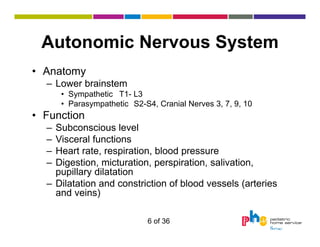
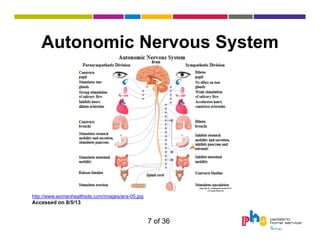
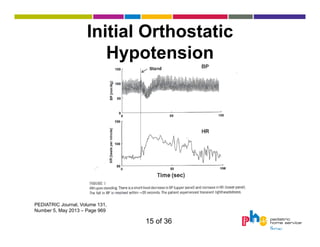
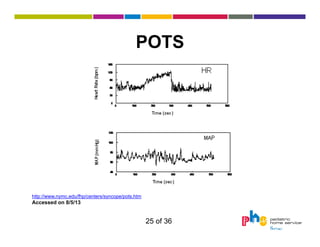
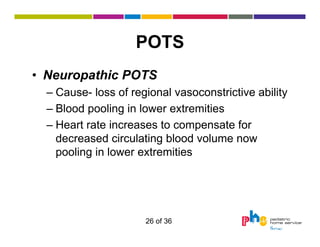
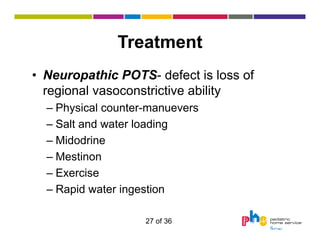
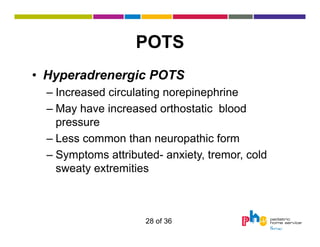
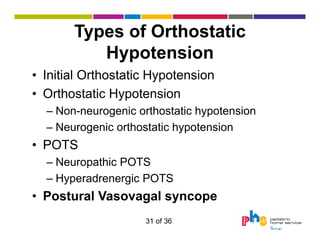
The document discusses dysautonomia and Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS). It defines POTS as excessive increase in heart rate when upright, and describes its two main forms - neuropathic POTS caused by loss of vasoconstriction and hyperadrenergic POTS with increased norepinephrine. Treatment depends on the form but may include physical countermaneuvers, salt, water, medications and exercise. Postural vasovagal syncope, characterized by fainting, is the most common type of orthostatic intolerance.