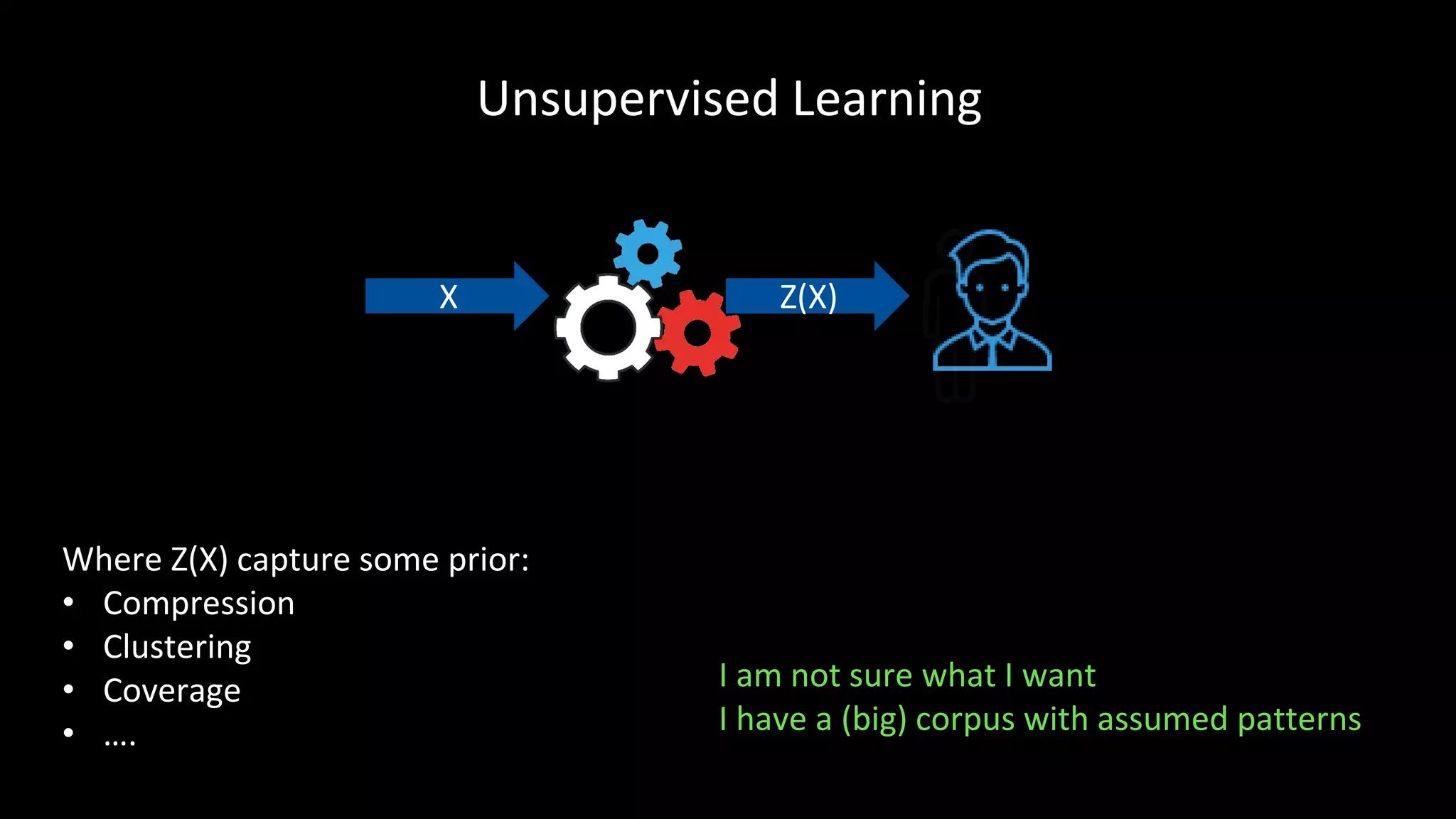
This document summarizes Matthias Gallé's presentation on human-centric machine learning at the 2017 Rakuten Technology Conference. It discusses supervised learning where the goal is formalized and large labeled datasets are available, unsupervised learning where patterns are discovered in unlabeled data, and interactive learning which allows users to provide feedback to guide the machine learning model. Specific applications mentioned include machine translation, exploratory search, active learning, and removing the burden of labeling from humans.





![Example: Active Learning
Give initiative to the algorithm
allow action of type: “please, label instance x”
Cognitive effort of labeling a document 3-5x higher than labelling a word [1]
Feature labelling:
• type(feedback) ≠ type(label)
• information load of a word label is small
• word sense disambiguation
[1] Raghavan, Hema, Omid Madani, and Rosie Jones. "Active learning with feedback on features and instances." Journal of
Machine Learning Research7.Aug (2006): 1655-1686.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matthiasgallertcfinal-171114074028/75/Human-Centric-Machine-Learning-12-2048.jpg)
![Conclusion
If you really want to solve a problem, don’t be prisoner of your
performance indicator
Ask yourself:
1. Does it really capture success?
does it align with human judgment?
2. What does the [machine | human] best?
3. Can you remove the burden from humans by smarter algorithms?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matthiasgallertcfinal-171114074028/75/Human-Centric-Machine-Learning-13-2048.jpg)