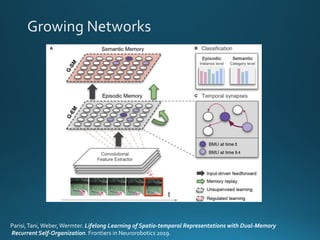
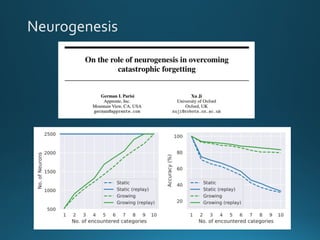
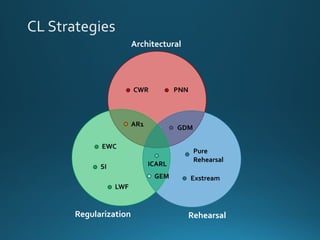
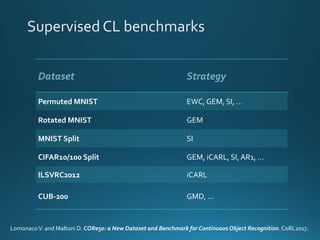
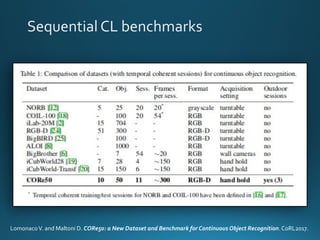
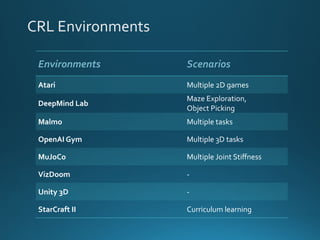
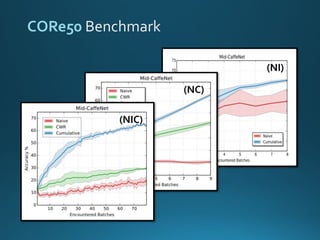
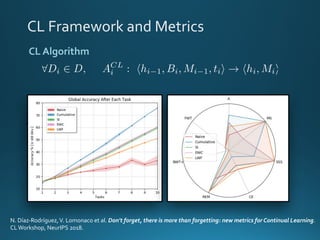
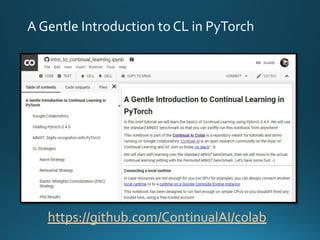
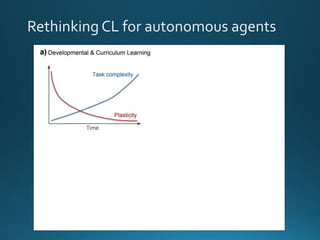
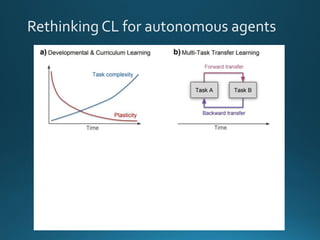
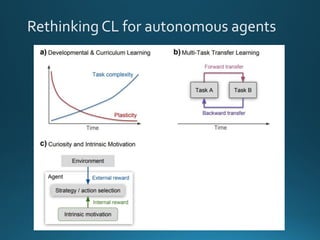
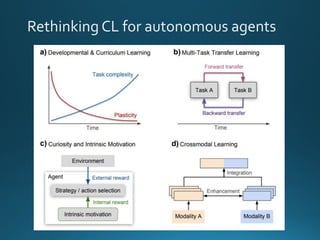
The document discusses continual lifelong learning (CL) in neural networks, emphasizing the challenges of catastrophic forgetting, where new training can overwrite old knowledge. It highlights various strategies and benchmarks for CL, including different neural network architectures and real-world applications in autonomous agents and robots. The paper also touches on future developments needed to enhance CL, such as improving robustness and efficiency.