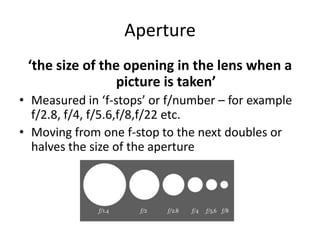
This document provides an introduction to basic photography concepts including exposure, shutter speed, aperture, ISO, composition, and flash. It explains that exposure is controlled by aperture, shutter speed, and ISO settings and discusses the effects of these variables. Aperture affects depth of field while shutter speed can freeze or blur motion. ISO impacts image quality and noise. The document also covers composition techniques like the rule of thirds and leading lines. Quick tips for portraits emphasize perspective, lighting, and background. The overall message is that practice and experimentation are key to improving photographic skills.