MATLAB can be used to work with matrices, perform mathematical operations, generate random numbers, and create script and function files. Key features include storing variables and matrices, indexing matrix elements, performing operations on real and complex numbers, and using functions like sum, diag, and random number generators. Help commands provide documentation on elementary, advanced, and matrix functions in MATLAB. M-files allow storing and running scripts and functions.



![MATLAB Variables
Vectors
column vectors row vectors
⎧1 ⎫
⎪ ⎪
a = ⎨2 ⎬ a = {1 2 3}
⎪3 ⎪
⎩ ⎭
>>a=[1;2;3]; >>a=[1,2,3];
>>a >>a
a= a=
1 1 2 3
2
3 use comma
use semi-colon
to separate rows to separate columns
MATLAB Variables
Matrices
⎡1 2 3⎤
2-dimensional matrices a=⎢ ⎥
⎣4 5 6⎦
>>a=[1,2,3;4,5,6];
>>a
a=
1 2 3
4 5 6
again, separate columns with commas and rows
with semi-colons
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab1-111019135649-phpapp02/85/Matlab-4-320.jpg)
![MATLAB Variables
Indexing Matrix elements
A vector is a special type of matrix
row vector is a 1 x n matrix, 1 row n columns
column vector is a n x 1 matrix, n rows 1 column
>>a=[1,2,3];
>>a(2) could also reference by a(1,2)
ans = note, a(2,1) would produce an error
2 because “a” only has one row
MATLAB Variables
Indexing Matrix elements
more examples
⎡1 2 3⎤ >>a=[1,2,3;4,5,6];
a=⎢ ⎥
⎣4 5 6⎦
assigning
addressing
>>a(2,2)=9;
>>a(2,3) >>a
ans = a=
6 1 2 3
4 9 6
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab1-111019135649-phpapp02/85/Matlab-5-320.jpg)



![MATLAB Operations
Left() and Right(/) Matrix “division”
Math representation Matlab interpretation
C = A −1B >>C=AB;
C = BA −1 >>C=B/A;
Remember, A must be square and
full rank (linearly independent
rows/columns)
MATLAB Operations
Matrix Transpose
Math representation Matlab interpretation
C = AT >>C=A’;
For complex-valued matrices, complex conjugate transpose
⎡1 2 3⎤
A=⎢ ⎥ a = [1 + j2 3 + j4]
⎣4 5 6⎦
>>B=A’; >>b=a’;
⎡1 4 ⎤
B = ⎢2 5⎥ ⎡1 − j2 ⎤
⎢ ⎥ b=⎢ ⎥
⎢3 6⎥
⎣ ⎦ ⎣3 − j4 ⎦
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab1-111019135649-phpapp02/85/Matlab-9-320.jpg)






![MATLAB m-files
Function Files
Matlab identifies function files from script files by
using the “function” and “return” keywords
Syntax: function [list of outputs] = filename (inputs)
the name of the function file must be
the same name as the function
MATLAB m-files
Function Files
The function file x2.m
>>r=3; >>h=x2(4.2);
>>d=x2(r); >>h
>>d h =
d = 17.64
9.0 >>
>>
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab1-111019135649-phpapp02/85/Matlab-16-320.jpg)
![MATLAB m-files
Function Files
Multiple Inputs and Outputs
outputs in square brackets, [ ] inputs in parentheses ( )
MATLAB m-files
Function Files
variables created in the function are not
retained in the workspace, except for the
output variables
the function does not have access to
workspace variables, except for the inputs
variables passed to the function are “copies” of the
workspace variables. Changing their value inside
the function has no effect on their value in the
workspace.
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab1-111019135649-phpapp02/85/Matlab-17-320.jpg)

![MATLAB Flow Control
The “for” statement
for index = start : [increment :] end
statements
end
increment is optional, if increment is not specified
increment defaults to 1
index, start, increment, and end do not need to be integer
valued
index can be incremented positive (increment > 0)
or negative (increment < 0)
loop stops when index > end (or index < end)
MATLAB Flow Control
example
script file to cycle through x values
function file to generate the y values
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab1-111019135649-phpapp02/85/Matlab-19-320.jpg)
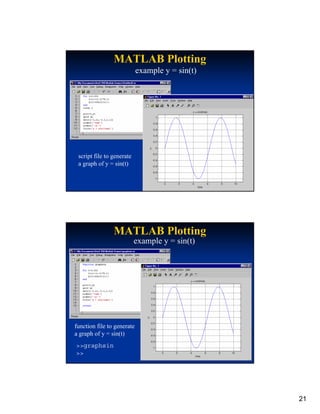
![MATLAB Plotting
Basic 2D plotting functions
plot(x1,y1[,x2,y2,x3,y3.....])
xlabel(‘x axis name’)
ylabel(‘y axis name’)
title(‘graph name’)
Additional functions
grid on
grid off
axis([xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax])
MATLAB Plotting
example y = sin(t)
the “plot” function alone
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab1-111019135649-phpapp02/85/Matlab-20-320.jpg)
![MATLAB Plotting
Adding a Legend for multiple graphs
“legend” remembers
the order the graphs
were plotted
MATLAB Plotting
Plot function in some detail
•PLOT(X,Y) plots vector Y versus vector X
•If X is a scalar and Y is a vector, length(Y) disconnected
points are plotted.
•If Y is complex, PLOT(Y) is equivalent to PLOT
(real(Y),imag(Y)).
Additional functions
grid on
grid off
axis([xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax])
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab1-111019135649-phpapp02/85/Matlab-22-320.jpg)

