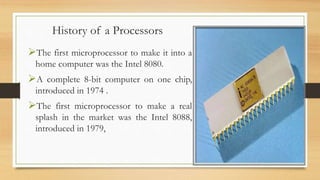
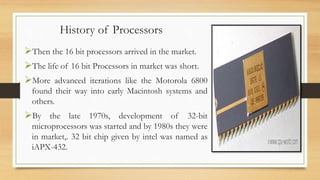
The document explains the significance and functionality of microprocessors in computing, detailing their historical development from the Intel 8080 to modern multi-core processors. It highlights the key features of processors, including their operational mechanisms, uses, and challenges such as cache and memory issues. Additionally, it lists top manufacturers and provides information on the price range of various processors.