This document discusses the economic model of monopolistic competition. Key assumptions of this model include:
- Firms produce differentiated products and have some degree of monopoly power over their own products but face competition from close substitutes.
- The industry contains a large number of small firms relative to the overall market size.
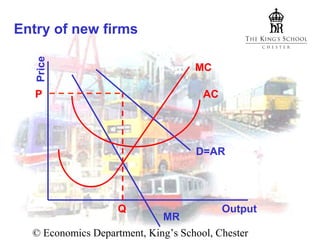
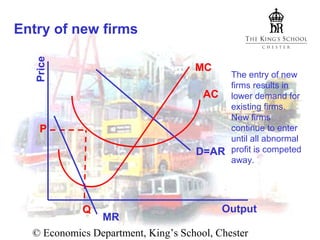
- There is free entry into the industry, so abnormal profits will attract new competition over time.
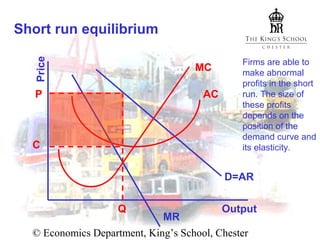
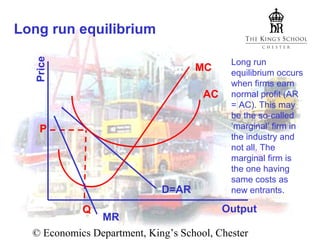
In the short run, firms can earn abnormal profits that depend on demand elasticity. In the long run, entry of new firms increases supply and reduces prices until all abnormal profits are eliminated and firms earn only normal profits. The market reaches long-run equilibrium.