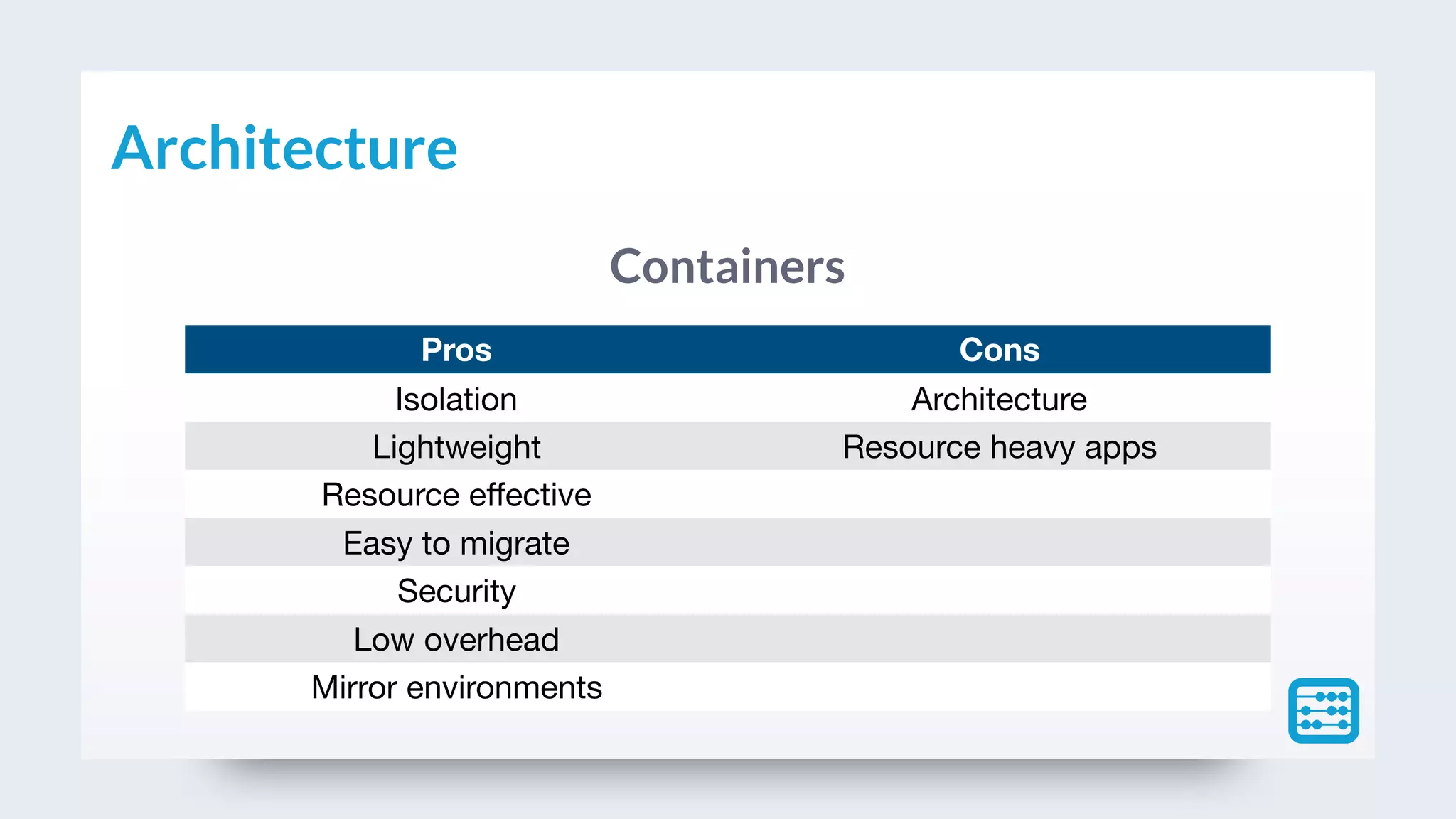
This document provides an overview of Docker basics including requirements, software, architecture, and concepts. It discusses traditional servers, virtual machines, and containers. Key advantages and disadvantages of each approach are listed. Docker concepts like images, containers, layers, Dockerfile, registry, and hub are defined. Common Docker commands are also outlined.
































![Docker images
Command Description Example
docker images List all images
docker images image name List all images with a name
docker pull image name:[tag] Pull image from repository docker pull hello-world
docker history image name Show history of an image docker history hello-world
docker rmi image name Delete specific image docker rmi hello-world](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dockerbasics-190311171325/75/Docker-basics-34-2048.jpg)

![Run containers
docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE[:TAG|
@DIGEST] [COMMAND] [ARG…]
docker run hello-world](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dockerbasics-190311171325/75/Docker-basics-36-2048.jpg)






