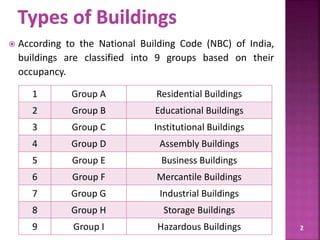
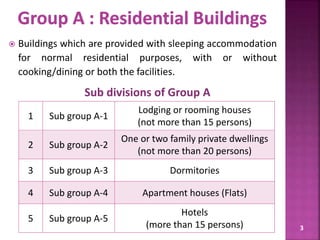
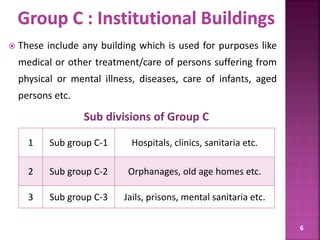
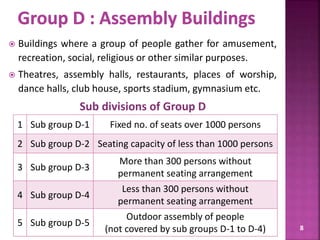
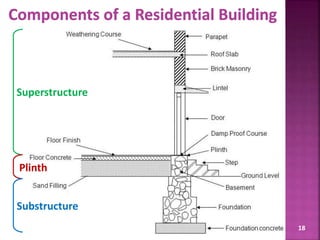
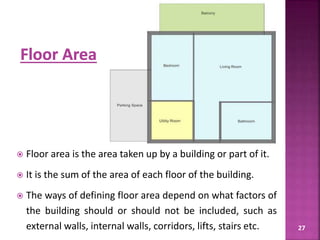
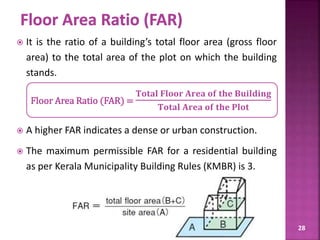
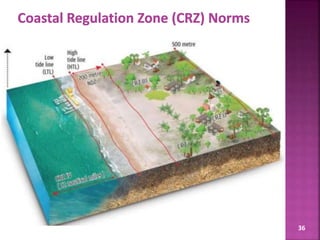
The document discusses the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) rules in India. It states that the rules were first framed in 1991 to regulate human and industrial activity near coastal areas to protect the fragile coastal ecosystems. The rules restrict certain activities like large constructions, industries, waste disposal etc. within 500m of the high tide line. The regulation zone is divided into 4 categories - CRZ-1 to CRZ-4, with varying levels of restriction on activities in each.