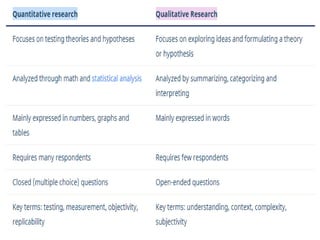
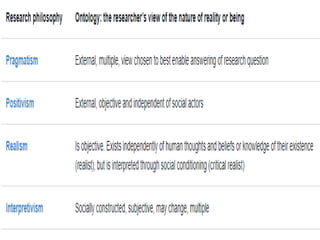
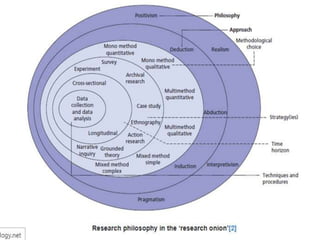
The document discusses the differences between qualitative and quantitative nursing research, highlighting their methodologies, data collection methods, and when to use each approach. Quantitative research focuses on numbers and statistical analysis to confirm theories, while qualitative research emphasizes understanding experiences through words. It also suggests a mixed methods approach for a comprehensive analysis and outlines common strategies for analyzing both types of data.