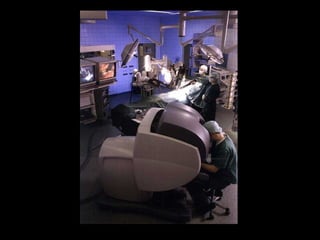
The document discusses two research studies:
1. TeleMed, a system that aims to control a microscope from a computer for use in pathology and medicine. It allows remote off-site control of microscope functions through software and an interface board.
2. A comparative study of the antibacterial properties of three chili pepper varieties on human dental microflora. It found that C. frutescens was most effective at inhibiting two bacterial species, while C. annuum var. longgum worked best against one isolate. Minimum inhibitory and bactericidal concentrations were determined.