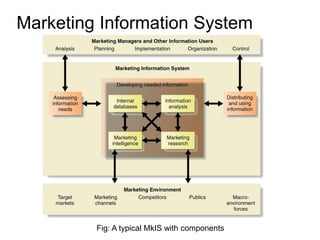
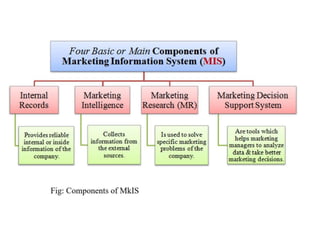
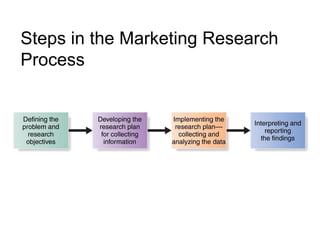
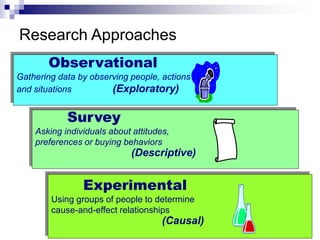
The document provides an overview of Marketing Information Systems (MKIS), detailing their role in gathering, processing, and distributing data to aid marketing decision-making. It discusses various components, applications, and advantages of MKIS in business, emphasizing the system's importance in enhancing marketing effectiveness and efficiency. Additionally, it highlights challenges such as maintenance and the risk of incorrect data impacting system performance.