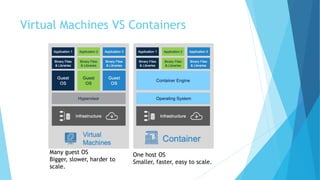
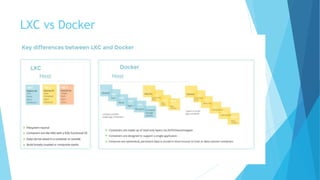
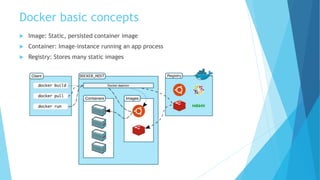
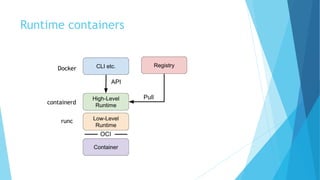
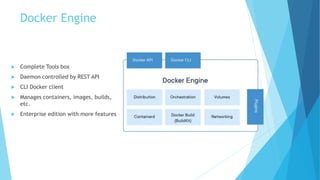
This document provides an overview of Docker and the Open Container Initiative (OCI), highlighting the differences between virtual machines and containers. It explains Docker's purpose as a user-friendly tool for building and managing containers, along with key concepts like images, containers, and Dockerfiles. Additionally, it covers essential commands and tools such as Docker Compose, registries, and the Docker engine for running containerized applications.