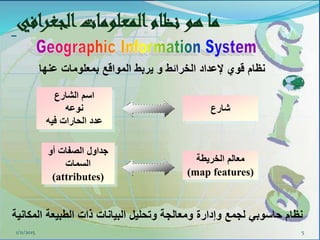
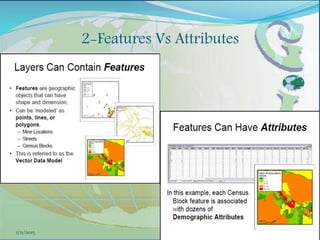
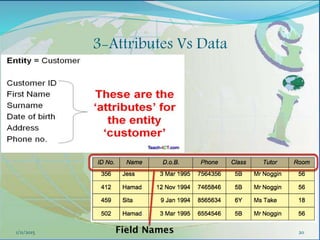
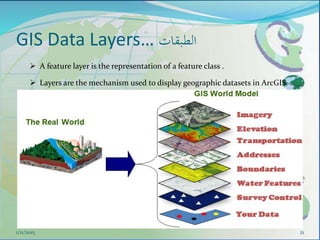
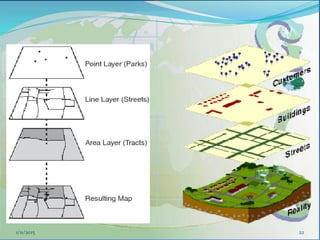
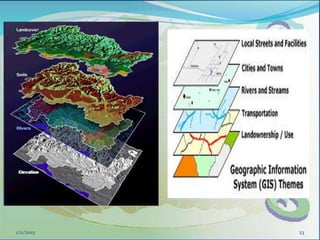
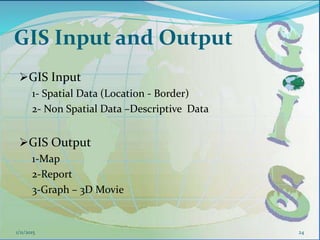
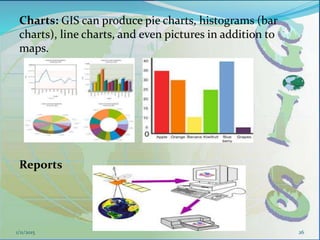
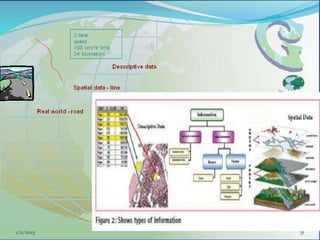
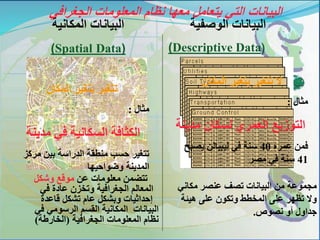
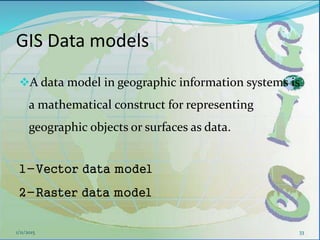
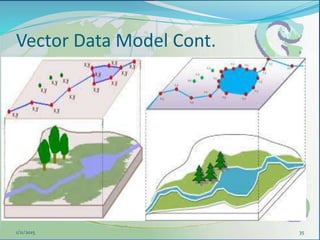
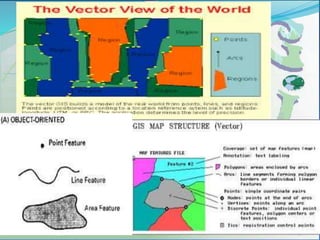
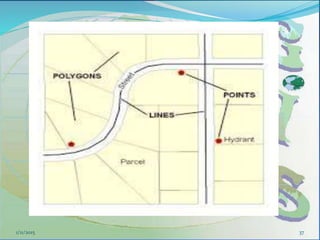
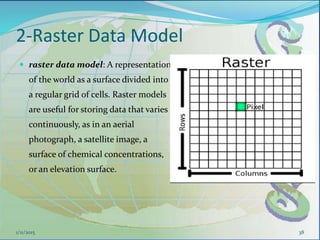
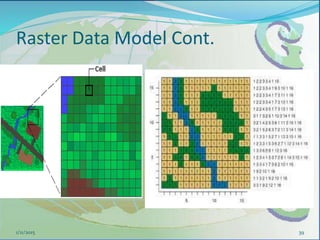
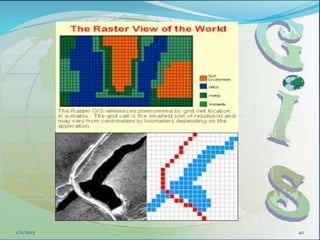
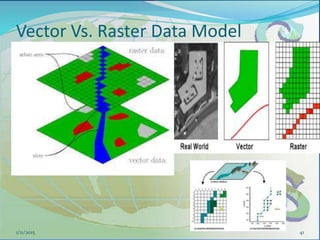
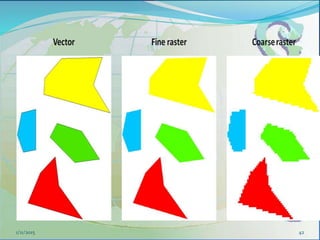
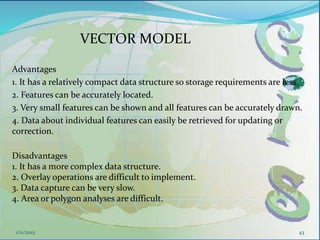
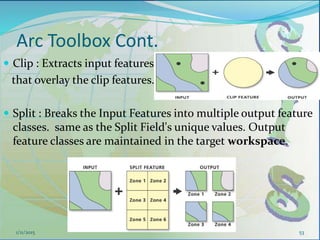
This document provides an introduction to geographic information systems (GIS). It defines GIS as a system that connects maps and information about locations to support analytical processes. A GIS consists of a database, maps, and computer hardware and software that allow for the collection, management, analysis and display of geographically referenced data. The document discusses key GIS concepts such as layers, features, and attributes. It also provides examples of how GIS is used in various fields such as local government, natural resource management, transportation, business, and more.