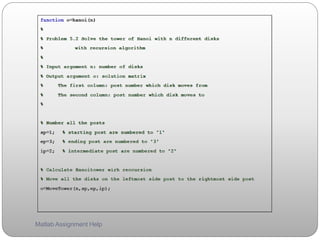
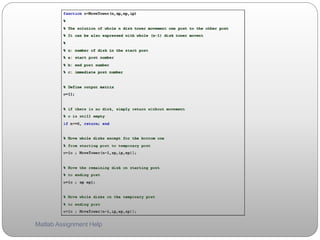
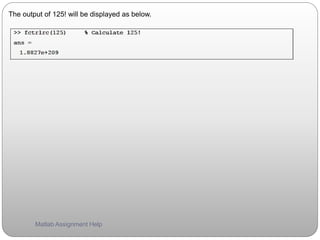
The document presents assignments focused on using recursion algorithms in MATLAB, specifically for calculating factorials and solving the Tower of Hanoi puzzle. It details the recursive method for calculating n! and provides a structured approach to solving the Tower of Hanoi with n disks, highlighting the rules and movements required. Additionally, it compares the performance of recursive vs. non-recursive methods in programming.



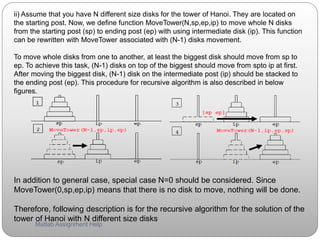
![1. If N is smaller than 1, just return (in the special case of MoveTower(0,sp,ep,ip))
2. Output Å MoveTower(N-1,sp,ip,ep) (move N-1 disks from sp to ip)
3. Output Å [sp ep] (move the biggest disk from sp to ep)
4. Output Å MoveTower(N-1,ip,ep,sp) (move N-1 disks from ip to ep)
Matlab Assignment Help](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabassignmentexperts-211222070319/85/Control-System-Homework-Help-7-320.jpg)
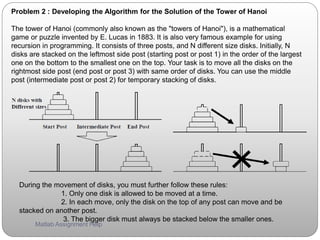
![Problem 3 : Solving the Tower of Hanoi with recursive algorithm
Now, generate the function or m-file for the solution of “tower of Hanoi” with 5 different size
disks. Use recursive approach. Your function has input argument of ‘n’, number of disk on the
starting post, and output argument of ‘o’, matrix for disk movements (each row represents each
movement from the post indicated in the first column to the post shown in the second column.
For example, [1 3] means movement from post 1 to post 3) Function name (and m-file name)
should be ‘hanoi_your_kerberos_name’ and upload it to 2.003 MIT Server site. You submit
hardcopy of your function code as well as the solution of the tower of Hanoi with 5 different size
disks. Execution of m-file should provide the following result in case of N=1:
Solution:
By using your own algorithm, the function to solve the tower of Hanoi is shown as below.
Please, see the comments for each line.
Matlab Assignment Help](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabassignmentexperts-211222070319/85/Control-System-Homework-Help-8-320.jpg)