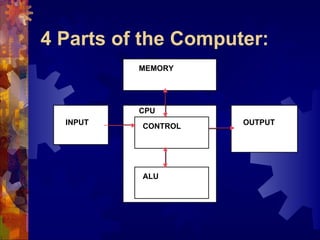
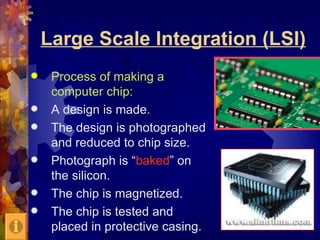
This document discusses the key components and functions of computers. It describes the three types of computers based on size and storage capacity, as well as the four main parts of a computer: input, output, memory, and the central processing unit (CPU). The CPU is made up of the control unit and arithmetic logic unit. Memory is divided into random access memory (RAM) and read only memory (ROM). The document also defines common computer terms like bits, bytes, and memory sizes and provides an overview of how computer chips are made.