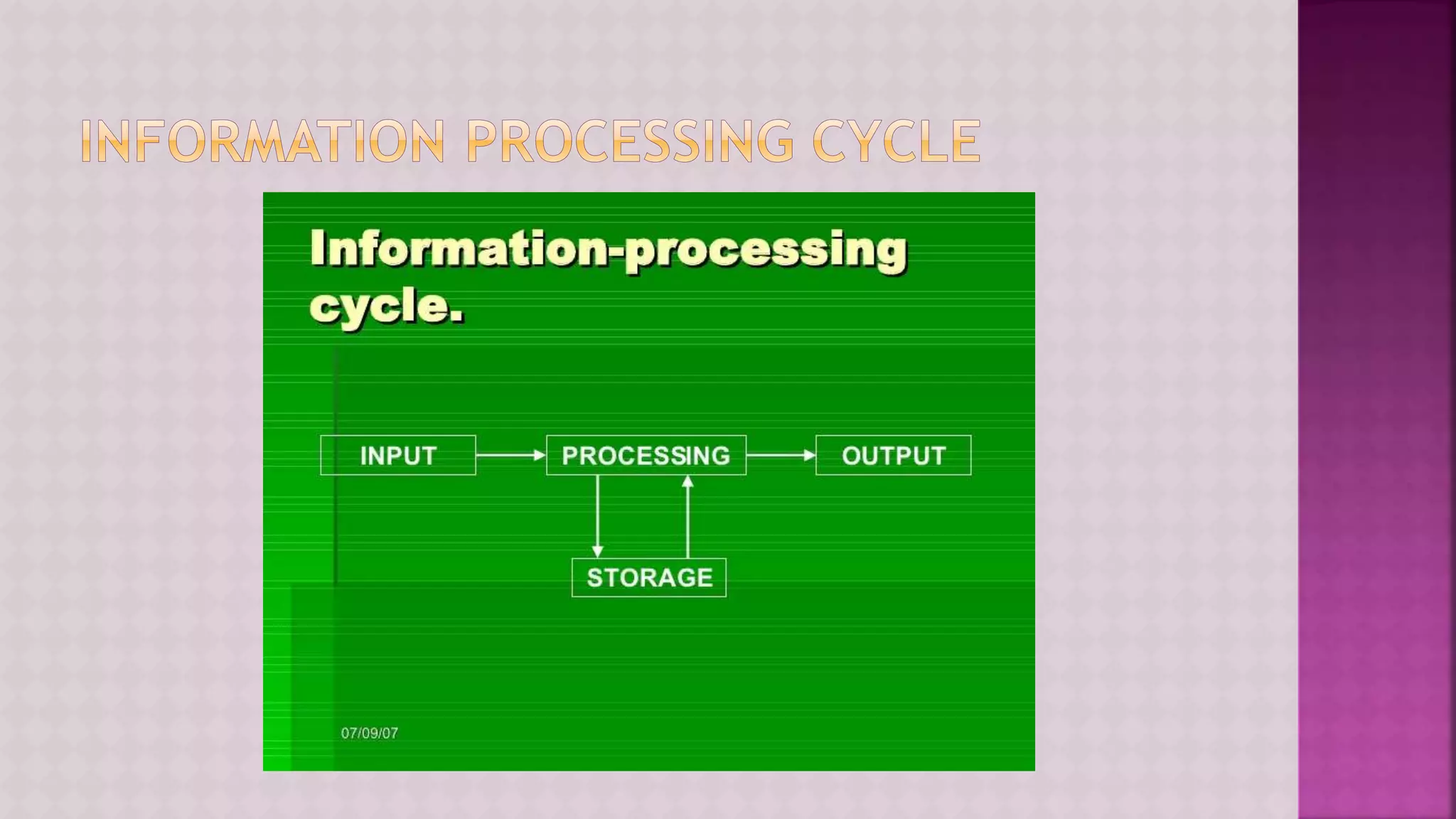
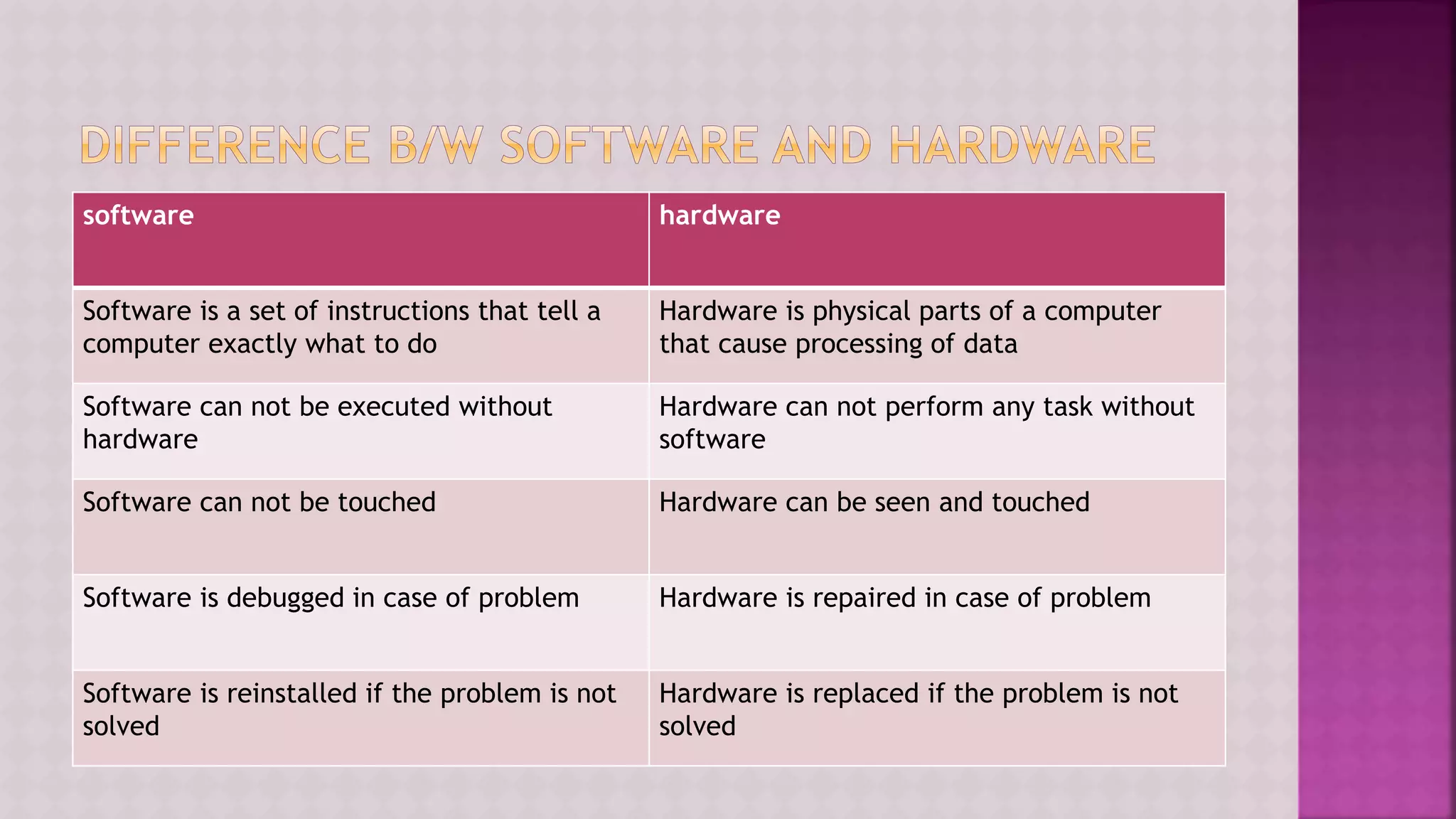
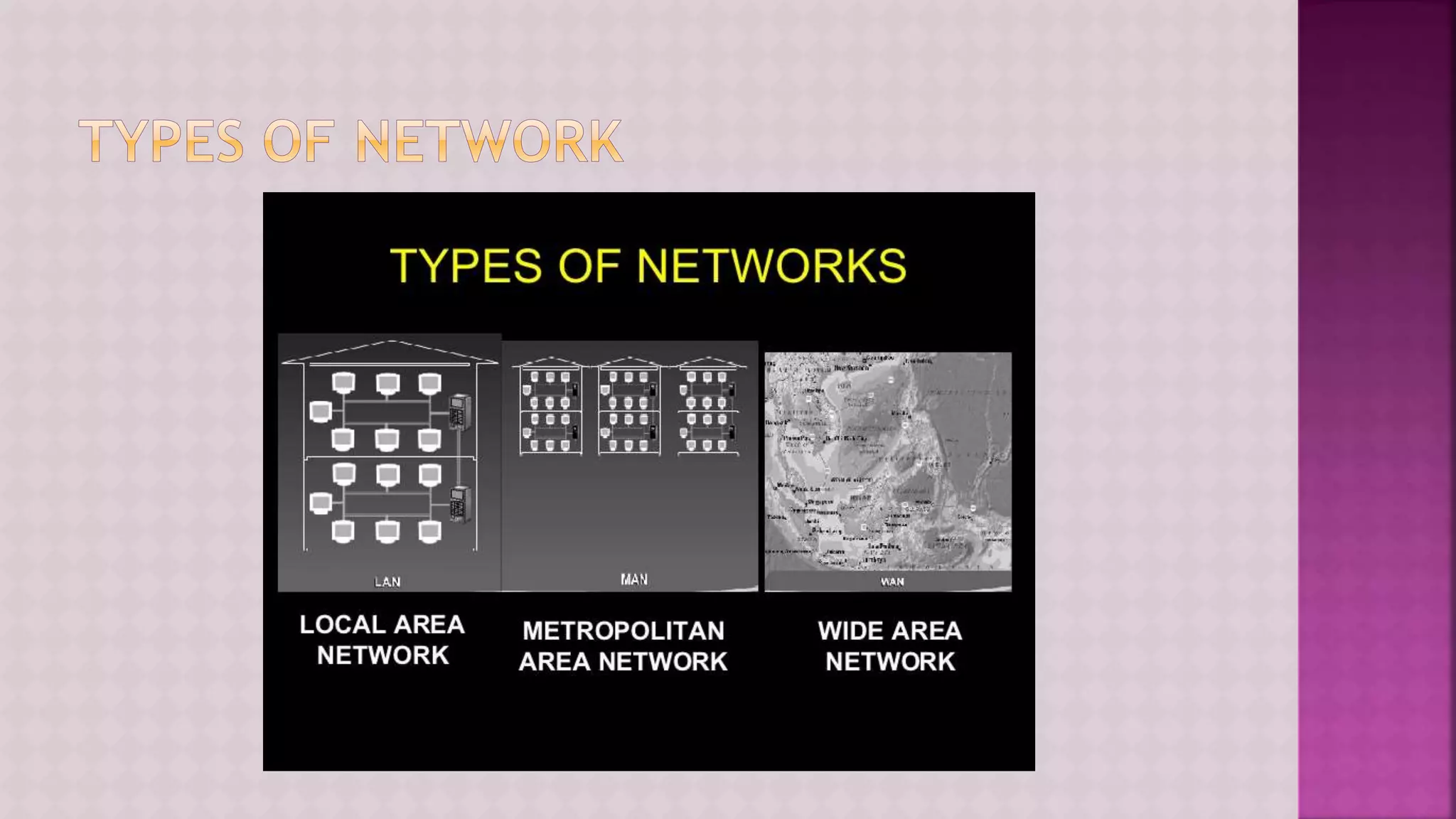
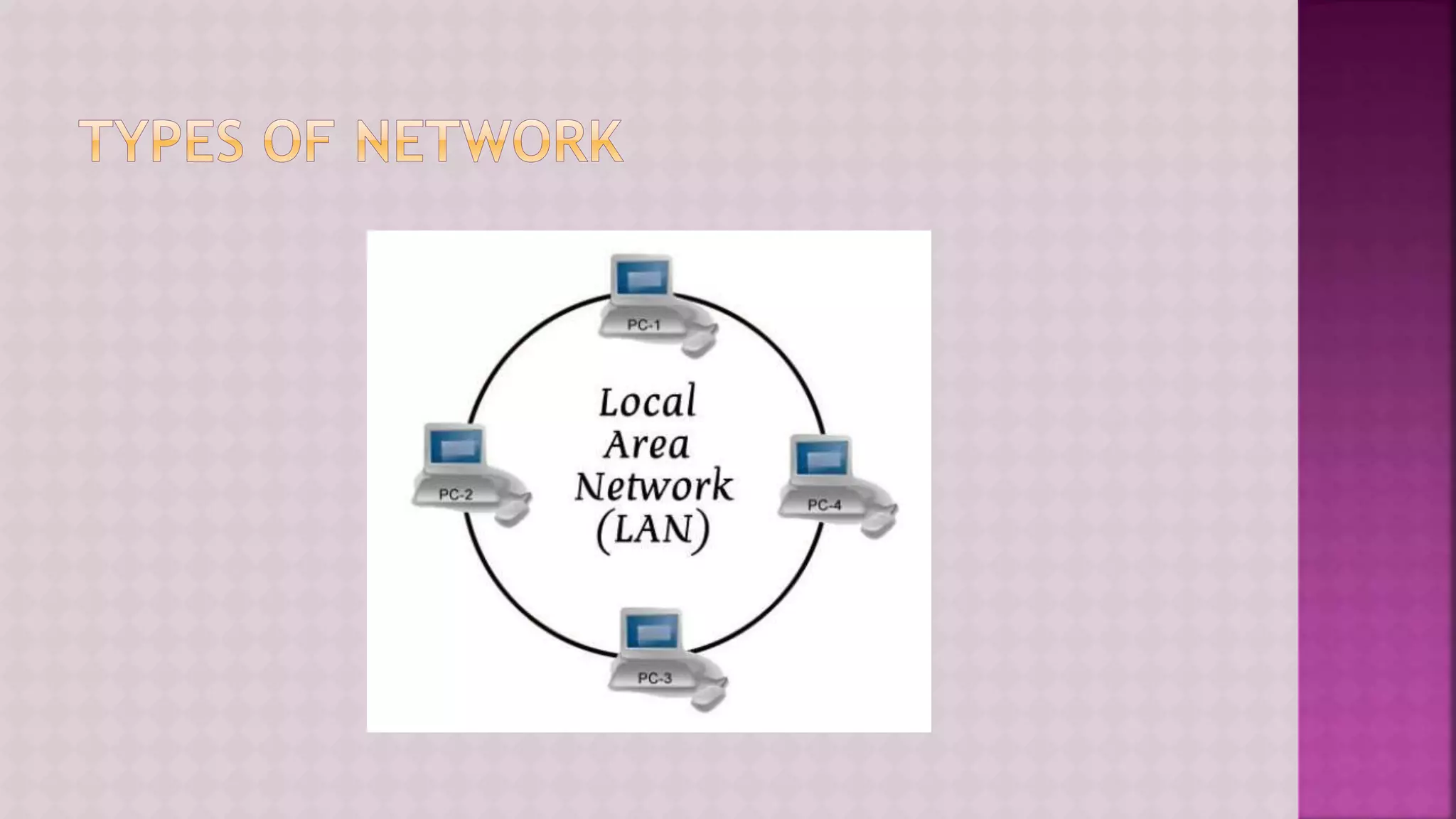
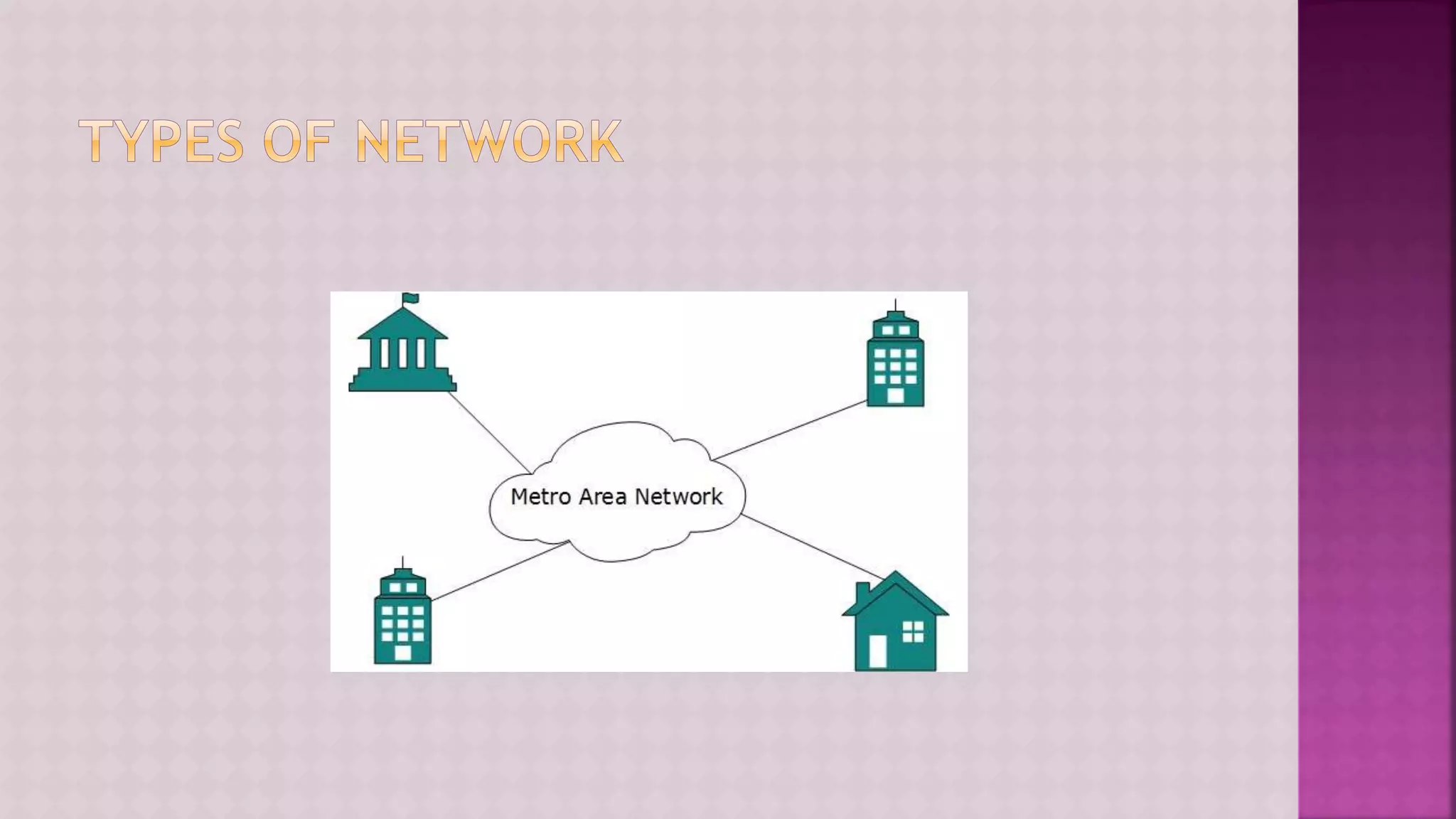
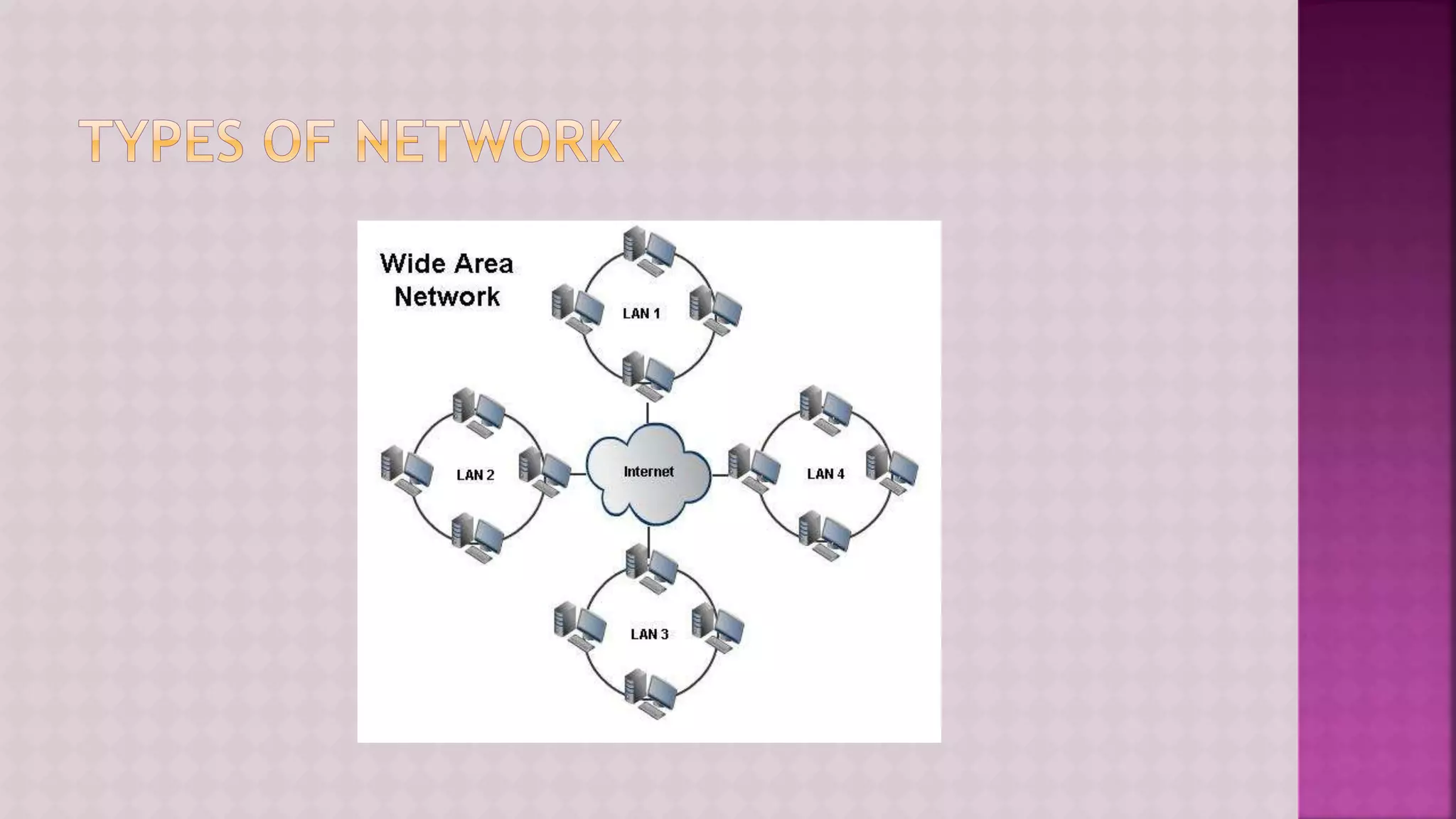
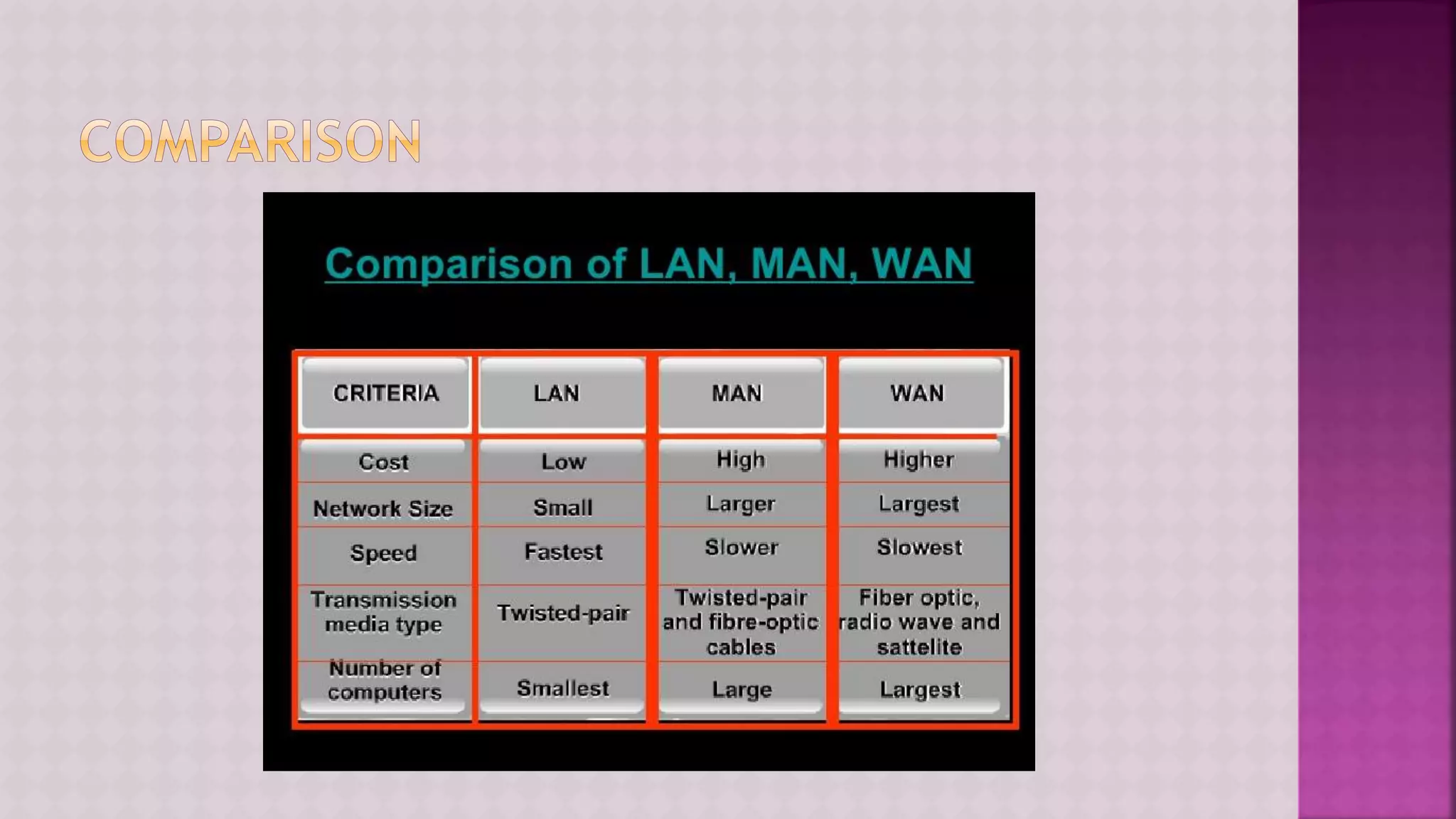
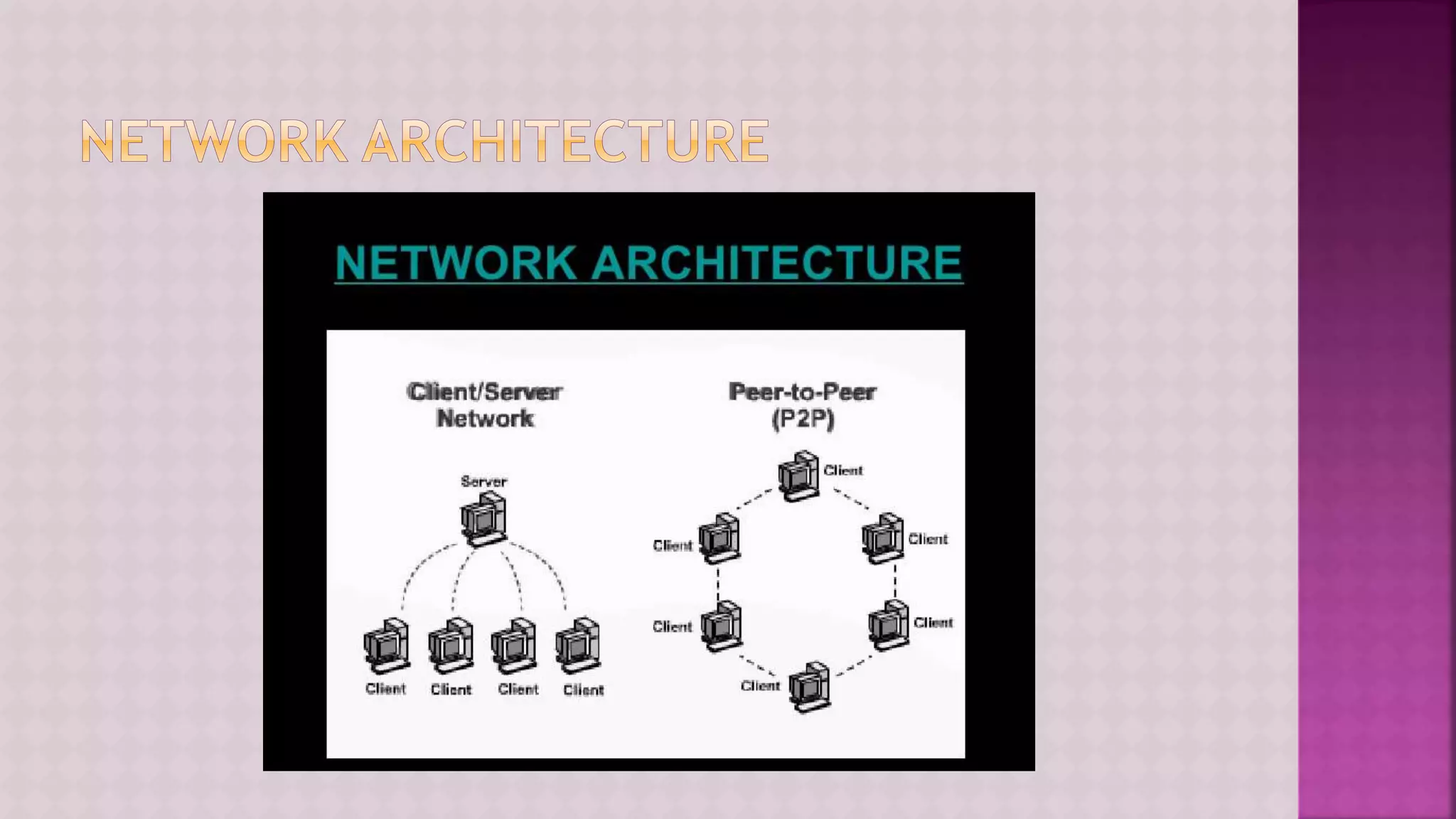
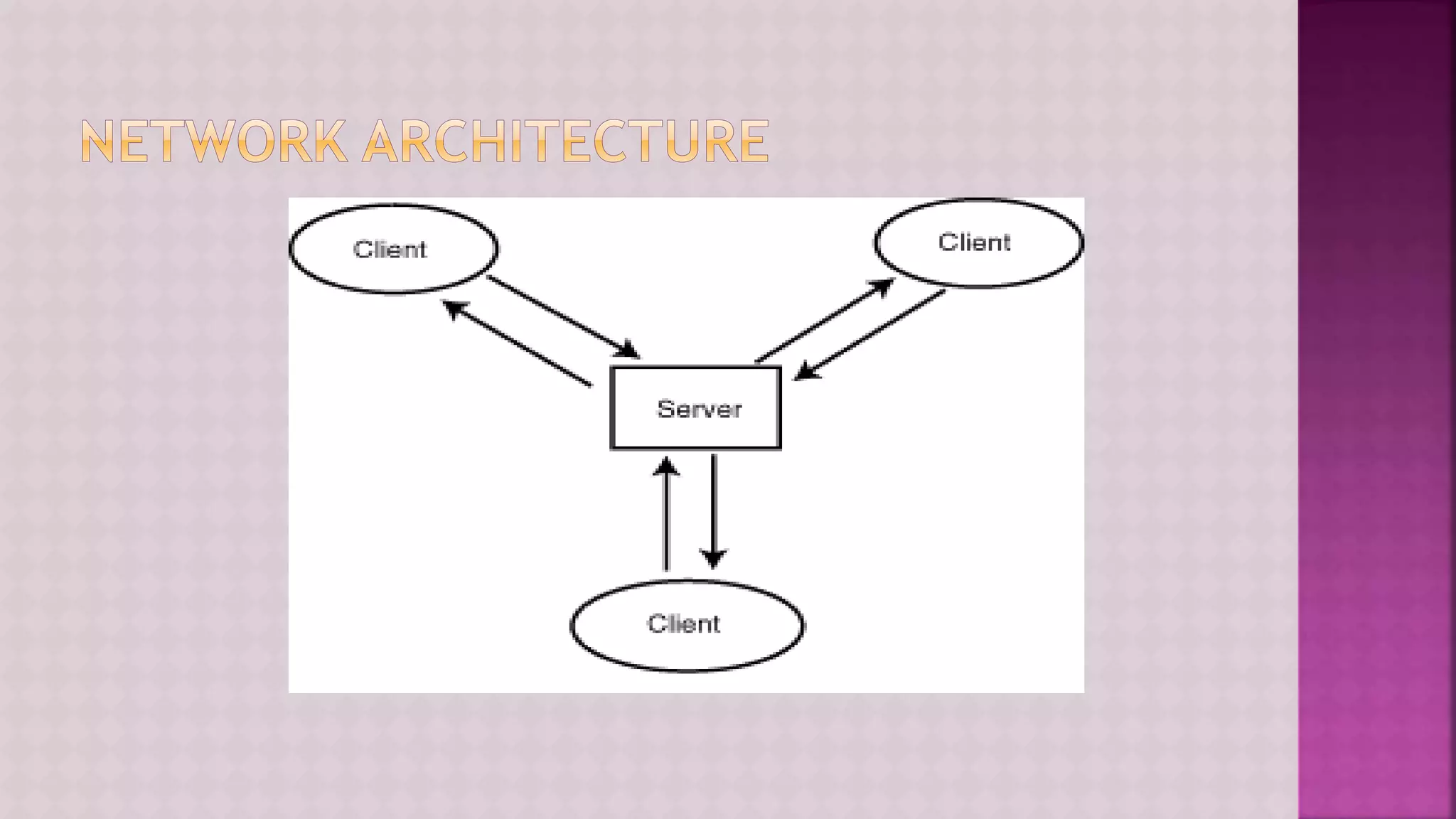
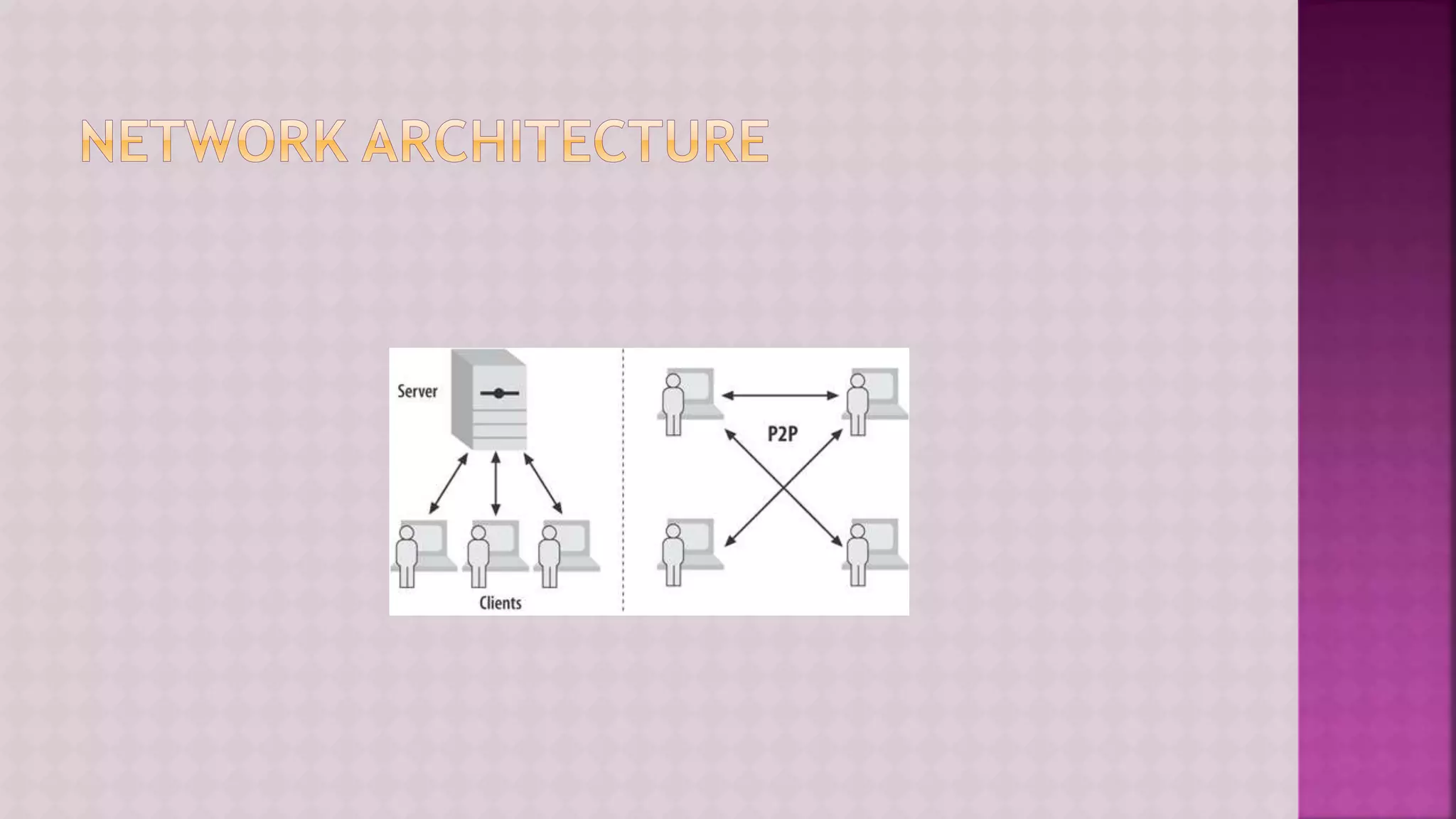
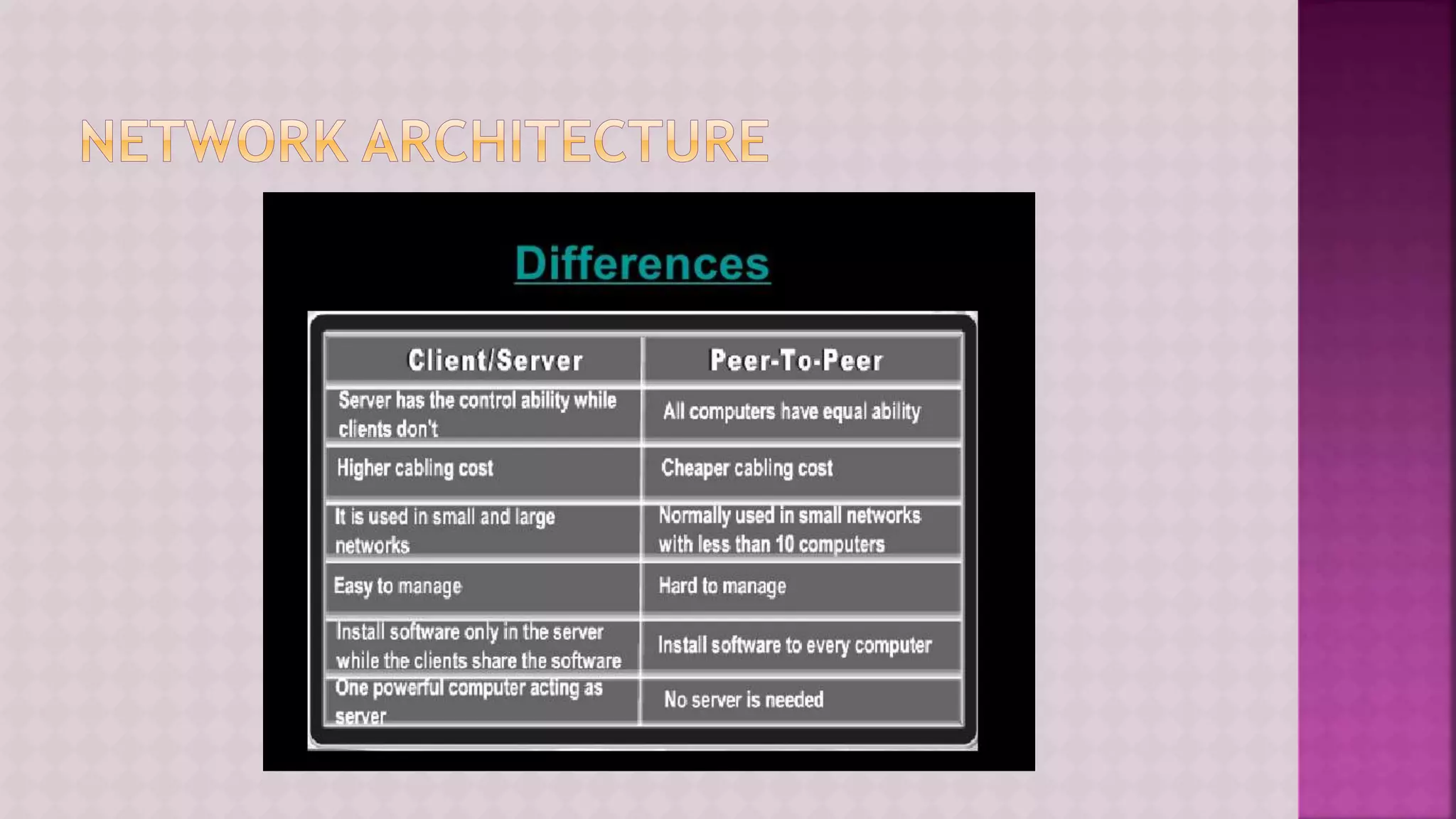
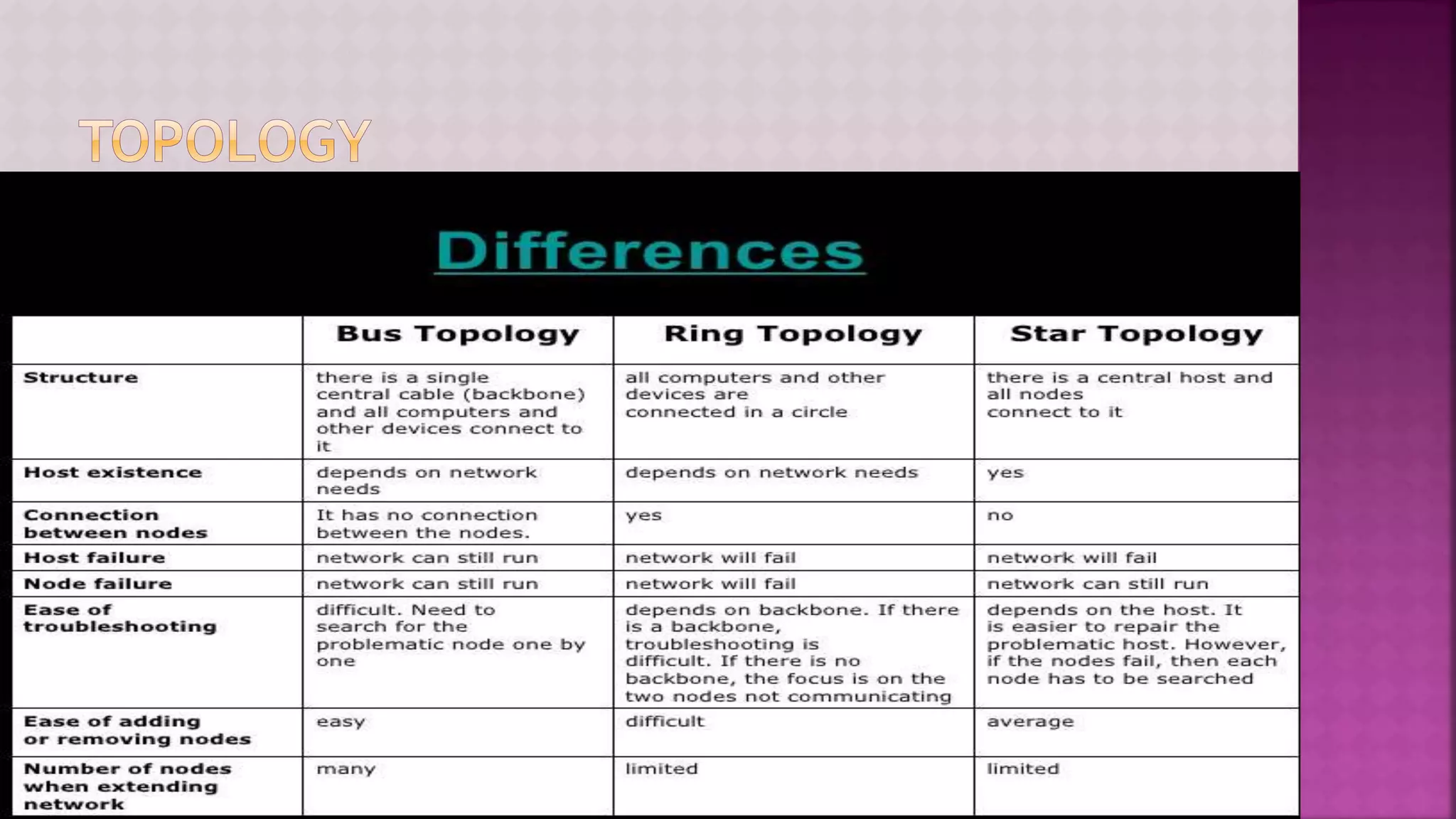
The document provides a comprehensive overview of computers, covering their fundamental operations—input, processing, output, and storage—as well as the roles of hardware and software. It explains the interconnections in information technology, the significance of networks, and various network topologies. Additionally, the document discusses applications like e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and different types of software along with input and output devices.