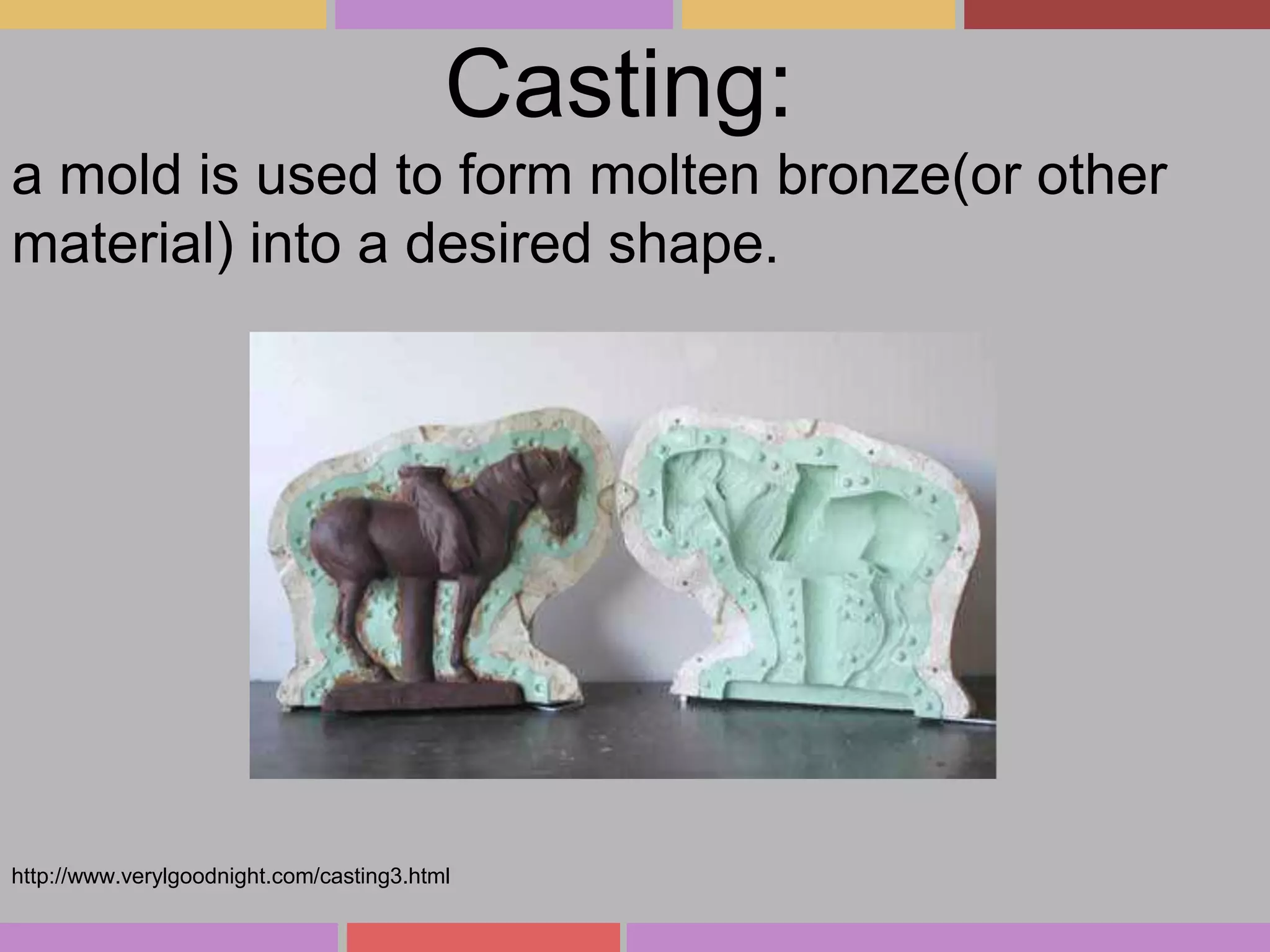
Sculpture has existed since prehistoric times, with early works created for religious or symbolic purposes. Major ancient civilizations like Egypt, China, Greece, and Rome produced sculptures that recorded both religious and political aspects of their societies. Techniques like carving, casting, constructing, and modeling were used. In subsequent eras, artists strived for perfection of the human form or moved towards abstraction. Contemporary sculptors continue redefining the art form using diverse materials and concepts. For a work to be considered sculpture, it must demonstrate skillful use of form, convey some message or emotion, and effectively employ sculpting techniques.