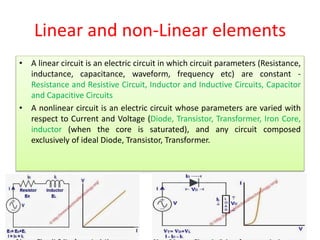
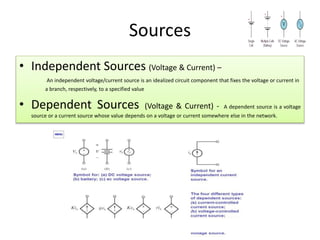
The document provides an overview of circuit theory, including classifications of circuit elements (active vs passive, lumped vs distributed, bilateral vs unilateral, linear vs non-linear). It defines various electrical concepts such as voltage, charge, and current, and explains the differences between independent and dependent sources. Key examples are provided for each category of circuits and components.