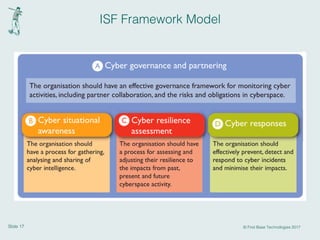
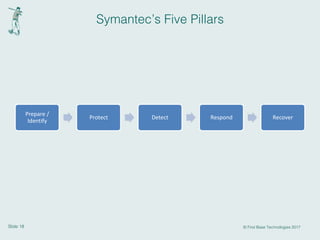
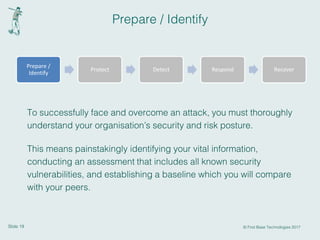
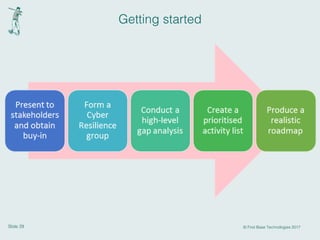
This document discusses cyber resilience and provides guidance on developing a cyber resilience strategy. It defines cyber resilience as an organization's ability to continue operations despite adverse cyber events. The document recommends that organizations implement the five pillars of cyber resilience: prepare/identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover. For each pillar, it provides examples of specific activities organizations can undertake such as conducting risk assessments, implementing security controls, establishing incident response plans, and developing disaster recovery processes. The overall message is that cyber resilience requires a strategic, comprehensive approach across people, processes, and technologies to withstand various cyber threats.