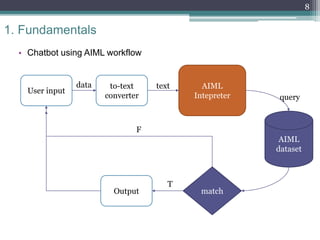
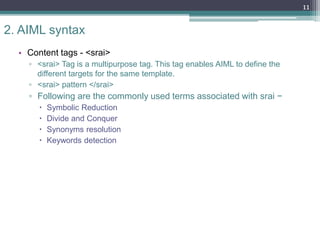
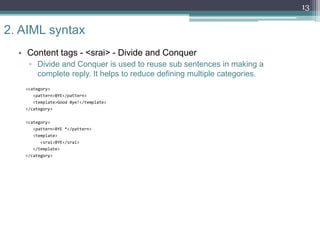
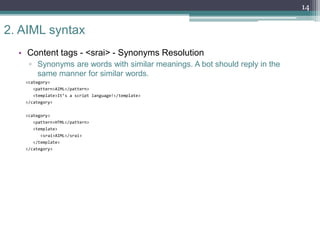
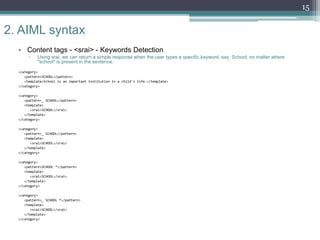
The document provides an overview of AIML (Artificial Intelligence Markup Language), which is a scripting language used to create chatbots. It discusses fundamentals such as what a chatbot is, the history and purpose of AIML, and how the AIML workflow functions. The document then examines the syntax of AIML, including common tags used like <category>, <pattern>, and <template>. It also reviews how tags like <star>, <srai>, <set>, <get>, and <condition> work. Finally, it discusses training a chatbot using AIML, provides conclusions on limitations and further development opportunities with AIML.