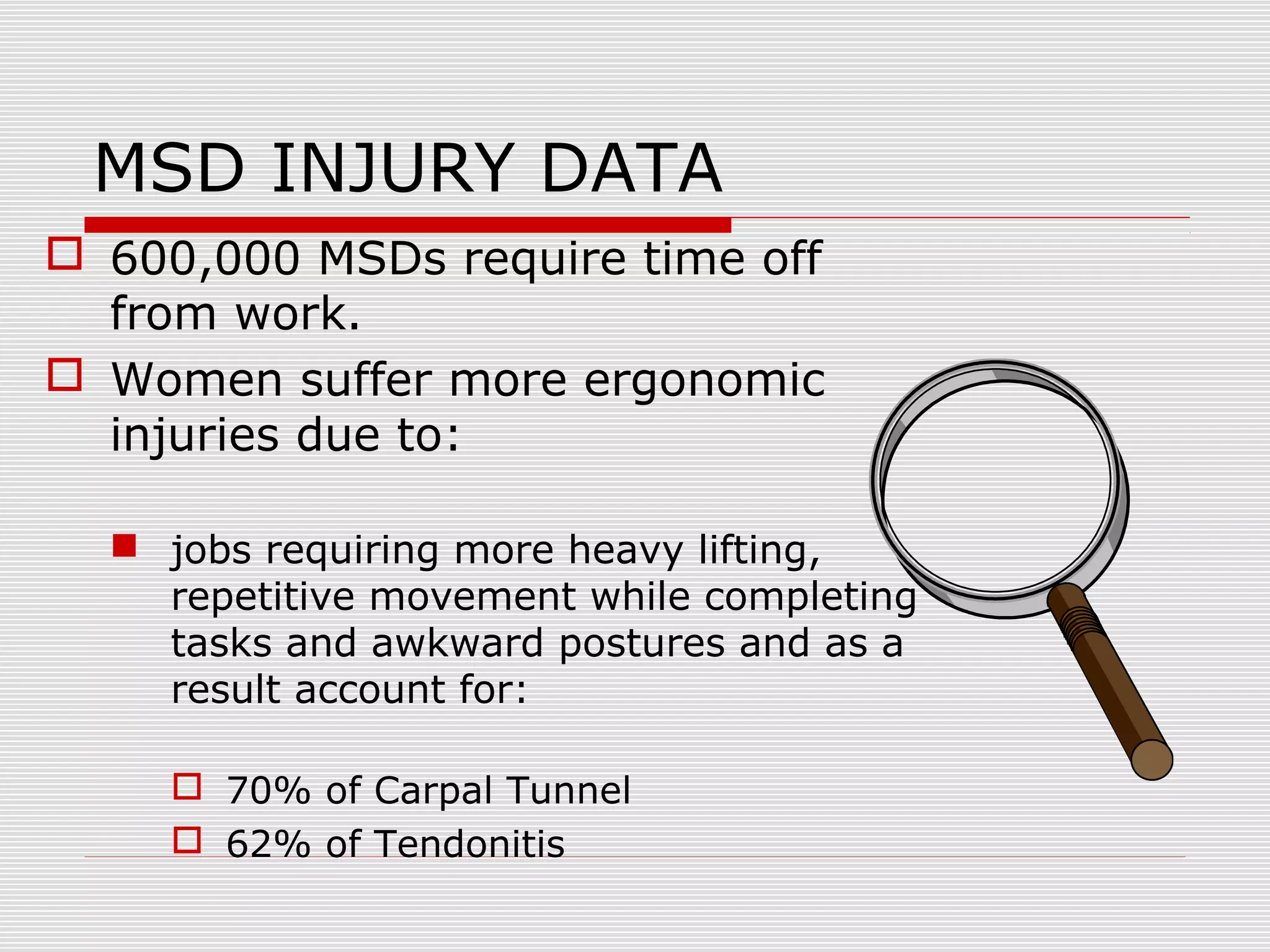
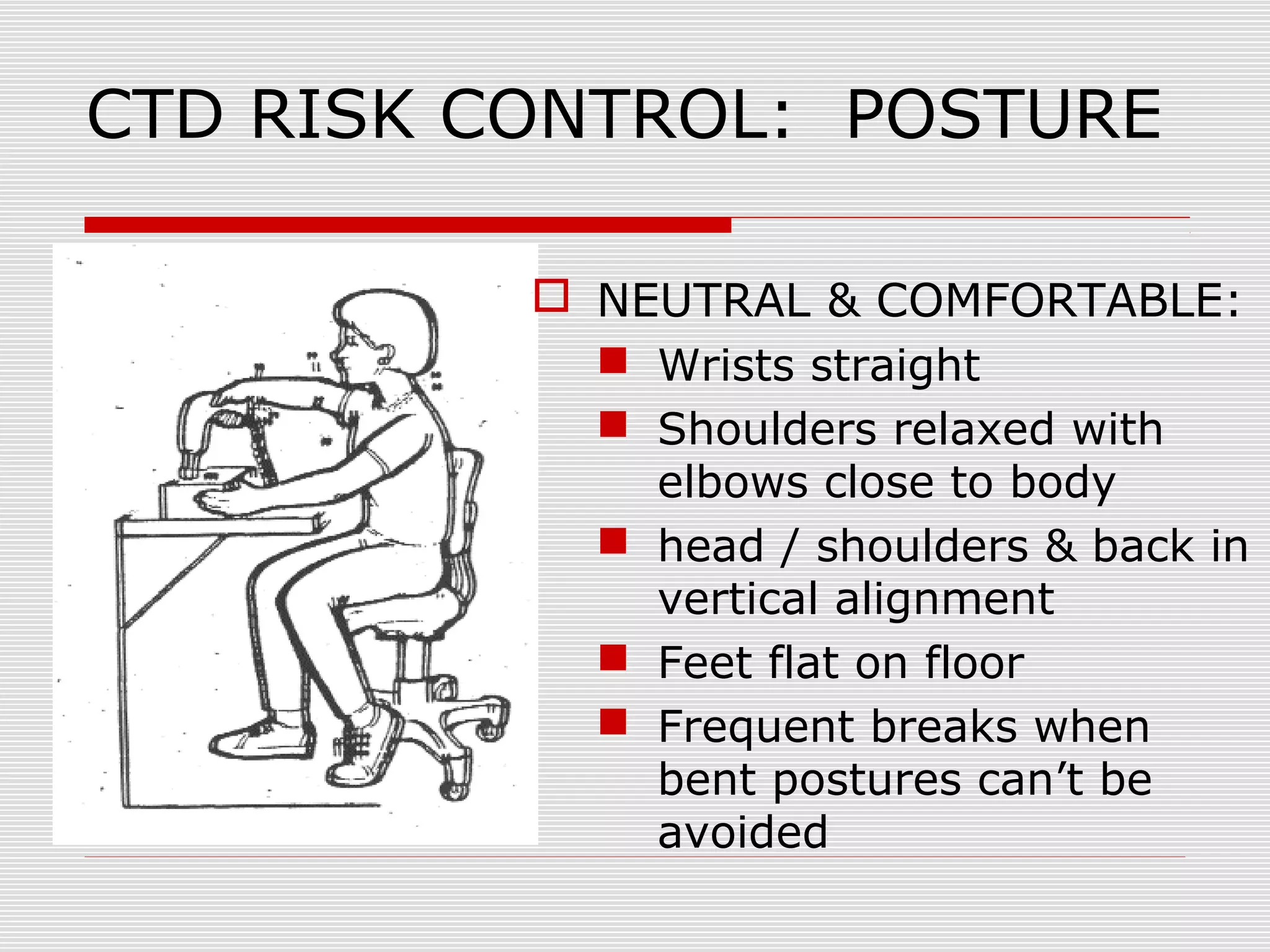
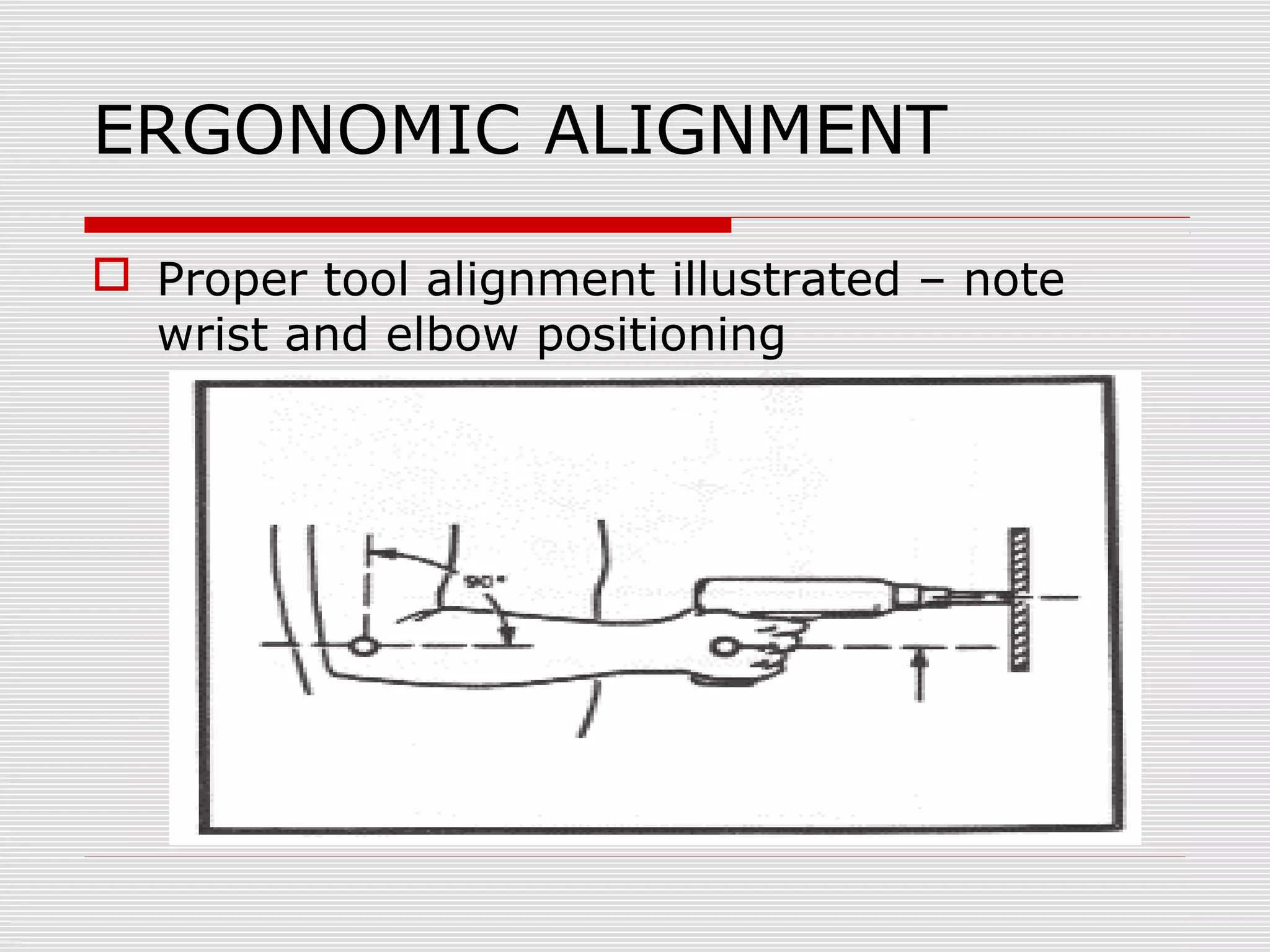
This document discusses office ergonomics and how to design workstations to prevent musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). It defines ergonomics as designing tools and tasks to fit the worker, not the other way around. It notes that MSDs cause 600,000 injuries requiring time off work annually, with women more affected due to job duties. Proper ergonomic setup of chairs, keyboards, monitors and other equipment can help reduce repetitive stress and injuries by promoting neutral postures. Questions about ergonomic issues can be directed to the Safety and Environmental Health department.