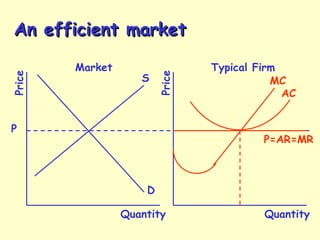
This document introduces market structure models and their characteristics. It discusses the four main market structures: perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly and monopoly. It outlines their key characteristics such as the number and size of firms, nature of products, barriers to entry and examples. It then examines how firm behavior is affected differently under each market structure in terms of pricing, costs, branding and profitability. The document emphasizes that more competitive market structures are generally more efficient for allocating resources.