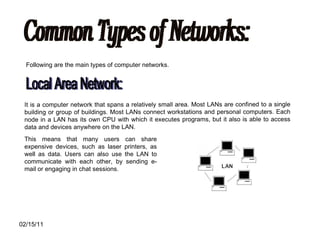
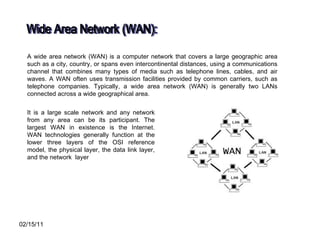
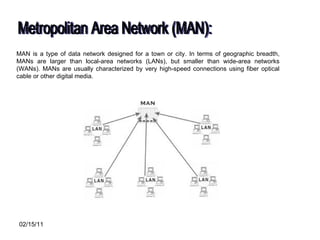
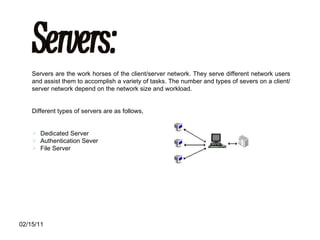
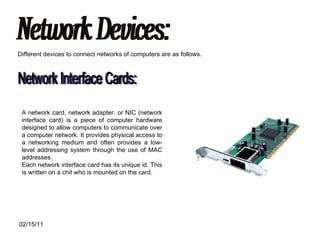
The document discusses various types of computer networks such as local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and metropolitan area networks (MANs) and explains how they differ in size and geographic reach. It also describes common network devices like switches, routers, and hubs that are used to connect computers in a network. Finally, the document outlines some benefits and disadvantages of computer networks like increased sharing of resources but also security issues and dependency on centralized servers.