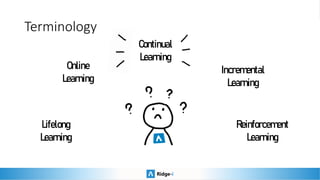
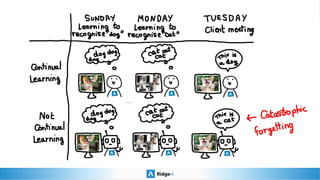
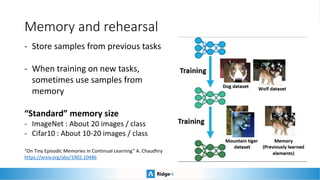
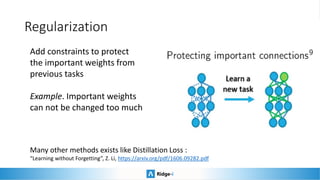
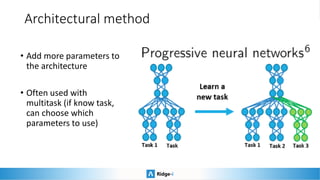
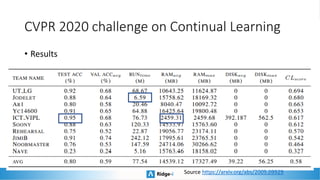
This presentation provides an introduction to continual learning, including definitions of key terms, challenges, and potential solutions. It defines continual learning as learning sequentially while avoiding forgetting previously learned classes without access to old data. The main challenge is catastrophic forgetting. Proposed solutions include memory/rehearsal techniques, regularization methods, architectural approaches, and meta-learning. Benchmarks are discussed to evaluate how well methods work, with most real-world applications prioritizing performance, speed, and memory constraints over continual learning abilities. Recent challenges show pretrained models and memory-based techniques have had success in industry applications.