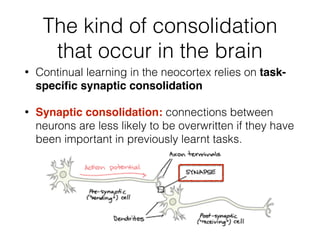
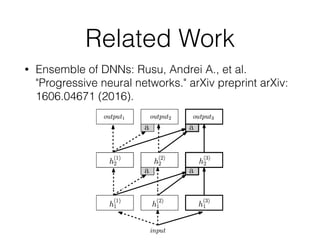
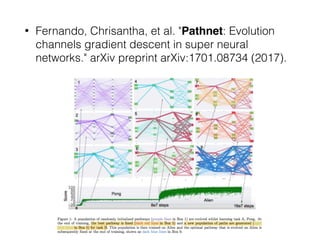
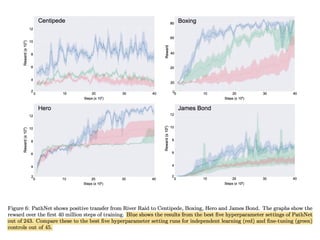
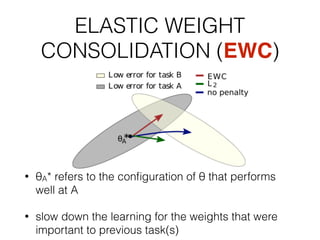
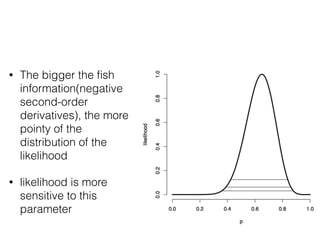
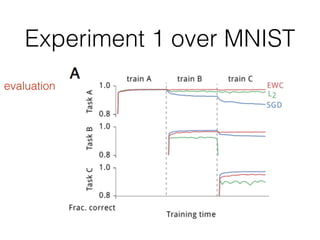
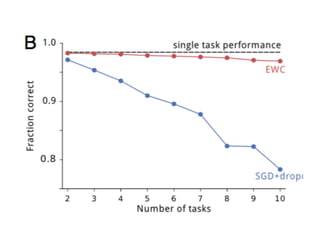
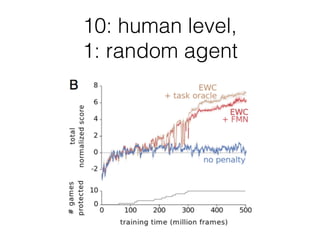
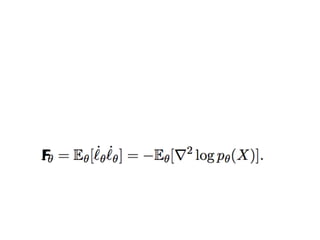EWC is a technique to prevent catastrophic forgetting in neural networks. It works by constraining important parameters learned from previous tasks to stay close to their original values when training on new tasks. The importance of parameters is determined by calculating how much changing each parameter would affect the loss on a previous task. EWC then regularizes the loss function to slow learning more for important parameters and allow less disruption to previous tasks. Experiments on MNIST and Atari demonstrate EWC allows neural networks to continually learn new tasks without forgetting previous ones.