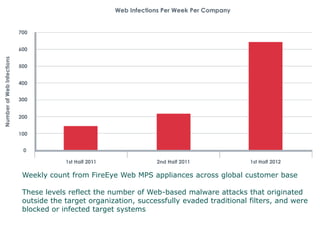
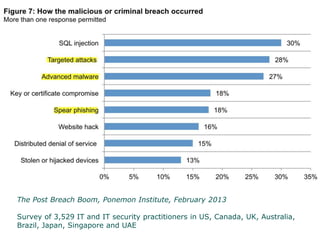
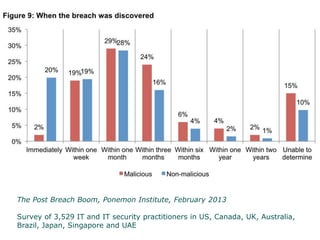
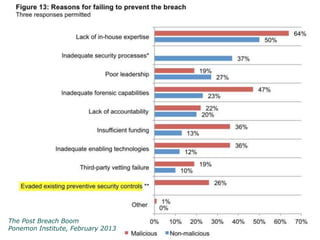
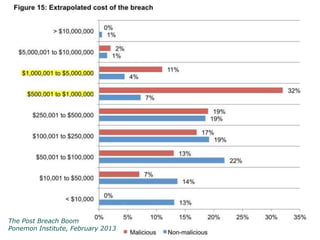
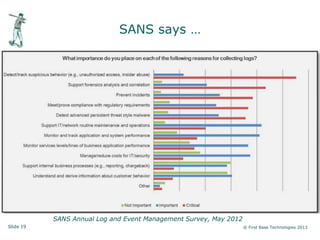
Peter Wood, CEO of First Base Technologies, gave a presentation on how big data and advanced analytics can help with cybersecurity challenges. He discussed how the threat landscape has become more complex with stealth malware and targeted attacks. Traditional defenses like signatures and firewalls may be insufficient. Big data can help through improved SIEM tools with real-time updates, behavior models, and correlation to detect advanced threats. However, big data analytics requires significant investment and specialized skills that are only available to large organizations currently. Cloud-based solutions may help other organizations also gain security benefits from big data.