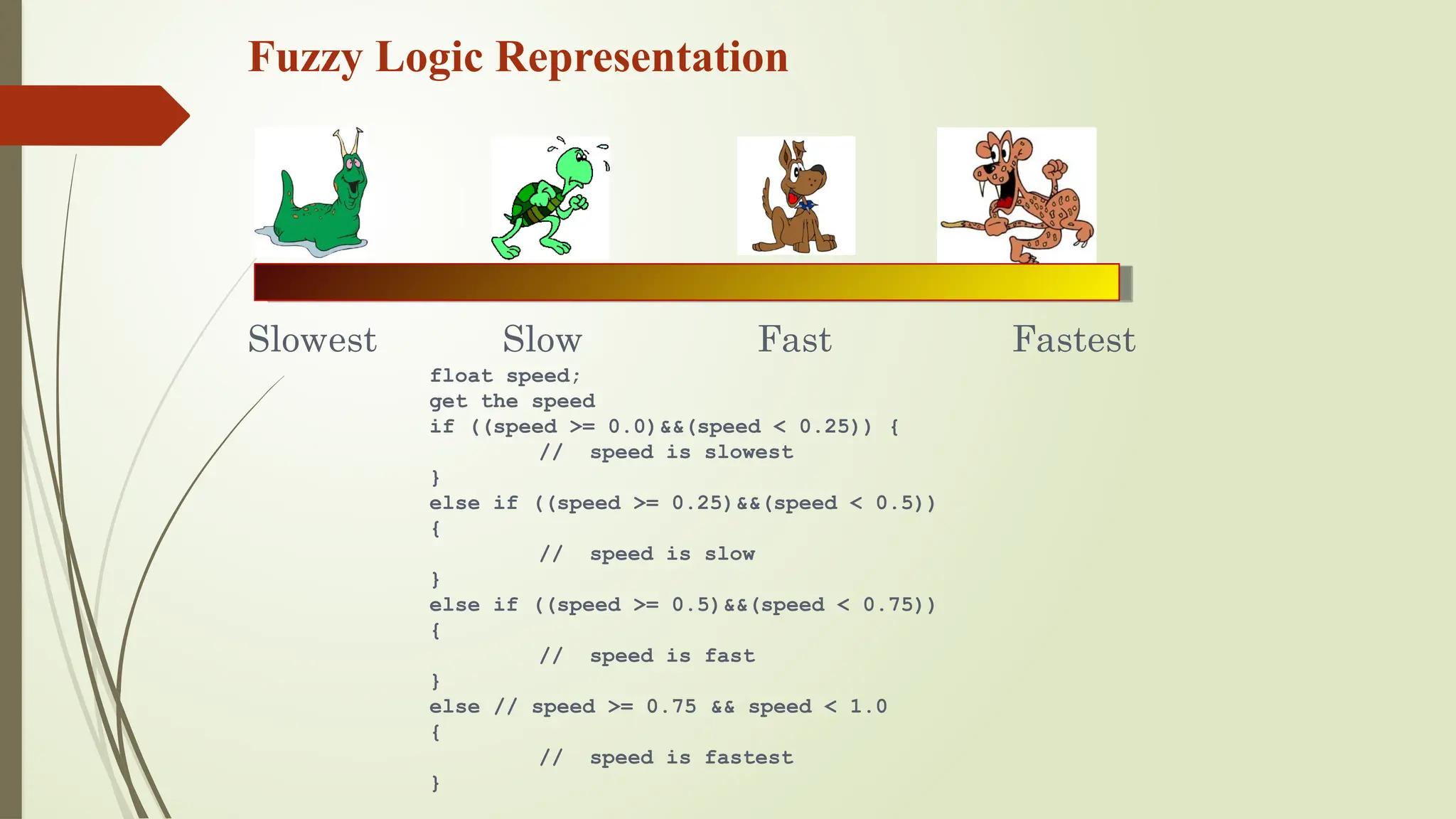
![Fuzzy Logic Representation
For every problem
must represent in
terms of fuzzy sets.
What are fuzzy
sets?
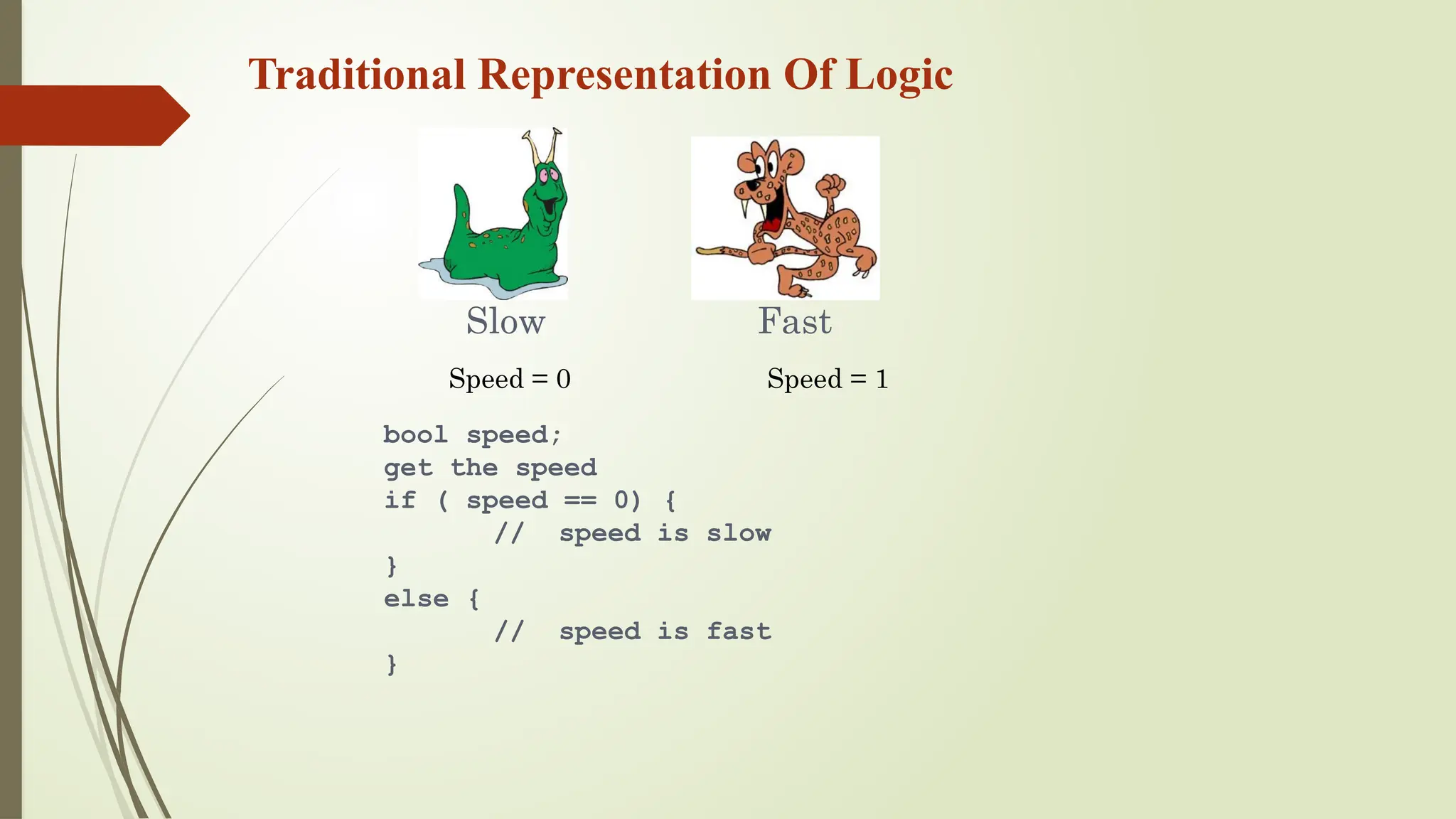
Slowest
Fastest
Slow
Fast
[ 0.0 – 0.25 ]
[ 0.25 – 0.50 ]
[ 0.50 – 0.75 ]
[ 0.75 – 1.00 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hod1-241109163356-e471c916/75/advances-in-soft-computing-transforming-technology-and-society-pptx-17-2048.jpg)