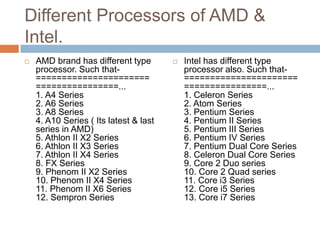
This document provides an introduction to computer processors. It discusses the main types of processors produced by Intel and AMD, including Celeron, Pentium, Core i3/i5/i7, Athlon, Phenom, and FX series. It explains that the processor, also called the central processing unit (CPU), is the main component of a computer that executes stored program instructions. The CPU consists of a control unit that manages instruction flow and an arithmetic/logic unit that performs arithmetic and logic operations. Memory holds the data and instructions used by the CPU. Major processor vendors include Intel, AMD, Nvidia, IBM, Via, and Arm. Performance-enhancing technologies include core technology, turbo boost, virtualization,