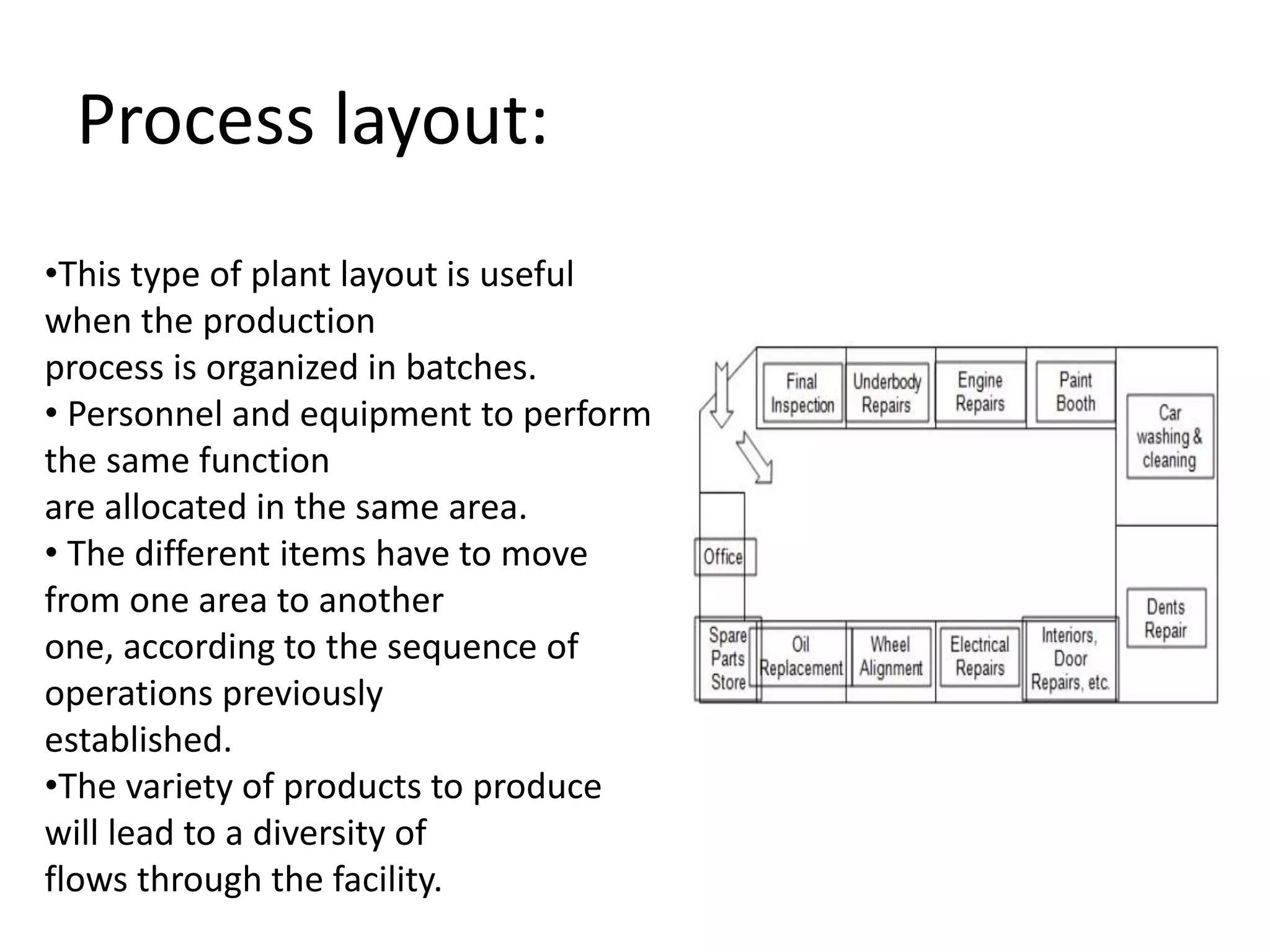
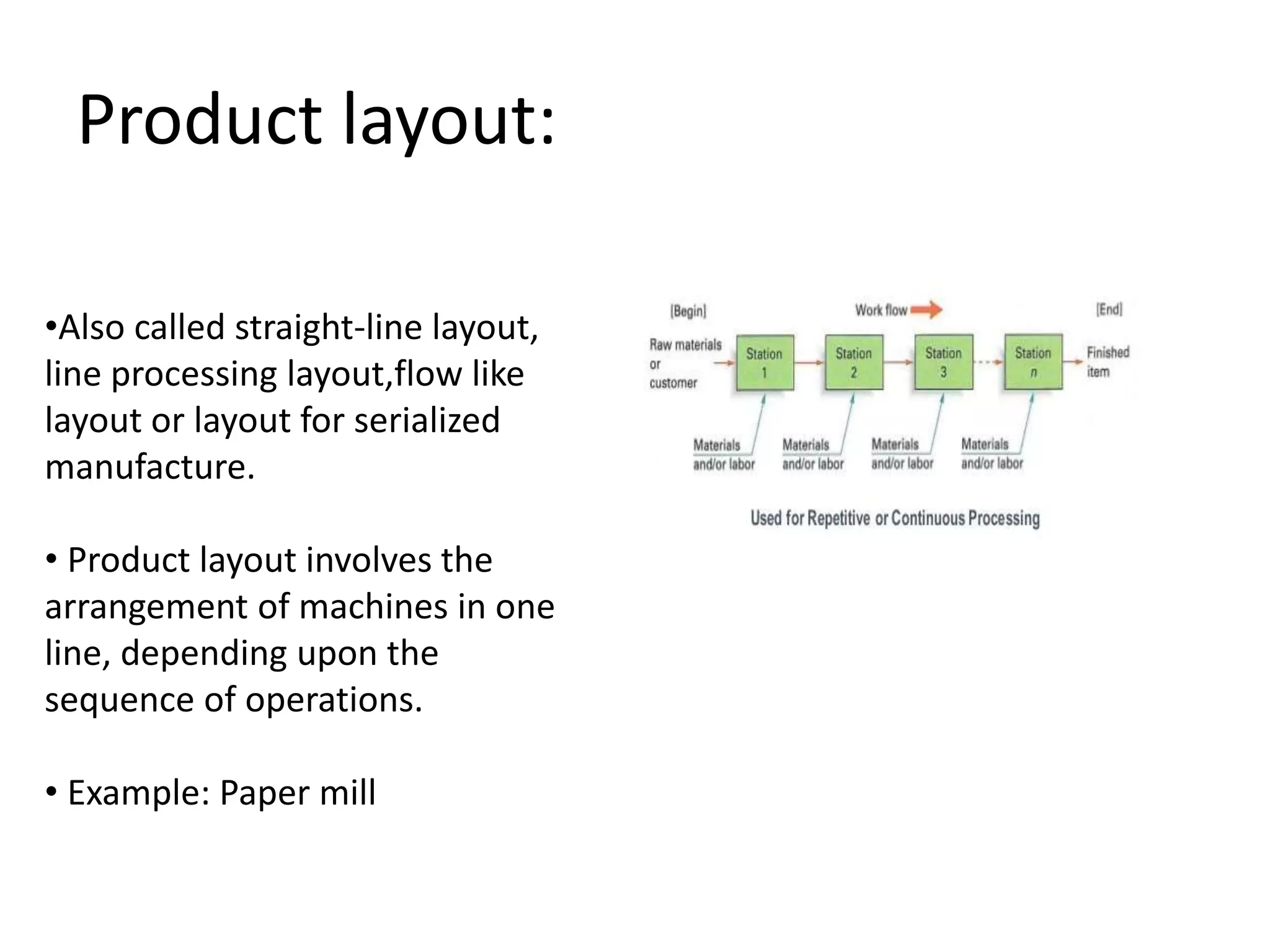
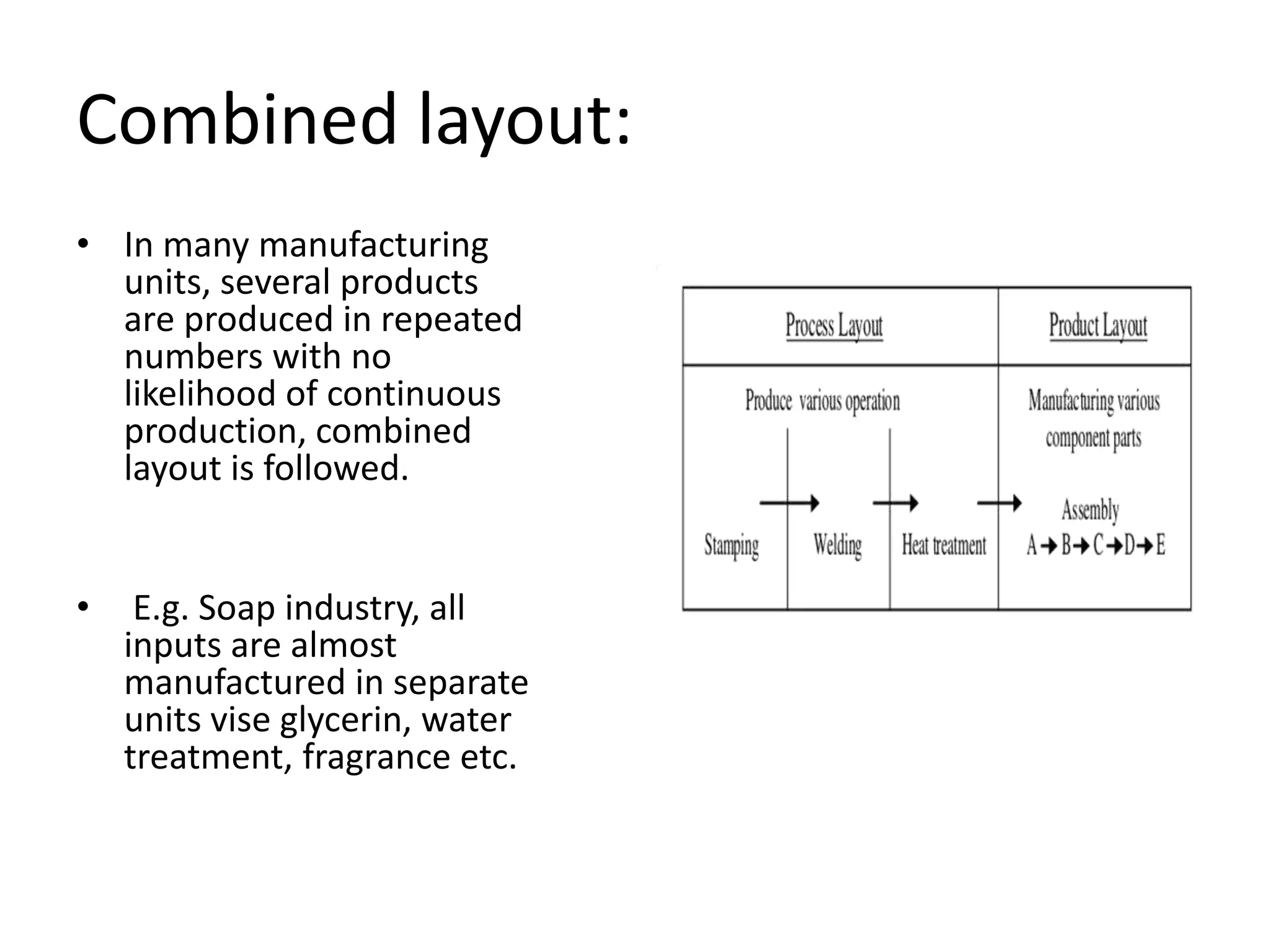
Production management involves converting raw materials into finished goods efficiently. An important part is selecting an optimal plant layout and location. The objectives of plant layout are to minimize costs of transportation, materials handling, and maximize efficiency. The main types of layouts are process, product, and combined, each suited to different production needs. Factors like production process, scale, machines, and space influence the best layout choice. Location selection aims to minimize total costs while accessing raw materials, labor, markets, and infrastructure.