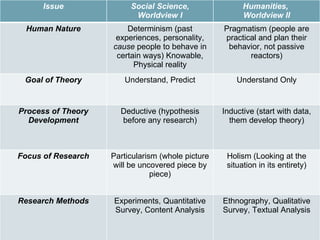
Communication can mean different things but generally refers to how people interact and share meaning. Communication theories aim to understand and predict communication behaviors by examining concepts like agenda setting. Research methods like surveys, experiments, textual analysis, ethnography are used to study communication and develop theories in either a deductive or inductive manner. The goal is to understand communication processes at both individual and societal levels.