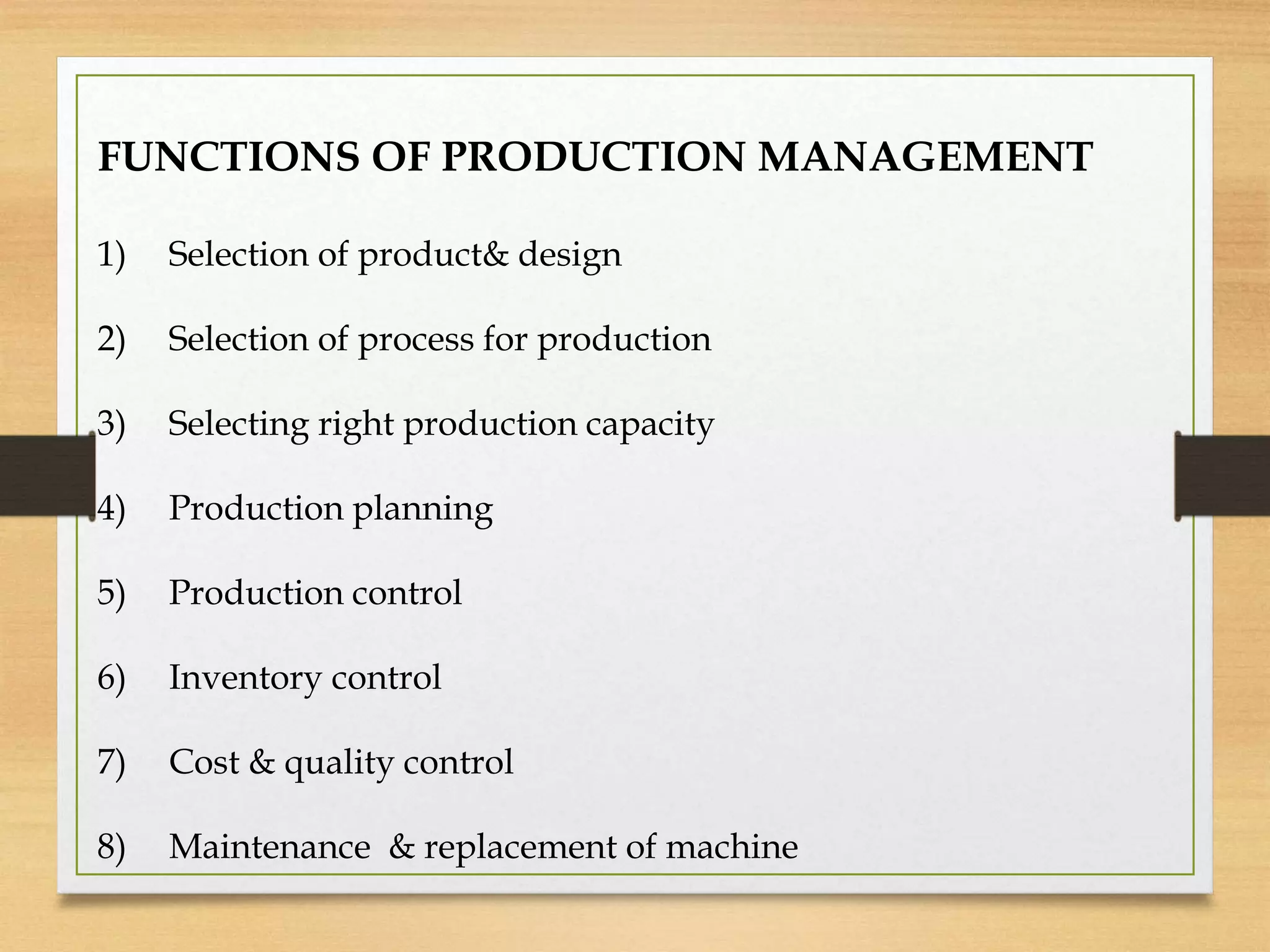
This presentation provides an introduction to production management. It discusses production management as dealing with planning, directing, coordinating, and controlling production activities. The objectives of production management are listed as quality, quantity, time, effectiveness, efficiency, capacity utilization, and cost. Functions of production management include selecting products and processes, production planning and control, inventory control, and cost and quality control. Key factors that affect plant location and layout are also outlined. Different types of plant layouts like process, product, mixed, and static layouts are defined.