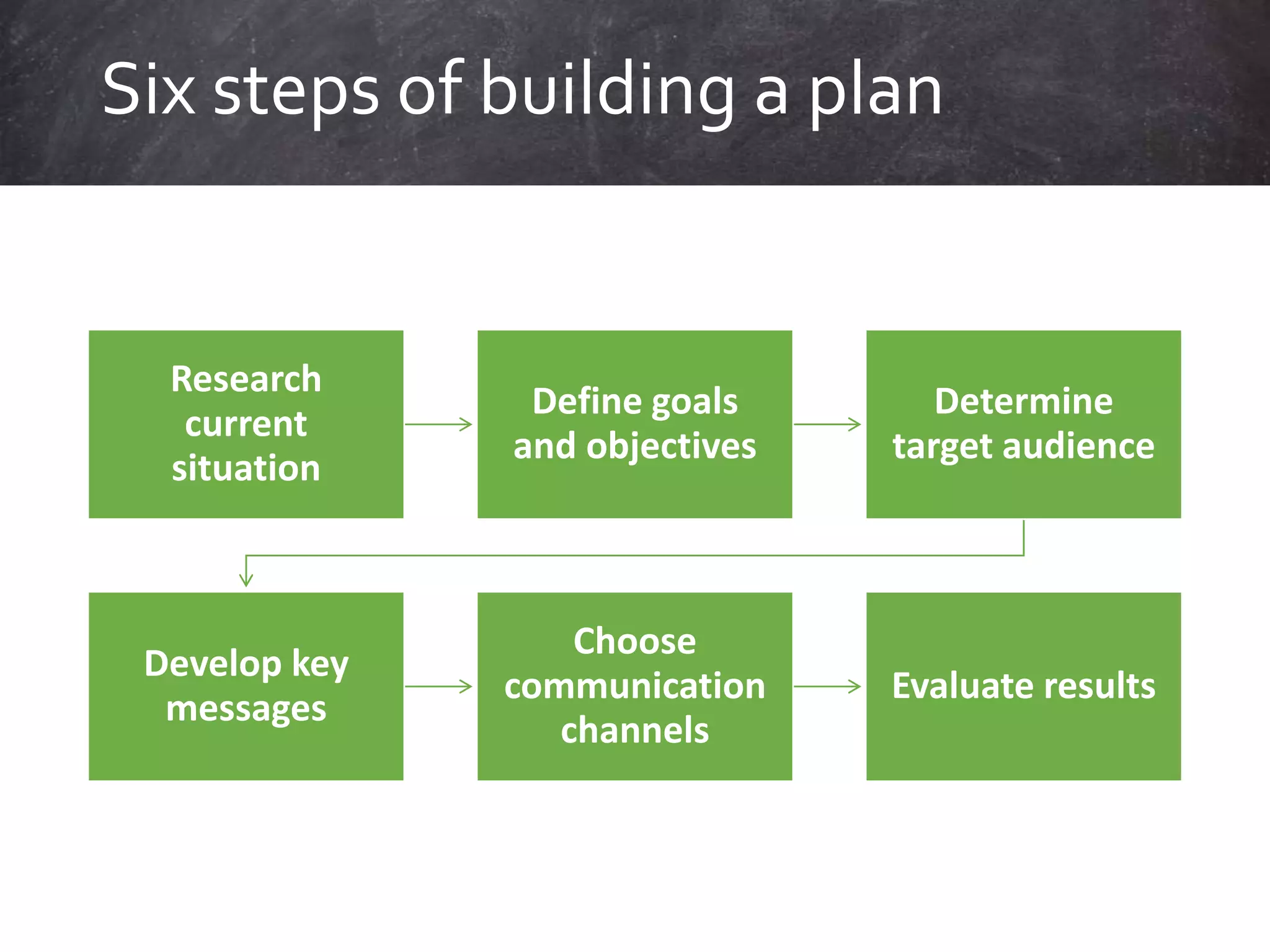
We communicate for several key reasons: to persuade others, provide or seek information, and express emotions. Communication planning involves defining goals, identifying target audiences, developing key messages, selecting appropriate communication channels, and evaluating results. The planning process helps ensure messages are effectively received, understood, and acted upon by intended audiences.