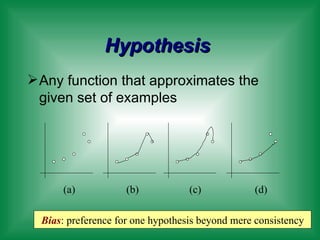
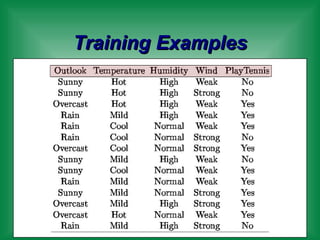
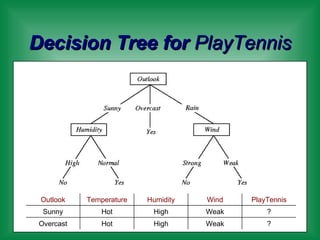
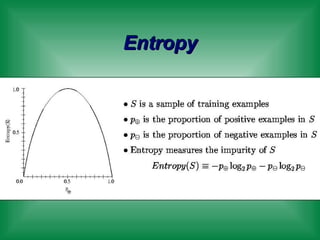
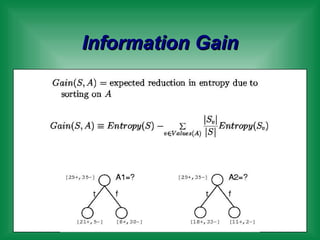
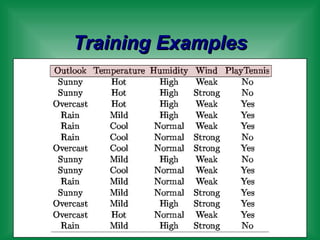
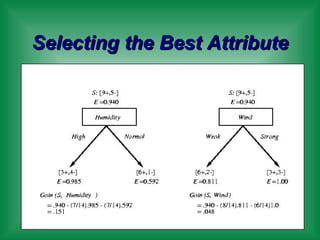
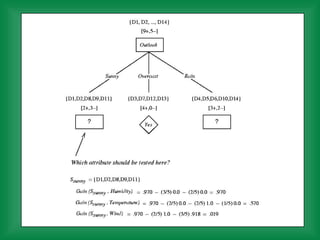
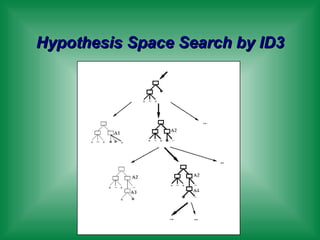
This document provides an overview of machine learning and the ID3 decision tree algorithm. It discusses key concepts in machine learning including supervised and unsupervised learning. It also describes how the ID3 algorithm builds decision trees from training examples by selecting attributes that provide the most information gain at each step, resulting in a hypothesis space search. The document notes that the ID3 algorithm has biases like preferring shorter trees and attributes with high information gain near the root.