Welding – A joining process of two materials that coalesced (blend) at their contacting surfaces by the application of pressure and/or heat.
– Weldment – The assemblage made by welding multiple components together
– Sometime a filler material to facilitate coalescence.
Advantages: portable, permanent, stronger than the parent materials with a filler metal, the most economical method to join in terms of material usage and fabrication costs .
Disadvantages: Expensive manual Labor, high energy and dangerous, does not allow disassemble and defects
Applications: Constructions, Piping, pressure vessels,boilers and storage tanks, Shipbuilding, Aerospace, Automobile and Railroad Fusion welding - coalescence is accomplished by melting the two parts to be joined, in some cases adding filler metal to the joint
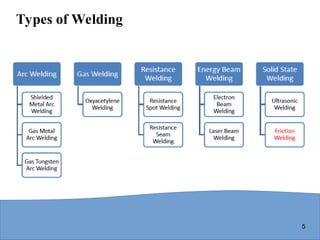
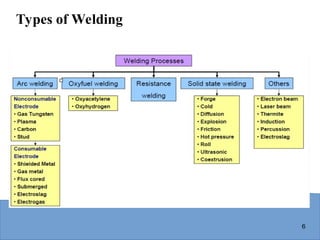
Examples: arc welding, resistance spot welding, oxyfuel gas welding
Solid state welding - heat and/or pressure are used to achieve coalescence, but no melting of base metals occurs and no filler metal is added
Examples: forge welding, diffusion welding, friction welding